By: Jeremy Kadlec | Updated: 2006-09-21 | Comments (2) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | > Query Plans
Problem
With system performance on the mind of most business and technical teams (management, DBA, developer, network admin), determining the issues is the first major challenge. So once you have determined which queries are causing issues, now comes the time to determine how to improve the performance of the query while reducing the reads and writes. In SQL Server 2000 the primary interface was Query Analyzer's graphical interface where it was necessary to hover over the object to determine the statistics. Does SQL Server 2005 have a more elegant approach reviewing the query plans?
Solution
SQL Server 2000 - Query Plan Options
There are three primary interfaces in SQL Server 2000 to access the query plan. First is via the SHOWPLAN_TEXT command, this command offers a textual view of the SQL Server optimizer's query plan. A more advanced command is the SHOWPLAN_ALL command. This command provides the estimated IO, CPU, row size, parallelism, etc. A final option is use the graphical query plans from Query Analyzer which can be activated by CTRL + K. Each component of the query is broken down and the read, writes, etc. statistics are available for each.
SQL Server 2000 - Query Plan Commands
| ID | Command | Example |
| 1 | SHOWPLAN_TEXT - Simple view of the optimizer results | SET SHOWPLAN_TEXT ON GO SELECT TOP 1 a.au_lname AS 'AuthorLastName', a.au_fname AS 'AuthorFirstName', t.title AS 'Title', t.pubdate AS 'PublicationDate' FROM dbo.Authors a INNER JOIN dbo.TitleAuthor ta ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN dbo.Titles t ON ta.title_id = t.title_id WHERE a.state = 'CA' |
| Corresponding Output | ||
| 2 | SHOWPLAN_ALL - Detailed view of the optimizer results | SET SHOWPLAN_ALL ON GO SELECT TOP 1 a.au_lname AS 'AuthorLastName', a.au_fname AS 'AuthorFirstName', t.title AS 'Title', t.pubdate AS 'PublicationDate' FROM dbo.Authors a INNER JOIN dbo.TitleAuthor ta ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN dbo.Titles t ON ta.title_id = t.title_id WHERE a.state = 'CA' |
| Corresponding Output | ||
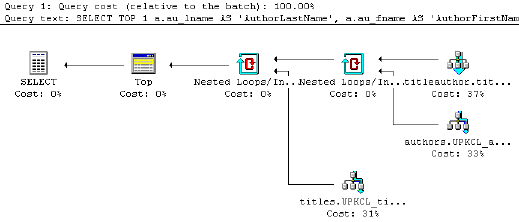
| 3 | Graphical Query Plan - Graphical view of the query plan data from the SQL Server optimizer
This feature is activated by CTRL + K in Query Analyzer |
SELECT TOP 1 a.au_lname AS 'AuthorLastName', a.au_fname AS 'AuthorFirstName', t.title AS 'Title', t.pubdate AS 'PublicationDate' FROM dbo.Authors a INNER JOIN dbo.TitleAuthor ta ON a.au_id = ta.au_id INNER JOIN dbo.Titles t ON ta.title_id = t.title_id WHERE a.state = 'CA' |
 |
SQL Server 2005 - Query Plan Related Dynamic Management Views
SQL Server 2005 continues to support the SQL Server 2000 options listed above in addition to the introduction of the dynamic management views below. These new dynamic management views support reviewing the current query plan and the associated performance metrics:
The query below provides a fairly complete view of the query plan metrics (IO, CPU, memory, etc.) as well as the query plan in XML format based on the cached query plans in your environment. Try this query out on your SQL Server 2005 server:
| USE master; GO SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_query_stats qs CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(qs.plan_handle); GO -- Reference - SQL Server 2005 Books Online |
Next Steps
- Once you have pinpointed the queries in your environment which have plagued your performance, begin to review the query plans and begin to tune these individual queries.
- As a best practice have 2 separate Management Studio sessions to compare the results of the original query and the query as it is being tuned.
- Stay tuned for additional tips from MSSQLTips.com on techniques to improve query performance.
- Check out MSSQLTips.com for a complete list of performance tuning tips such as SQL Server 2000 Query Analyzer Short Cuts.
About the author
 Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.
Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2006-09-21






