By: Manvendra Singh | Updated: 2012-09-17 | Comments (13) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | > Performance Tuning
Problem
We have a number of SQL Server hosts with multiple SQL Server instances. From time to time we have CPU issues, but we are not sure which instance is causing the issue. How do you find which SQL Server instance is causing CPU pressure on machine with multiple SQL Server instances? Check out this tip for ideas on how to find the correct SQL Server instance which is causing CPU pressure.
Solution
Today, some of the users reported that one of their applications is running very slow. I logged in on the database server to check what is going wrong on the database server. The issue was CPU pressure. One of the SQL Server Instance was taking most of the CPU, but we had three SQL server instances on this box, so it was quite difficult to find the correct SQL Server instance which is utilizing all of the CPU.
Steps to identify the SQL Server instance utilizing most of the CPU
Step 1:- First launch Windows Task Manager to find out the CPU utilization for your database server. Below is screenshot of the Task Manager at the time of the issue I experienced. You can see all three instances have the same executable i.e. 'sqlservr.exe' and also you can see 76% of the CPU is being utilized by the first sqlservr.exe process.
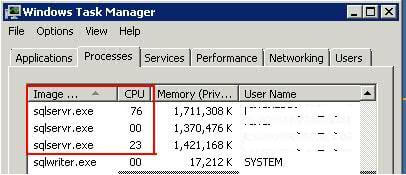
Based on reviewing Windows Task Manager, one immediate option to determine which SQL Server instance is using all of the CPU is to run each SQL Server instances with a different domain account. For example, "Domain\SQLDev" for the development environment, "Domain\SQLTest" for the test environment, etc. Unfortunately, in my circumstance all of the SQL Server instances were running under same domain account. In the image above the accounts have been erased, but they would be found in the fourth column i.e. "User Name".
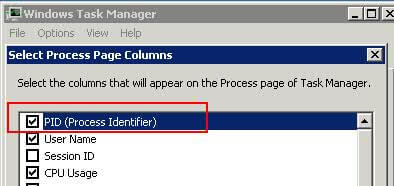
Step 2:- Now we will add the PID (Process Identifier) column in Windows Task Manager to in order to find out the PID for each process. The PID is the Windows Operating System Process Identifier assigned to each process running on the machine. In order to enable this column, ensure the "Processes" tab is active then click on the "View" menu, then choose the "Select Columns..." option. Once on the "Select Process Page Columns" screen click the check box for the option PID and then press the "OK" button to return to the Processes tab of Windows Task Manager.
Step 3:- Now you can see the PID for the 'sqlservr.exe' process which is utilizing most of the CPU. In our example, the PID of this SQL Server instance is 2352.
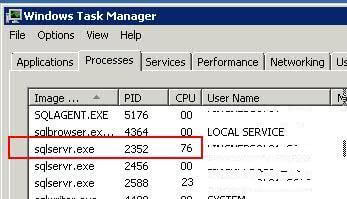
Now our next step is to determine which SQL Server instance is running this PID. We have two methods to get this information. First, is the SQL Server configuration manager and second method is the SQL Server error log.
From SQL Server 2005 onwards, it is very easy to find the PID for the SQL Server instances using the SQL Server Configuration manager. However, with SQL Server 2000 and earlier, it is not as straight forward. We will proceed with the assumption that community members are using SQL Server 2005 and beyond.
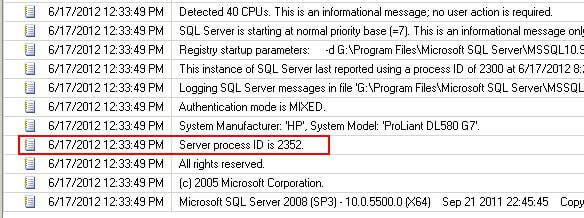
Step 4:- Whenever we start a SQL Server instance, a PID which is also know as the "Server process ID" is assigned to that instance and this information is logged in the SQL Server error log. You can see an example of this in the screenshot below. The "Server process ID" is normally one of the first entries in the log.
Step 5:-Another option is identify the correct PID for your SQL Server Instance is by using the SQL Server configuration manager. This can be accomplished by launching the SQL Server Configuration Manager and clicking on the "SQL Server Services" option in the left pane. On right side of this interface, you can see the Process ID values associated with the SQL Server services.

By correlating the information from Windows Task Manager and the SQL Server Error Log\SQL Server Configuration Manager you can correctly determine the SQL Server instance which is utilizing most of the CPU. At this point you can review the SQL Server processes on the aforementioned instance to determine the culprit process(es) which are causing CPU pressure.
Next Steps
- Use this tip to reduce your troubleshooting time to find the SQL Server instance which is responsible for high CPU utilization.
- Read about how to find out how much CPU a SQL Server process is really using.
- Read more tips on SQL Server Performance Tuning.
About the author
 Manvendra Singh has over 5 years of experience with SQL Server and has focused on Database Mirroring, Replication, Log Shipping, etc.
Manvendra Singh has over 5 years of experience with SQL Server and has focused on Database Mirroring, Replication, Log Shipping, etc.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2012-09-17






