By: Daniel Calbimonte | Updated: 2021-10-15 | Comments (15) | Related: > SQL Server Agent
Problem
Sometimes we have a T-SQL process that we need to run that takes some time to run or we want to run it during idle time on the server. We could create a SQL Agent job manually, but is there any simple way to create a scheduled job?
Solution
This tip contains T-SQL code to create a SQL Agent job dynamically instead of having to use the SSMS GUI.
I am going to create a stored procedure named sp_add_job_quick that takes a few parameters to create the job. For my example, I will create a SQL Agent job that will call stored procedure sp_who and the job will be scheduled to run once at 4:00 PM.
Creating a Stored Procedure to create SQL Agent jobs
In this sample we are going to create a job dynamically using T-SQL Code:
USE msdb
go
CREATE procedure [dbo].[sp_add_job_quick]
@job nvarchar(128),
@mycommand nvarchar(max),
@servername nvarchar(28),
@startdate nvarchar(8),
@starttime nvarchar(8)
as
--Add a job
EXEC dbo.sp_add_job
@job_name = @job ;
--Add a job step named process step. This step runs the stored procedure
EXEC sp_add_jobstep
@job_name = @job,
@step_name = N'process step',
@subsystem = N'TSQL',
@command = @mycommand
--Schedule the job at a specified date and time
exec sp_add_jobschedule @job_name = @job,
@name = 'MySchedule',
@freq_type=1,
@active_start_date = @startdate,
@active_start_time = @starttime
-- Add the job to the SQL Server
EXEC dbo.sp_add_jobserver
@job_name = @job,
@server_name = @servername
This is a stored procedure named sp_add_job_quick that calls 4 msdb stored procedures:
- sp_add_job creates a new job
- sp_add_jobstep adds a new step in the job
- sp_add_jobschedule schedules a job for a specific date and time
- sp_add_jobserver adds the job to a specific server
Let's invoke the stored procedure in order to create the job:
exec dbo.sp_add_job_quick @job = 'myjob', -- The job name @mycommand = 'sp_who', -- The T-SQL command to run in the step @servername = 'serverName', -- SQL Server name. If running locally, you can use @servername=@@Servername @startdate = '20130829', -- The date August 29th, 2013 @starttime = '160000' -- The time, 16:00:00
If everything is OK, a job named myjob will be created with a step that runs the sp_who stored procedure that will run on August 29th at 4:00PM.
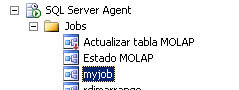
Explanation of the SQL Agent job creation code
Here I will walk through the code and what each step does.
The sp_add_job is a procedure in the msdb database that creates a job.
EXEC dbo.sp_add_job
@job_name = @job
The sp_add_jobstep creates a job step in the job created. In this tip, the step name is process_step and the action is a TSQL command.
EXEC sp_add_jobstep
@job_name = @job,
@step_name = N'process step',
@subsystem = N'TSQL',
@command = @mycommand
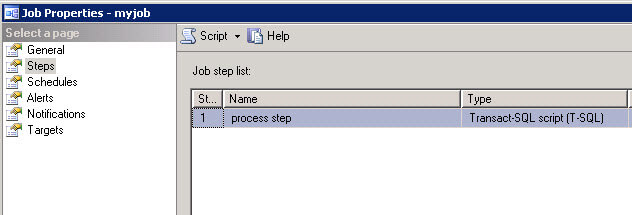
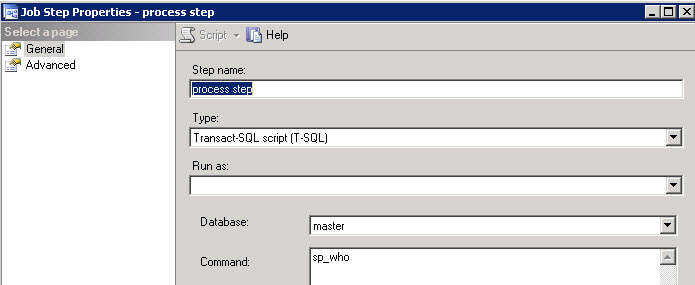
In the declare section we are assigning to the @mycommand variable the stored procedure sp_who.
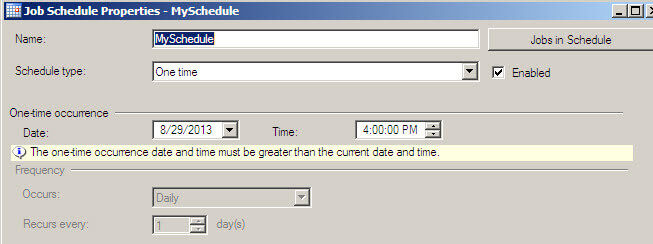
The following section let's you create the schedule for the job in T-SQL. The schedule name is MySchedule. The frequency type is once (1). If you need to run the job daily the frequency type is 4 and weekly 8 . The active start time is 16:00:00 (4PM). The start date uses the date assigned to the startdate variable '20130823'.
exec sp_add_jobschedule @job_name = @job, @name = 'MySchedule', @freq_type=1, @active_start_date = @startdate, @active_start_time = @starttime
Some additional values for the sp_add_job
Some other parameters than can be useful for the sp_add_job stored procedure are the following:
Enabled
The @enabled parameter is used to set the status of the job. If enable is 0, the job is disabled. Otherwise, it is enabled.
Example
The following examples show how to enable (1) and disable (0) the jobs.
- @enabled=1
- @enabled=0
Description
It is an optional parameter used to describe the functionality of the job. It is a best practice to add a good explanation of what the job does. The description supports 512 characters.
Example
This parameter is used to describe the job itself.
- @description=N'This job is used for...'
Start_step_id
Sometimes, we do not start the job in step 1, but we start at another step. You can decide which one is the first step in the job with this parameter.
Example
The following example will start the job at step 3.
- @start_step_id =3
Category_id
You can use the category id instead of using the category name. The find the category ID and the category name, use the following query:
use msdb go select category_id, name from dbo.syscategories GO
Example
- @category_id=3
Delete_level
This parameter indicates if the job will be deleted. By default it is 0 which means that the job will not be deleted after execution. We can delete the job after a successful or a failure or even after completion. For this parameter we created an exclusive article for you: Automatic cleanup of SQL Server Agent scheduled jobs.
For more information about the sp_add_job, go to the next steps section.
Some additional parameters for the sp_add_job_step
Some other parameters than can be useful for the sp_add_job_step stored procedure are the following:
Subsystem
The @subsystem parameter is used to define the job action. Possible values are the CmdExec, Distribution, Snapshot, LogReader, Merge, ANALYSISQUERY, ANALYSISCOMMAND, SSIS, PowerShell, TSQL.
Examples
- @subsystem=N'CmdExec'
- @subsystem=N'PowerShell'
- @subsystem=N'ANALYSISCOMMAND'
- @subsystem=N'TSQL'
On_success_action
The @on_success_action parameter is used to define what to do if the step is executed successfully. You can quit the job reporting success (value equal to 1), quit reporting a failure (2), go to the next step (3) and finally, go to an specific success step id (4).
Examples
- @on_success_action=1
- @on_success_action=2
- @on_success_action=3
On_fail_action
The @on_fail_action parameter is used to define what to do if the step is executed with failure. You can quit the job reporting success (value equal to 1), quit reporting a failure (2), go to the next step (3) and finally, go to an specific success step id (4).
Examples
The following examples will show how to quit when the step success (1) and also will show how to quit on failure (2) and how to go to the next step (3):
- @on_success_action=1
- @on_success_action=2
- @on_success_action=3
Retry_attempts
The @retry_attempts parameter is used to define the number of retries in case the job fails.
Examples
The following examples show how to set the number of retry attempts to 1, 2 or 3:
- @retry_attempts=1
- @retry_attempts=2
- @retry_attempts=3
Retry_intervals
The @retry_intervals parameter is the number of minutes to wait between attempts.
Examples
The following example will show how to set the @retry_interval parameter into 15, 30 and 60 minutes.
- @retry_intervals=15
- @retry_intervals=30
- @retry_intervals=60
Command
The @command parameter depends on the subsystem, if the subsystem is TSQL, the command will be T-SQL statements, if the subsystem is CmdExec, the command will be the command line and so on.
Examples
The following example is an ANALYSISCOMMAND:
@command=N'<Batch xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/analysisservices/2003/engine"> <Parallel> <Process xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:ddl2="http://schemas.microsoft.com/analysisservices/2003/engine/2" xmlns:ddl2_2="http://schemas.microsoft.com/analysisservices/2003/engine/2/2" xmlns:ddl100_100="http://schemas.microsoft.com/analysisservices/2008/engine/100/100"> <Object> <DatabaseID>Adventure Works DW</DatabaseID> <CubeID>Adventure Works DW</CubeID> </Object> <Type>ProcessFull</Type> <WriteBackTableCreation>UseExisting</WriteBackTableCreation> </Process> </Parallel> </Batch>'
The following example copies a backup from the C drive to the D drive using PowerShell:
@command=N'Copy-Item "C:\adw.bak" -Destination "d:\"'
The following example copies a backup from the C drive to the D drive:
@command=N'copy c:\adw.bak d:'
Some additional parameters for the sp_add_schedule
Some other parameters than can be useful for the sp_add_schedule stored procedure are the following:
Freq_type
The @freq_type parameter is used to define how often will be the run the job. The number 1 is to run once, the number 4 to run daily, the number 8 to run weekly, 16 monthly, 64 when the SQL Agent service starts and 128 when the computer is idle.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the frequency to run weekly:
- @freq_type=8
Active_start_date
The @active_start_date parameter is used to define the date that the job will start. The format is YYYYMMDD.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the active start date to 2021-10-14:
- @active_start_date=20211014.
Active_end_date
The @active_end_date is used to the date that the job will end. The format is YYYYMMDD.
Examples
The following example shows how to set the active end date to 2021-10-15:
- @active_end_date=20211015
Additional tables to find information about SQL Agent jobs
Here are some system tables in the msdb database that you can use to get job information. If you need to retrieve job information you may need them.
- dbo.sysjobactivity - shows the current information of the jobs
- dbo.sysjobhistory - shows the execution result of the jobs.
- dbo.sysjobs - shows the information of the jobs programmed.
- dbo.sysjobsshedules - shows the job schedule information like the next run date and time of the jobs.
- dbo.sysjobservers - shows the servers assigned to run jobs
- dbo.sysjobsteps - shows the job steps
- dbo.sysjobsteplogs - let you see the logs of the steps configured to display the output in a table
SQL Agent Job stored procedures
You also have these stored procedures in the msdb database to retrieve job information:
- sp_helpjob
- sp_helpjobactivity
- sp_helpjobcount
- sp_helpjobhistory
- sp_helpjobhistory_full
- sp_helpjobhistory_sem
- sp_helpjobhistory_summary
- sp_helpjobs_in_schedule
- sp_help_jobschedule
- sp_help_jobserver
- sp_help_jobstep
- sp_help_jobssteplog
I am not going to explain each system stored procedure, but in the next steps you can find links with an explanation for each.
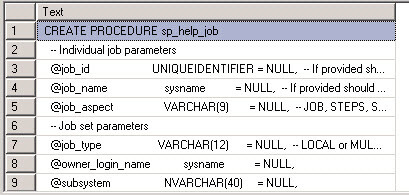
If you want to modify and create your own procedures based on the Microsoft system stored procedures you can review the code using sp_helptext. In this example, we are reviewing sp_help_job. For example, to see the T-SQL code for sp_help_job code use this command:
sp_helptext '[dbo].[sp_help_job]'
The code is displayed here:
Next Steps
For more information about creating jobs with T-SQL refer to these links:
About the author
 Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.
Daniel Calbimonte is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP, Microsoft Certified Trainer and 6-time Microsoft Certified IT Professional. Daniel started his career in 2001 and has worked with SQL Server 6.0 to 2022. Daniel is a DBA as well as specializes in Business Intelligence (SSIS, SSAS, SSRS) technologies.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2021-10-15






