By: Simon Liew | Updated: 2016-11-23 | Comments (4) | Related: > Availability Groups
Problem
Automatic Seeding for an Availability Group (AG) is a new addition to the way databases can be added into an AG in SQL Server 2016. This tip will give an introduction on Automatic Seeding and compare performance adding databases into an AG between Automatic Seeding and adding a database to an AG using backup and restore.
Solution
Since the introduction of AG, adding a database into an AG involves a database
backup and
restore operation quite similar to configuring database mirroring.
As part of the backup and restore process, the database backup needs to reside
on a (shared) folder accessible to all SQL replicas for the restore operation.
Starting with SQL Server 2016, Automatic Seeding is introduced as a new way to add databases into an AG. Automatic Seeding reads the database files directly and streams the bytes to the secondary using the database mirroring endpoints without requiring an explicit backup and restore of the database during the process. This also means the I/O overhead involved with backup and restore operation to a physical file can now be avoided.
During Automatic Seeding, the Dynamic Management View (DMV) sys.dm_exec_requests exposes some information such as the percent_complete of the streaming. These are background processes which means it is scheduled internally by SQL Server. Transaction log truncation will be blocked during the Automatic Seeding activity. So, this is an important consideration if workloads are allowed on the database prior to the completion of the seeding process.
SELECT r.session_id, r.status, r.command, r.wait_type , r.percent_complete, r.estimated_completion_time FROM sys.dm_exec_requests r JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions s ON r.session_id = s.session_id WHERE r.session_id <> @@SPID AND s.is_user_process = 0 AND r.command like 'VDI%'
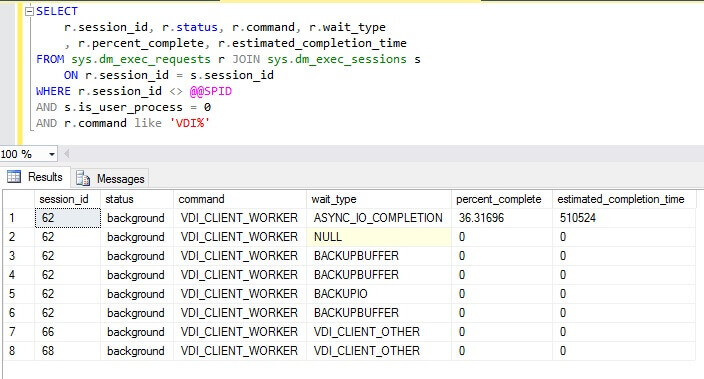
Automatic Seeding is a replica level setting and applies to all the databases in the AG. A documented trace flag 9567 can be turned on for the primary SQL instance during the automatic seeding process to enable compression of the data stream. This trace flag can significantly reduce the transfer time, but at the same time increases the load on the server CPU utilization.
There are two DMVs to view information on Automatic Seeding activity.
| DMV |
Description |
|---|---|
| sys.dm_hadr_physical_seeding_stats | Provides statistics during the automatic seeding process |
| sys.dm_hadr_automatic_seeding | Provides status on automatic seeding process |
Test Configuration
Below is some high-level information of the testing environment configuration. The database used in this test is not TDE-enabled.
| Database size | 60 GB |
| Database space used | 47 GB |
| Transaction log size | 5 GB |
| Backup size without compression | 47 GB |
| Backup size with compression | 400 MB |
| AG nodes | 2 |
| Network links | 10.0 Gpbs |
| Storage | SAN storage (rotating media) on RAID-10 |
The same database is restored each time prior to adding the database into the AG. The AG endpoint and AlwaysOn_health XE are created prior to starting the test.
Test Results
| Test | Test Scenario | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Automatic Seeding without TF9567 | 12 mins 05 secs |
| 2 | Backup and restore without backup compression | 13 mins 30 secs |
| 3 | Automatic Seeding with TF9567 | 2 mins 56 secs |
| 4 | Backup and restore with backup compression | 5 mins 12 secs |
Summary
The backup and restore method to add a database into an AG is still applicable and fully supported. The similar conditions to add databases into an AG are still applicable to both Automatic Seeding or backup / restore such as the database must be in the FULL recovery model and have a current full backup.
The test database only contains a single table containing the same values, hence the database backup compression can compress to an impressive backup size of only 400 MB. Disregarding this fact, adding databases into an AG using Automatic Seeding with TF9567 outperformed the equivalent of the backup and restore method with compression.
Tests Configuration and Steps
Below are the steps I used for the different tests.
Test 1 – Automatic Seeding without TF9567
- Restore the test database on the primary SQL instance.
- The script to be executed on the primary SQL instance below can be easily generated using the New Availability Group Wizard. To use Automatic Seeding, the script only needs to include an additional argument SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC.
Script to be executed on primary SQL instance.
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname] WITH (AUTOMATED_BACKUP_PREFERENCE = PRIMARY, DB_FAILOVER = OFF, DTC_SUPPORT = NONE) FOR DATABASE [dbname] REPLICA ON N'<primary_server_instance>' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://<primary_server>.<fully_qualified_domain_name>:5022' , FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL , AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT , BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50 , SECONDARY_ROLE(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = NO) , SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC), N'<secondary_server_instance>' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://<secondary_server>.<fully_qualified_domain_name>:5022' , FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL , AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT , BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50 , SECONDARY_ROLE(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = NO) , SEEDING_MODE = AUTOMATIC); GO
- On the secondary SQL instance, an additional line of code is required to grant the AG permission to create the database.
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname] JOIN; GO ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname] GRANT CREATE ANY DATABASE; GO
- When automatic seeding is enabled for an AG, new databases will automatically get added to the secondary. If you do not want this behavior, the script below will disable the automatic seeding on the primary SQL replica.
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname] MODIFY REPLICA ON ' <primary_server_instance>' WITH (SEEDING_MODE = MANUAL) GO
Test 2 - Backup and restore without backup compression
- Restore the test database on the primary SQL instance.
- The script below is generated using the New Availability Group Wizard and then executed in a SQLCMD mode to allow continuation of the backup and restore operation immediately after each step.
--- YOU MUST EXECUTE THE FOLLOWING SCRIPT IN SQLCMD MODE.
:Connect <primary_server_instance>
USE [master]
GO
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname]
WITH (AUTOMATED_BACKUP_PREFERENCE = PRIMARY,
DB_FAILOVER = OFF,
DTC_SUPPORT = NONE)
FOR DATABASE [dbname]
REPLICA ON N'<primary_server_instance>' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://<primary_server>.<fully_qualified_domain_name>:5022'
, FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
, AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT
, BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50
, SECONDARY_ROLE(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = NO)),
N'<secondary_server_instance>' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://<primary_server>.<fully_qualified_domain_name>:5022'
, FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
, AVAILABILITY_MODE = SYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT
, BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50
, SECONDARY_ROLE(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = NO));
GO
:Connect <secondary_server_instance>
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [agname] JOIN;
GO
:Connect <primary_server_instance>
BACKUP DATABASE [agname] TO DISK = N'\\<fileshareserver>\dbname.bak' WITH COPY_ONLY, FORMAT, INIT, SKIP, REWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5
GO
:Connect <secondary_server_instance>
RESTORE DATABASE [agname] FROM DISK = N'\\<fileshareserver>\dbname.bak' WITH NORECOVERY, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5
GO
:Connect <primary_server_instance>
BACKUP LOG [agname] TO DISK = N'\\<fileshareserver>\dbname.trn' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NOSKIP, REWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5
GO
:Connect <secondary_server_instance>
RESTORE LOG [agname] FROM DISK = N'\\<fileshareserver>\dbname.trn' WITH NORECOVERY, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5
GO
:Connect <secondary_server_instance>
-- Wait for the replica to start communicating
begin try
declare @conn bit
declare @count int
declare @replica_id uniqueidentifier
declare @group_id uniqueidentifier
set @conn = 0
set @count = 30 -- wait for 5 minutes
if (serverproperty('IsHadrEnabled') = 1)
and (isnull((select member_state from master.sys.dm_hadr_cluster_members where upper(member_name COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS) = upper(cast(serverproperty('ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS') as nvarchar(256)) COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS)), 0) <> 0)
and (isnull((select state from master.sys.database_mirroring_endpoints), 1) = 0)
begin
select @group_id = ags.group_id from master.sys.availability_groups as ags where name = N'SeedAG'
select @replica_id = replicas.replica_id from master.sys.availability_replicas as replicas where upper(replicas.replica_server_name COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS) = upper(@@SERVERNAME COLLATE Latin1_General_CI_AS) and group_id = @group_id
while @conn <> 1 and @count > 0
begin
set @conn = isnull((select connected_state from master.sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states as states where states.replica_id = @replica_id), 1)
if @conn = 1
begin
-- exit loop when the replica is connected, or if the query cannot find the replica status
break
end
waitfor delay '00:00:10'
set @count = @count - 1
end
end
end try
begin catch
-- If the wait loop fails, do not stop execution of the alter database statement
end catch
ALTER DATABASE [dbname] SET HADR AVAILABILITY GROUP = [agname];
GO
Test 3 – Automatic Seeding with TF9567
- Restore the test database on the primary SQL instance.
- Enable Trace Flag 9567 on the primary SQL Server instance.
DBCC TRACEON(9567, -1)
- Execute the script from Test 1.
Test 4 - Backup and restore with backup compression
- Restore the test database on the primary SQL instance.
- Enable backup compression on the primary SQL Server instance.
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'backup compression default', N'1' GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO
- Execute the script from Test 2.
Next Steps
- Automatically initialize Always On availability groups
- Trace Flags (Transact-SQL)
- More Always On Availability Group tips
About the author
 Simon Liew is an independent SQL Server Consultant in Sydney, Australia. He is a Microsoft Certified Master for SQL Server 2008 and holds a Master’s Degree in Distributed Computing.
Simon Liew is an independent SQL Server Consultant in Sydney, Australia. He is a Microsoft Certified Master for SQL Server 2008 and holds a Master’s Degree in Distributed Computing.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2016-11-23






