By: Almoustapha Cisse | Updated: 2010-09-23 | Comments | Related: > SharePoint
Problem
Corporations that have offices in diverse geographical areas might need to cater information to each country in its specific language. Traditional multilingual implementations rely on separate environments for each language. Consequently, there are challenges configuring and managing the following:
- Language packs
- Setting the default language based on the user
- Site variations: Synchronizing sites' content across multiple environments.
Solution
Microsoft attempted to provide a solution with SharePoint 2007 multilingual site publishing.
Step 1: Install the Operating system's Language Packs
It is important to install the language specific files for the operating system, in this case Windows Server 2008:
Step 2: Install the WSS 3.0 and MOSS 2007 language packs on the Web Front End servers
Important: In contrary to what several blogs and white papers suggested by recommending the installation of the 'MOSS language pack only, it is important to install the language packs for both WSS 3.0 and MOSS 2007 and their respective service packs.
The first step in configuring a multilingual SharePoint environment is to install the language packs for each language on all Web Front End servers. If you installed SharePoint in just English and need to be able to publish in English and French, you are going to need to install the French language packs. Should you need to publish additional languages, you are going to need to install the language packs for those languages separately. The respective language ID is created in c:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\web server extensions\12\template\
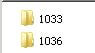
There is a specific language ID for each language.
| Language | Identifier |
|---|---|
| English | 1033 |
| French | 1036 |
| German | 1031 |
| Arabic | 1025 |
Run the SharePoint Products and Technologies Configuration Wizard
Step 3: Create the top level site collection
It is important to use a publishing site in order to leverage variations in a multilingual environment.
Go to Central Administration > Application Management > Click Create Site Collection
Under Select a Template, click Publishing and select any of the publishing templates.
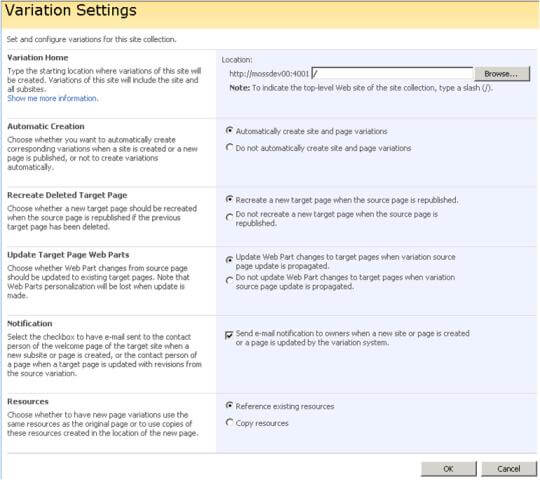
Step 4: Enable Site Variations
- On the new top-level site, Go to Site Actions > Under Site Collection Administration, Click Variations
- Under Location, enter a forward slash (/)
- Review the settings and choose the desired options
- Click OK
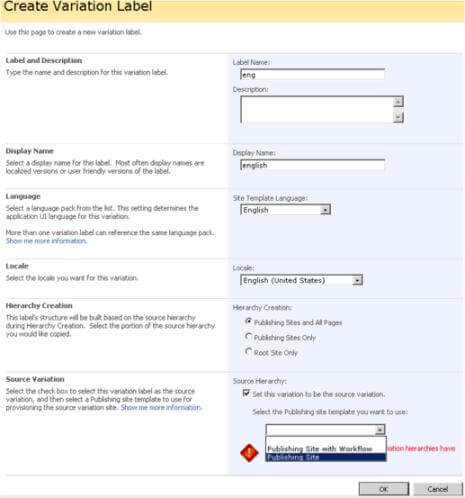
Step 5: Configure Variation Labels
- Create the "Root" label (English)
- Go to Site Settings->Site Collection Administration
- Click Variation Labels
- On the 'Variation Labels' screen, click 'New Label' and create an English label
- Remember to check Set this variation to be the source variation (see screenshot)
Note: You may simply choose a Publishing Site or a Publishing Site with Workflow. Some people find the workflows annoying as SharePoint sends a notification at each variation event.
- Click OK.
- Create the French label
- Go to Site Settings->Site Collection Administration
- Click Variation Labels
- On the 'Variation Labels' screen, click 'New Label' and create the French label (see screenshot)
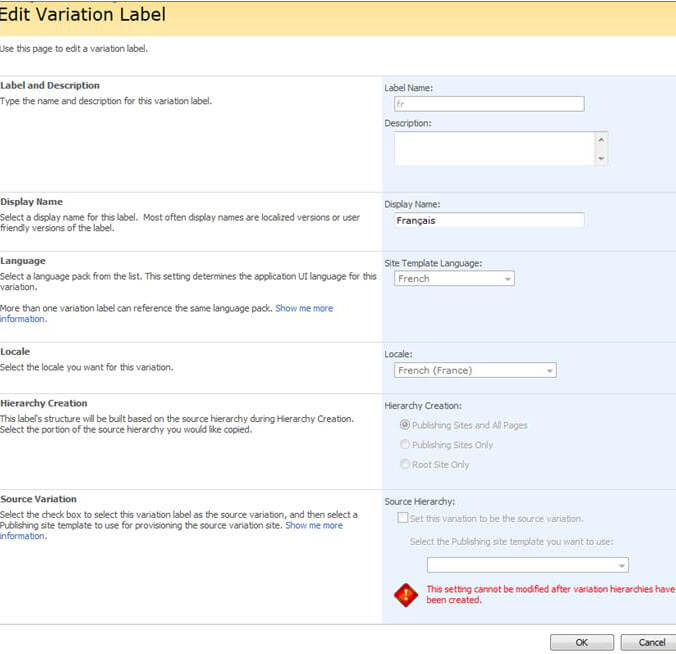
Note: You may create more labels for additional languages providing you have installed their language packs.
Step 6: Create Hierarchies
The last step after creating the variation label for each language is to create the variation hierarchies, which will generate a site for each label.
- Create the variation hierarchies
- Go to Site Settings->Site Collection Administration
- Click Create Hierarchies
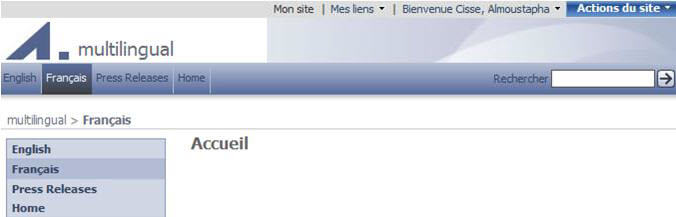
Step 7: Set the browser default language
Setting the right default language for site users is very important as it allows the browser to automatically direct users to their language site
- Tools > Internet Options
- Under General, Click Languages and Add
- Select French (for this Scenario) and Click OK
Note: You could have your default language (i.e. English) listed and remove any other language in the Language Preference list. Or you may have several languages listed but you are going to need to have your default language moved on the top of the list by using the "Move up" button.
Important: In the French site, all the system generated content is automatically translated in to French. However, navigation items and propagated content would need to be manually translated by a human being. Finally, as content managers start adding content to the site root site (English), they may leverage the site's "Translation Management Library" and workflow to assign translation tasks to French translators for the content translation into French.
Limitations and workarounds
There are limitations to using multilingual SharePoint. Here is a few of them:
Search:
The default search result page for the French site displays in English. There are two alternatives to alleviate the issue:
- Option 1: create a separate Search Center in each variation site
- Option 2: customize the default Search Center to auto-detect the language and display the result in that particular language
Web Parts:
- When you add a Web Part into the root site (English), the same Webpart appears in the variation site (French). And when you translate that Webpart in the variation site (French), it will also appear in the English. In reality, the same Webpart is showing up on both places. Consequently, I recommend turning off the Update Target Page Webpart option under the site's Variation Settings
Customizing/Troubleshooting variations
The SharePoint timer executes the variation process like any other automated or scheduled SharePoint process.
- The first troubleshooting tip is to always review your variation logs:
- Go to Site Settings->Site Collection Administration > Variation Logs
- You may troubleshoot or customizing sites' variations by viewing the objects' relationship by inserting the following section at the end of the site collection URL: Relationships%20List/AllItems.aspx (i.e.: http://mossdev00:4001/sites/multilingual/Relationships%20List/AllItems.aspx)
- Variation Manifest file (XML): Open the manifest page using STSADM
- Correlate the Group ID & Object ID with those in the relationships page
Conclusion
MOSS 2007 provides support for multiple languages deployments in a single framework in order to server corporate users across the globe. Despite some limitations, the MOSS 2007 publishing feature allows the propagation of content across variations sites.
Next Steps
- For additional information in planning in deploying Multilingual Solutions, you may refer to the following document by Brandinelli, L (Plan for building multilingual solutions by using SharePoint Products and Technologies)
About the author
 Almoustapha Cisse
Almoustapha CisseThis author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2010-09-23






