By: Jeremy Kadlec | Updated: 2006-09-20 | Comments (3) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | > Database Design
Problem
Rarely do we (Developers and DBAs) have sufficient time for our projects and every day tasks. So when it comes to building a new system, inevitability what happens is time is limited and individual tables end up being built instead of a comprehensive data model. As the system grows, we hope that the front end code is correct and keeps the data related, but when you have a data problem it may take hours to check and validate that the data is correct. So how can we break this cycle and migrate from building table by table to a comprehensive data model?
Solution
Working with your team and letting them know the time needed is the first step. The second step is exploring data modeling tools to streamline the process to be able to work on projects and daily tasks. With SQL Server 2005, Management Studio includes the Visual Data Modeling tools. This tool set enables you to graphically build your data model and translates the model into the appropriate T-SQL commands.
What are the capabilities of SQL Server 2005's Visual Data Modeling tools?
The chart below outlines the primary activities that can be performed in SQL Server 2005's Visual Data Modeling tools:
| ID | Task | Directions | Screen Shot |
| 1 | Create a new data model | Management Studio | root | Databases | database name | Database Diagrams | Right click on the folder | New Database Diagram | Yes (if prompted) | 
|
| 2 | Portions of the Visual Data Modeling interface | When a new data model is created the a blank slate is available. Four options are available to interact with the tool:
|
 |
| 3 | Add existing tables to the data model | Right click on the main work space and select the 'Add Table...' option
Highlight the tables that need to be added to the model and then press the 'Add' button |

|
| 4 | Create new tables | Right click on the main work space and select the 'New Table...' option
Enter the column names, data types and null configurations |

|
| 5 | Add Primary Key | Right click on the column that you would like to make the primary key and select the 'Set Primary Key' option | 
|
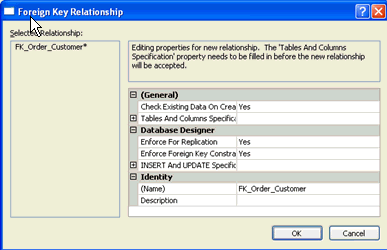
| 6 | Building Referential Integrity | To build referential integrity, drag and drop the primary key from the parent table to the foreign key on the child table
Then set the properties for the referential integrity To display the referential integrity labels, click on the 'Show Relationship Labels' on the database diagram tool bar |

|
| 7 | Index Management | Right click on the table and select the 'Indexes\Keys...' option
To create an index click on the 'Add' button and provide a name then configure the index properties To drop an index select the index from the list on the left and press the 'Delete' button |

|
| 8 | Constraint Management | Right click on the table and select the 'Check Constraints...' option
To create an constraint click on the 'Add' button and provide a name then configure the constraint properties To drop a constraint select the constraint from the list on the left and press the 'Delete' button |

|
| 9 | Saving a change script | To save a T-SQL script of all changes since the last time the model was saved, click the 'Generate Change Script' from the Database Diagram tool bar
Click the 'Yes' button to save the contents to a text file in the file system |
|
| 10 | Add notes to the data model | As a best practice, annotations should be added to the model to help document the database design
This can be accomplished by right clicking on the workspace and selecting 'New Text Annotation' option and entering the comments
|
 |
| 11 | Finalized Data Model | Once the entire model is completed all of the tables, columns, primary keys, foreign keys, data types, etc should be configured | 
|
| 12 | Sharing the data model | To share the data model, it is possible to print the model or share it online in Management Studio
To print the model select File | Print To show the page breaks, select the 'View Page Breaks' icon from the database diagram tool bar
|
What are the benefits of using the SQL Server 2005 Management Studio tool?
- Be able to use a more intuitive point and click interface to build your data models
- Have the ability to issue a save script for change management purposes and to review the T-SQL commands
- Ability to share the data model with other users electronically or by printing a physical copy
Caution - Word to the wise...this is a live data modeling tool
- This data modeling tool is designed to make changes to the database when the model is saved, which means this tool is primarily intended for development environments
- You are making changes to the database, this is not a mock up tool
- There is no undo button, once you save CTRL + Z will not bring back your table and data
- If you drop a table in this model, you will drop it from your database, so be sure when you drop tables
- Tables are dropped and temp tables are created with the needed columns and the old tables are dropped
- Indexes are created on the fly which can have a performance impact on the system
Next Steps
- If you have had a hard time writing queries or working with a user because you could not "see the data model" then reverse engineer one of your databases and share the information with your team. See if this helps the coding and communication process
- If you are starting on a new project, rather than building individual tables, use the Visual Data Modeling tools with SQL Server 2005 Management Studio. See if using this tool streamlines the process and gives you a better understanding of the system from the start.
- Once you start using the tool, be sure to make your changes in the development environment, save the change script via the tool and then save the data model to retain all of the work in the development environment. Next migrate the script from development to test and from test to production.
About the author
 Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.
Jeremy Kadlec is a Co-Founder, Editor and Author at MSSQLTips.com with more than 300 contributions. He is also the CTO @ Edgewood Solutions and a six-time SQL Server MVP. Jeremy brings 20+ years of SQL Server DBA and Developer experience to the community after earning a bachelor's degree from SSU and master's from UMBC.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2006-09-20