By: Rajendra Gupta | Updated: 2015-07-03 | Comments (3) | Related: > Database Mirroring
Problem
An issue you will face at some point in your career is SQL Server database corruption. SQL Server database corruption causes issues where data cannot be accessed correctly and often queries are aborted and do not complete correctly. A feature in SQL Server Database Mirroring is the ability to automatically fix corrupted database pages and in this tip we will look at how this is done.
Solution
Automatic Page Repair is one of the features of SQL Server Database Mirroring which helps us replace a corrupt page by getting a good copy from a partner database. This functionality works bi-directionally (i.e. if the Mirrored Database page is corrupt or a page on the Principal Database is corrupt). In this tip we will demonstrate this feature.
Let's say we have a database configured for mirroring and we want to corrupt the database so we can test out this feature.
Note - Do NOT perform this test in a PRODUCTION environment. The example is intended to demonstrate the process of recovering a page with Database Mirroring.
The first thing we are going to do is to find an object in our database that we can make changes to with a text editor to create corruption. Run the below script on the principal database to find the index ids for table "Test".
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(object_id), name, index_id, type_desc FROM sys.indexes where OBJECT_NAME(object_id)='test' ORDER BY 1
We will use the clustered / primary key index which has an index id of 1 as shown below.
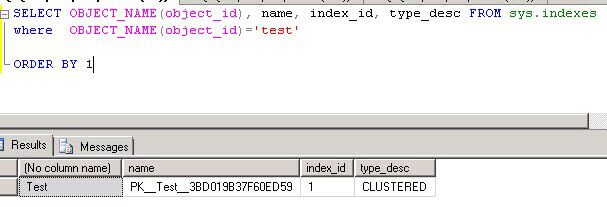
Next we will use the DBCC IND command to get the page id and we will randomly select a page number that we will modify to corrupt a page in the database. The parameters we pass to DBCC IND are the DatabaseName, TableName and IndexID as shown below.
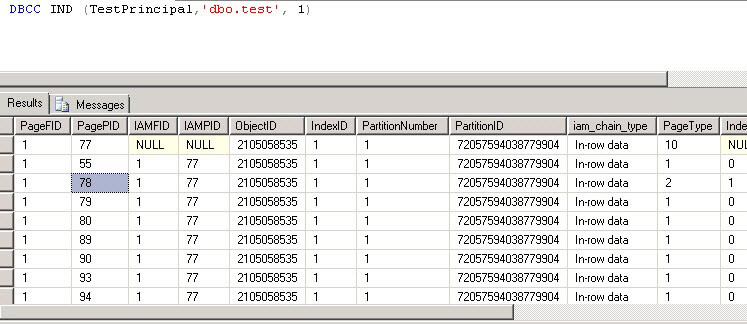
Now we will use the DBCC PAGE command to read the page we selected. In this example, I have selected page 78 as shown above. We also need to enable trace flag 3604 before running DBCC PAGE so we can see the output in SSMS. The parameters we pass to DBCC PAGE are the DatabaseName, PageFID, PageID and the data output option.
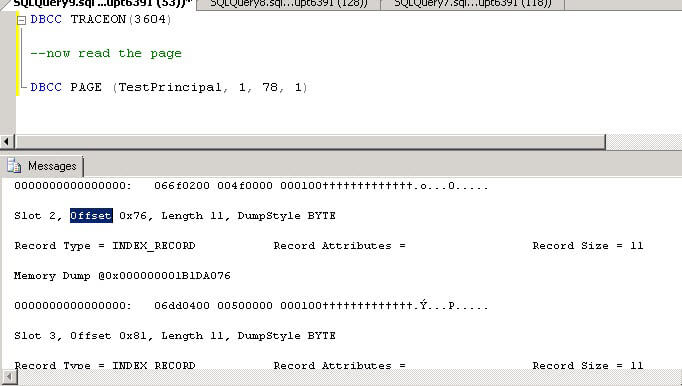
To hack the data and corrupt page 78 in the database we need to find the position in the file we want to change. We will need to convert the record offset as shown above which has a hex value of 76. If we convert that to decimal, the value is 118. So the point in the database file that I am going to hack can be calculated as follows:
Page Number x Number of Bytes Per Page + Record Offset ( 78 x 8192 + 118 = 639094 )
In order to corrupt the page in my demo database, I have to take my principal database offline. To corrupt the page I used XV132 text editor. Open the database data file using this tool and search for 639094 as shown below. Change a value and then save the file and exit the tool.
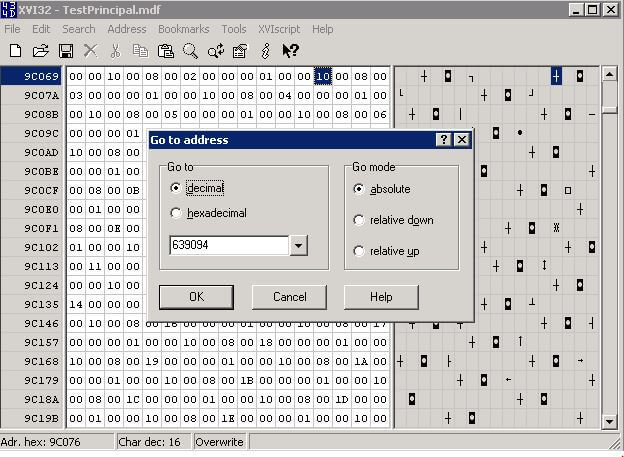
Bring the database back online and perform a DBCC CHECKDB for the database. As you can see below, the Test table has some corruption.
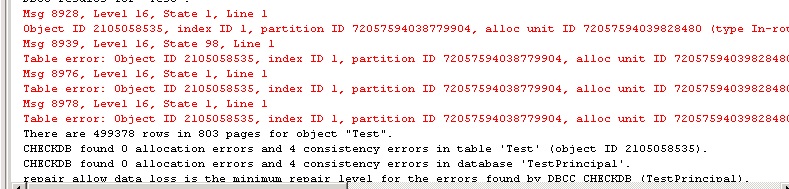
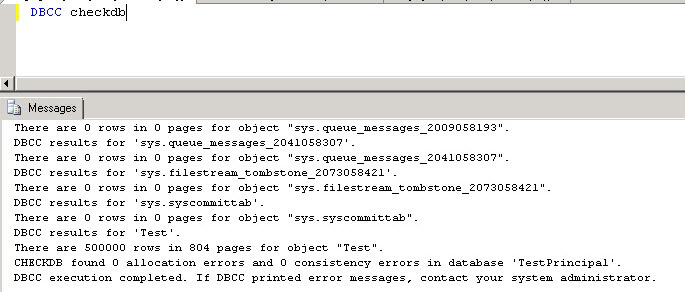
Once mirroring is re-established and the data is synchronized perform another DBCC CHECKDB on the principal database to see if the page has been fixed. In the below screenshot we can see that there is no longer any database corruption, because the page has been replaced by mirroring.
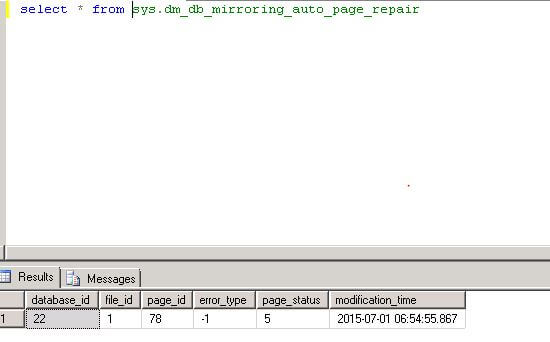
To confirm that a fix was done, we can use DMV sys.dm_db_mirroring_auto_page_repair to show if there have been any fixes. The output shows page_status equals 5 (automatic page repair succeeded).
The SQL Server Error Logs also has entries for automatic page repair as well.

If the page is also corrupt on the partner database, the page_status will be 6 which means irreparable. This indicates that an error occurred during the page-repair attempt, for example, because the page is also corrupted on the partner, the partner is disconnected, or a network problem occurred. This state is not terminal, if corruption is encountered again on the page, the page will be requested again from the partner. If the page I/O error caused any deferred transactions, after you repair the page, the principal/primary tries to resolve those transactions.
Automatic Page Repair Notes
On the principal/primary database, automatic page repair is tried only when the database is in the SYNCHRONIZED state and the principal/primary is still sending log records for the database to the mirror/secondary.
When the principal identifies a page read error, it marks the page with an 829 error and inserts a row into the suspect_pages table in MSDB with the error status then requests the page from the partner. If the mirror is successful in reading the page it returns the page to the principal where it is applied. After the page is repaired the principal marks the page as restored (event_type = 5) in the suspect_pages table.
Similarly, when the mirror identifies a page read error, it marks the page with an 829 error and inserts a row into the suspect_pages table in MSDB with the error status information. It requests the page from the principal and sets the mirror session to a SUSPENDED state. If the principal is successful in reading the page it returns the page to the mirror. Once the pages applied on the mirror, the mirror resumes the data mirroring session and marks the page as restored in the suspect_pages table with event_type = 4.
Error Types That Cause an Automatic Page Repair Attempt
1. Error number 823 - Action is taken only if the operating system performed a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) that failed on the data.
2. Error number 824 - Logical errors such as bad page checksum.
3. Error number 829 - A page has been marked as restore pending.
Automatic page repair cannot repair the following control page types
1. File header page - Page ID 0.
2. Page 9 - The database boot page.
3. Allocation pages: Global Allocation Map (GAM) pages, Shared Global Allocation Map (SGAM) pages, and Page Free Space (PFS) pages.
Next Steps
- Check out more about DMV sys.dm_db_mirroring_auto_page_repair.
About the author
 Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.
Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2015-07-03






