By: Atif Shehzad | Updated: 2009-07-29 | Comments (20) | Related: > Triggers
Problem
I have created some views to provide limited data access for an application. Several of these views are composed of more than one table and there are problems while performing insert, delete, or update operations on multi-base table views. I am required to seamlessly manage such problems, so that developers do not get direct access to the base tables for DML operations. In SQL Server 2000 and onwards there are INSTEAD OF triggers that can be used to carry out such tasks. Although these types of triggers can be used in a number of scenarios their primary function is to perform DML operations through such views. It looks like a powerful capability and I am interested to know about the implementation of INSTEAD OF triggers for various DML operations.
Solution
In SQL Server 2000 and later versions there are two types of DML triggers
- AFTER triggers
- INSTEAD OF triggers
Both of these work for insert, delete and update operations. Triggers created with FOR or AFTER keywords are both AFTER triggers. AFTER triggers do not work for views, so we will discuss the properties and functionality of INSTEAD OF triggers.
INSTEAD OF triggers cause their source DML operation to skip and they just execute the code provided inside them. Actual insert, delete or update operation do not occur at all. However they have their associated inserted and deleted tables simulating the DML operation. Inserted and deleted tables are widely used in operations inside triggers and I will show you some examples below . We will discuss further aspects of INSTEAD OF triggers by going through some examples for DML operations.
SETUP
In the following script we will create and populate two base tables and a create a view over both tables.
Script #1: Create and populate base tables and create view on these
USE AdventureWorks
GO
-- Create table for employees
CREATE TABLE Employees
(EmpCode VARCHAR(8) PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Designation VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, QualificationCode TINYINT,
Deleted BIT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0)
GO
-- Create look up table for employees qualification
CREATE TABLE Lib_Qualification
(QualificationCode TINYINT PRIMARY KEY, Qualification VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL)
GO
-- Add constraint to lib_qualification
ALTER TABLE dbo.Lib_Qualification ADD CONSTRAINT
FK_Lib_Qualification_Lib_Qualification FOREIGN KEY
( QualificationCode ) REFERENCES dbo.Lib_Qualification
( QualificationCode ) ON UPDATE NO ACTION
ON DELETE NO ACTION
GO
-- Add constraint to employees
ALTER TABLE dbo.EMPLOYEES ADD CONSTRAINT
FK_EMPLOYEES_Lib_Qualification FOREIGN KEY
( QualificationCode ) REFERENCES dbo.Lib_Qualification
( QualificationCode ) ON UPDATE NO ACTION
ON DELETE NO ACTION
GO
-- Insert data into lib_qualification table
Insert into lib_qualification VALUES (1, 'MS')
Insert into lib_qualification VALUES (2, 'MCS')
Insert into lib_qualification VALUES (3, 'BCS')
Insert into lib_qualification VALUES (4, 'MBA')
GO
-- Insert data into employees table
Insert into Employees VALUES ('405-21-1' ,'Emp1' ,'Designation1' ,1 ,0)
Insert into Employees VALUES ('527-54-7' ,'Emp2' ,'Designation2' ,2 ,0)
Insert into Employees VALUES ('685-44-2' ,'Emp3' ,'Designation3' ,1 ,0)
Insert into Employees VALUES ('044-21-3' ,'Emp4' ,'Designation4' ,3 ,0)
Insert into Employees VALUES ('142-21-9' ,'Emp5' ,'Designation5' ,2 ,0)
GO
-- Create view by two base tables
CREATE VIEW vw_EmpQualification
AS
SELECT EmpCode, Name, Designation, Qualification
FROM employees E inner join lib_qualification Q
ON E.qualificationCOde = Q.QualificationCode
WHERE deleted = 0
GO
Select * from vw_EmpQualification
GO
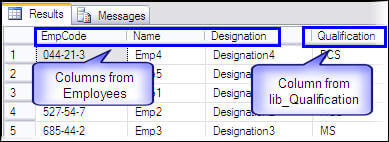
Now we are ready to create the INSTEAD OF trigger for insert, delete and update operations on view vw_empQualification.
In the examples I have chosen simple and common scenarios, but there is much that can be done using INSTEAD OF triggers in SQL Server.
INSTEAD OF INSERT Trigger for Insert operation
Our view is comprised of two base tables. If someone tries to insert values using the view the following error will be generated and the insert will fail.
View or function 'vw_EmpQualification' is not updatable because the modification affects multiple base tables.
At this point, the INSTEAD OF INSERT trigger provides us several options to handle insert operations on this view. For our example we will allow the users to insert data through this view, by having the trigger handle some logic for data integrity.
The INSTEAD OF INSERT trigger will be created using the following script for Insert operations
Script #2: Create INSTEAD OF trigger for handling delete operations on view
USE AdventureWorks
GO
CREATE TRIGGER INSTEADOF_TR_I_EmpQualification
ON vw_EmpQualification
INSTEAD OF INSERT AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @Code TINYINT
SELECT @Code = qualificationCode
FROM lib_Qualification L INNER JOIN INSERTED I
ON L.qualification = I.qualification
IF (@code is NULL )
BEGIN
RAISERROR (N'The provided qualification does not exist in qualification library', 16, 1)
RETURN
END
INSERT INTO employees (empcode, name, designation,qualificationCode,deleted)
SELECT empcode, name, designation, @code, 0
FROM inserted
END
GO
We have just used the key word INSTEAD OF versus using the FOR or AFTER keyword in the trigger header and our required INSTEAD OF INSERT trigger has been created. Now we will verify the insert statement on this view which has two base tables. The INSTEAD OF trigger will seamlessly handle the insert operation in the trigger without an error.
Script #3: Insert data in view and verify functionality of INSTEAD OF trigger
USE AdventureWorks
GO
-- Insert data in view
INSERT INTO vw_EmpQualification VALUES ('425-27-1', 'Emp8','Manager','MBA')
GO
-- To confirm the data insertion
SELECT * FROM vw_EmpQualification
GO
Inserted data is handled in the trigger and our inserted row is shown in the selected data below.
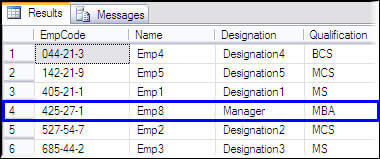
INSTEAD OF UPDATE Trigger for update operation
There may be several scenarios where using INSTEAD of triggers can solve this problem. In the case of views with multiple base tables, you may only issue update statements that affect a single base table at a time. If any update statement on our view affects multiple base tables at a time then the following error would be generated
View or function 'vw_EmpQualification' is not updatable because the modification affects multiple base tables.
The following script is for an INSTEAD OF UPDATE trigger is used to provided seemless update capability for multiple base tables.
Script #4: Create INSTEAD OF trigger for handling update operations on view
USE AdventureWorks
GO
CREATE TRIGGER INSTEADOF_TR_U_EmpQualification
ON vw_EmpQualification
INSTEAD OF UPDATE AS
BEGIN
IF (UPDATE(qualification)) -- If qualification is updated
BEGIN
DECLARE @code TINYINT
UPDATE employees
SET @code = L.qualificationcode
FROM lib_qualification L INNER JOIN inserted I
ON L.qualification = I.qualification
IF (@code is NULL )
BEGIN
RAISERROR (N'The provided qualification does not exist in qualification library',16, 1)
RETURN
END
UPDATE employees
SET qualificationCode = @code
FROM inserted I INNER JOIN employees E ON I.empcode = E.empcode
END
IF (UPDATE(EmpCode)) -- If employee code is updated
BEGIN
RAISERROR (N'You can not edit employee code, Transaction has been failed', 16, 1)
RETURN
END
IF (UPDATE(name)) -- If name is updated
BEGIN
UPDATE employees
SET name = I.name
FROM inserted I INNER JOIN employees E ON I.empcode = E.empcode
WHERE E.empcode = I.empcode
END
IF (UPDATE(designation)) -- If designation is updated
BEGIN
UPDATE employees
SET designation = I.designation
FROM inserted I INNER JOIN employees E ON I.empcode = E.empcode
WHERE E.empcode = I.empcode
END
END
GO
Now we can verify the proper functioning of our trigger for an update statement.
Script #5: Update data in view and verify functionality of INSTEAD OF trigger
USE AdventureWorks GO -- Update data in view UPDATE vw_EmpQualification SET designation = 'Designation4 Updated', Qualification = 'MCS' WHERE empcode = '044-21-3' GO -- To confirm the data update SELECT * FROM vw_EmpQualification GO
The INSTEAD OF UPDATE trigger handled the update and the update is reflected in the selected data below.
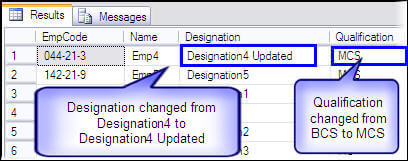
INSTEAD OF trigger for delete operation
INSTEAD OF trigger may be attached for delete operations. In our case we are required that when rows are deleted through the view, a deleted flag in the table should be marked "1" for those rows, but rows should not actually be deleted. Such rows may be deleted in bulk later at specified time if needed. For this we may create the following INSTEAD OF DELETE trigger.
Script #6: Create INSTEAD OF trigger for handling delete operations on view
USE AdventureWorks GO CREATE TRIGGER INSTEADOF_TR_D_EmpQualification ON vw_EmpQualification INSTEAD OF DELETE AS BEGIN update employees set deleted = 1 where empcode in (select empcode from deleted) END GO
To verify the implementation for deletes the following script can be used
Script #7: Delete data from view and verify functionality of INSTEAD OF trigger
USE AdventureWorks GO -- Delete data in view DELETE FROM vw_EmpQualification WHERE Designation = 'Manager' GO -- To confirm the data update SELECT * FROM vw_EmpQualification SELECT * FROM Employees GO
The deleted row still exist in the base table, but it is not shown in the view because the deleted flag is set to "1" in the base table.
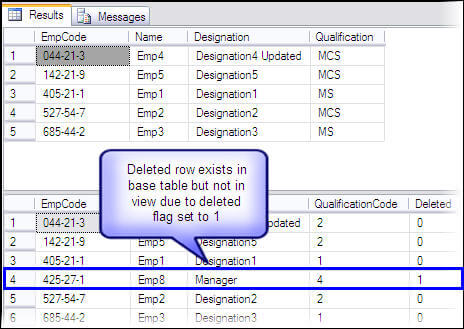
Summary
After going through these examples for implementing INSTEAD OF triggers for insert, update and delete operations on a view, there are some considerations that are required to keep in mind while planning to implement INSTEAD OF triggers.
- If you do not specify the INSTEAD OF or AFTER keyword in the trigger header and just use the FOR keyword, then by default an AFTER trigger will be created.
- You can have only one trigger for each of insert, update or delete option on a single table or view.
- If you have created an INSTEAD OF trigger on a table then you can not use the cascade option as an UPDATE and DELETE rule. Cascade for delete rule will be prohibited if INSTEAD OF trigger is defined for delete operation and same is the case for update operations.
- If you have already used cascade for delete or update options for a table then you can not create an INSTEAD OF trigger for that specific DML operation on that table.
- INSTEAD OF triggers do not work in a recursive manner. Even if you update the same table inside the INSTEAD OF trigger, the trigger will not be invoked a second time. So INSTEAD OF triggers can be used to avoid recursion.
- You can define both AFTER and INSTEAD OF triggers for the same DML operation on the same table.
- If defined on an object, an AFTER trigger can be invoked as a result of DML operations from inside the INSTEAD OF trigger.
- The deleted table for an INSTEAD OF INSERT trigger is always empty and the inserted table for INSTEAD OF DELETE trigger is always empty.
Next Steps
Keeping in mind the basic functionality of INSTEAD OF triggers, these can be used in a number of scenarios. Performance should be considered and properly tested before implementing INSTEAD OF triggers. In some scenarios they can boost the performance e.g. by skipping unnecessary roll backs, but sometimes they may be a threat to performance. Normally using INSTEAD OF triggers for DML operations on views is safe while implementing these for changing the flow of operations. Code implemented inside the INSTEAD OF trigger should be optimized as it performs alternative operations compared to the original requested DML operation.
- Click here for more information on INSTEAD OF INSERT triggers
- Click here for more information on INSTEAD OF UPDATE triggers
About the author
 Atif Shehzad is a passionate SQL Server DBA, technical reviewer and article author.
Atif Shehzad is a passionate SQL Server DBA, technical reviewer and article author.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2009-07-29






