By: Brady Upton | Updated: 2013-12-09 | Comments (7) | Related: More > Database Administration
Problem
I have a database table that gets groomed every night. How can I create a quick data warehouse to store all the data in a separate table so that it doesn't get groomed? The table only holds 60 days worth of data and I need to store more data for reporting purposes.
Solution
A lot of applications, including SCOM and even SSRS groom their databases so they don't grow out of control. For instance, in SSRS there is a table called ExecutionLogStorage in the ReportServer database. This table holds details about report executions. SSRS grooms this table so that it only keeps a specified number of days of data. This is good for performance reasons obviously because the larger the table grows, the worse it will perform. However, what if you need to keep more days than specified? You can probably change the number of days in a config file but then the table will begin to grow and the server will not perform optimally. In cases like this, I like to create what I call a table warehouse. A table warehouse is basically a new table that stores data from another table, but doesn't get groomed. A table warehouse will grow much larger than the source table, but the application doesn't use this table so it shouldn't effect performance, but it will effect disk space so make sure you plan accordingly. This is basically a data warehouse, but I like to think of a data warehouse as more than one table and I usually transform and massage the data before I move it to a data warehouse.
Some reasons why you might want to create a table warehouse include archiving data and reporting on older data that may get deleted in the future.
You can probably create this type of table several different ways but I like to use the UNION operator. In this tip, I'll show you the statement I use and we'll walk through it.
First, let's look at the ExecutionLogStorage table:
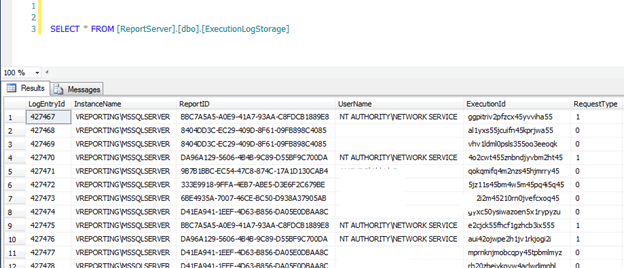
This table stores information such as InstanceName, UserName, Format, Parameters, Start/End Time, etc. By default, it only stores information for 60 days. Every night, SSRS grooms this table so that the 61st day of data is deleted. We need to keep more than 60 days of data so that's where the table warehouse comes into play.
First thing we'll need to do is create our table warehouse table that will hold the data. I don't need all the columns from the ExecutionLogStorage table so I'll just create my table warehouse to store InstanceName, UserName, Format, TimeStart, TimeEnd, TimeProcessing, Status, ByteCount and RowCount.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW](
[InstanceName] [nvarchar](38) NOT NULL,
[UserName] [nvarchar](260) NULL,
[Format] [nvarchar](26) NULL,
[TimeStart] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[TimeEnd] [datetime] NOT NULL,
[TimeProcessing] [int] NOT NULL,
[Status] [nvarchar](40) NOT NULL,
[ByteCount] [bigint] NOT NULL,
[RowCount] [bigint] NOT NULL
) Next we can use the following query to see the differences between the ExecutionLogStorage table and our new ExecutionLogStorageTW table:
SELECT MIN(TableName) AS TableName ,InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] FROM ( SELECT 'ELS' AS TableName ,els.InstanceName ,els.UserName ,els.[Format] ,els.TimeStart ,els.TimeEnd ,els.TimeProcessing ,els.[Status] ,els.ByteCount ,els.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorage] els UNION ALL SELECT 'ELSDW' AS TableName ,elstw.InstanceName ,elstw.UserName ,elstw.[Format] ,elstw.TimeStart ,elstw.TimeEnd ,elstw.TimeProcessing ,elstw.[Status] ,elstw.ByteCount ,elstw.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW] elstw ) tmp GROUP BY InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] HAVING COUNT(*) = 1
This query will UNION all the results from ExecutionLogStorage and ExecutionLogStorageTW and display the data that is different. As you can see from the results below there are 72325 results that are different. The TableName column displays the table that the data resides in, therefore you can see that all the data resides in the ELS (ExecutionLogStorage) table.
Since ExecutionLogStorageTW is empty it should show the exact results as:
SELECT * FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorage]
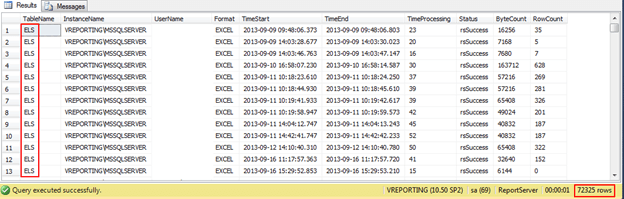
Now that I can see the differences, all I need to do is INSERT them into my new table using the following INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW] SELECT InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] FROM ( SELECT 'ELS' AS TableName ,els.InstanceName ,els.UserName ,els.[Format] ,els.TimeStart ,els.TimeEnd ,els.TimeProcessing ,els.[Status] ,els.ByteCount ,els.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorage] els UNION ALL SELECT 'ELSDW' AS TableName ,elstw.InstanceName ,elstw.UserName ,elstw.[Format] ,elstw.TimeStart ,elstw.TimeEnd ,elstw.TimeProcessing ,elstw.[Status] ,elstw.ByteCount ,elstw.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW] elstw ) tmp GROUP BY InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] HAVING COUNT(*) = 1
We can now query the COUNT on both tables and they should match:
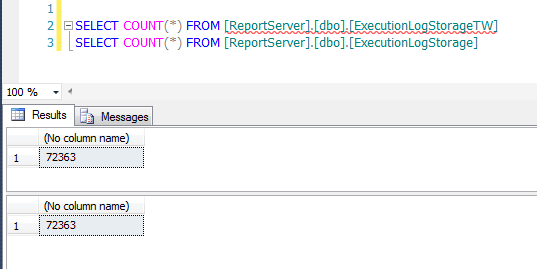
We now have two tables with identical data. But what happens when ExecutionLogStorage gets groomed? The query we are using will show that a difference exists and will re-INSERT the data. Since we only want to INSERT data from the ExecutionLogStorage (ELS) table we can just simply add to the HAVING clause
AND MIN(TableName) = 'ELS'
...making the complete statement look like this:
INSERT INTO [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW] SELECT InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] FROM ( SELECT 'ELS' AS TableName ,els.InstanceName ,els.UserName ,els.[Format] ,els.TimeStart ,els.TimeEnd ,els.TimeProcessing ,els.[Status] ,els.ByteCount ,els.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorage] els UNION ALL SELECT 'ELSDW' AS TableName ,elstw.InstanceName ,elstw.UserName ,elstw.[Format] ,elstw.TimeStart ,elstw.TimeEnd ,elstw.TimeProcessing ,elstw.[Status] ,elstw.ByteCount ,elstw.[RowCount] FROM [ReportServer].[dbo].[ExecutionLogStorageTW] elstw ) tmp GROUP BY InstanceName ,UserName ,[Format] ,TimeStart ,TimeEnd ,TimeProcessing ,[Status] ,ByteCount ,[RowCount] HAVING COUNT(*) = 1 AND MIN(TableName) = 'ELS'
You can schedule this with a SQL Agent job or run on demand. If the job was to fail, it will simply look at the differences between the tables since the last run and execute accordingly.
Next Steps
- Like I mentioned earlier, there may be other ways to complete this task. This is just one example that I found to be the quickest and easiest to setup.
- A data warehouse is much more complex to setup and is more common for analysis. This tip is meant to show a quick and easy way to replicate a few tables.
About the author
 Brady Upton is a Database Administrator and SharePoint superstar in Nashville, TN.
Brady Upton is a Database Administrator and SharePoint superstar in Nashville, TN.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2013-12-09






