By: Ahmad Yaseen | Updated: 2016-10-11 | Comments | Related: > Database Console Commands DBCCs
Problem
How can we control the number of processors assigned to the SQL Server DBCC CHECKDB command in order not to consume all of the serverís resources when CHECKDB is running?
Solution
Degree of parallelism is the number of processors that are assigned to run a single SQL statement. SQL Server manages to detect the best degree of parallelism for each query to generate the best execution plan. Maximum Degree of Parallelism (MAXDOP) is an instance level configuration that is used to restrict the number of processors used for parallel execution plans for performance purposes.
SQL Server 2016 introduces a new option to limit the number of processors assigned for the DBCC CHECKDB statement, overriding the instance level MAXDOP configuration. For this demo I am using a machine with 4 processors as we can see in the Task Manager window as shown below:

The instance level MAXDOP option is configured with the default value 0, which means that SQL Server parallel plans will use all processors available on that server, which is 4 in my case. This configuration can be checked and reconfigured from the Advanced tab of the Server Properties window using SQL Server Management Studio as follows:
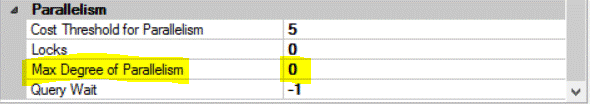
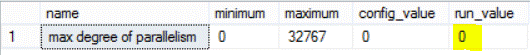
The MAXDOP option can be also checked using the sp_configure command as shown below:
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE GO sp_configure 'max degree of parallelism';
The query result will be like this:
If we execute the below DBCC CHECKDB statement and take into consideration that the DBCC CHECKDB command is a heavy command that will use a parallel execution plan to run (if applicable) using the instance level MAXDOP configuration value:
SET STATISTICS TIME ON DBCC CHECKDB (AdventureWorks2012) SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
We can grab the current session ID from the SSMS status bar as shown below:
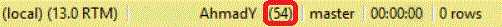
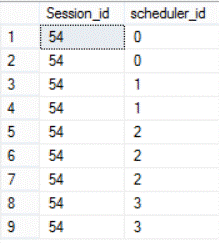
Then querying the sys.dm_os_tasks system object to check the number of schedulers used by that session during execution:
select Session_id , scheduler_id from sys.dm_os_tasks where session_id = 54
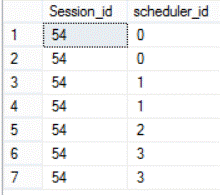
The result will show us that the DBCC CHECKDB command is using all available processors which is 4 in our situation (scheduler_id 0, 1, 2, 3) :
This took 3800ms to complete its execution:
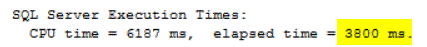
As mentioned previously, the DBCC CHECKDB can override the instance level MAXDOP option to be restricted to a specific number of processors. The below DBCC CHECKDB command will use only 3 processors to run:
SET STATISTICS TIME ON DBCC CHECKDB (AdventureWorks2012) WITH MAXDOP = 3; SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
Checking the number of schedulers again for that query (scheduler_id 0, 1, 3):
You will find that the DBCC CHECKED command is limited with only 3 processors although the SQL Server is configured to use all available 4 processors. This query took 4046ms to complete successfully:
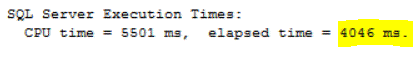
The below query also will restrict the DBCC CHECKDB command to use only 2 processors:
SET STATISTICS TIME ON DBCC CHECKDB (AdventureWorks2012) WITH MAXDOP = 2; SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
Which is clear when we check the number of schedulers used in the current session (scheduler_id 0, 1):
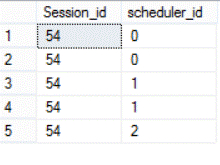
And the command took 4293ms to complete successfully.

Letís try it in another way. If the instance level MAXDOP option is configured with a value 1, which means that each query can use only one processor to run. This can be configured using sp_configure as below:
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'max degree of parallelism', N'1' GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO
The below command will override that value to use 3 processors to run:
DBCC CHECKDB (AdventureWorks2012) WITH MAXDOP = 3;
This can be clearly found by checking the number of schedulers used in that session:
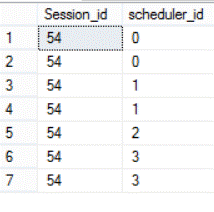
As you can see from the previous results, the DBCC CHECKDB command will run faster if it takes the benefits from more parallel threads. Each time we decrease the number of processors assigned to the command it will take longer to complete, but consume less CPU. Using this option allows us to prevent this command from consuming all server resources and degrading the serverís overall performance during its execution. So that is a decision you will need to make, to either run faster or limit the CPU resources used.
Next Steps
- DBCC CHECKDB WITH MAXDOP option also works with SQL Server 2014 SP2 version.
- Read more about SQL Server DBCC CHECKDB Overview.
- Check out What MAXDOP setting should be used for SQL Server.
About the author
 Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.
Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2016-10-11






