By: Dallas Snider | Updated: 2017-01-09 | Comments (3) | Related: > Analysis Services Development
Problem
I need to use SQL Server 2016 data as an input to WEKA. How can I connect WEKA to SQL Server 2016?
Solution
WEKA is an open source data mining application, written in Java, that provides a variety of machine learning algorithms. Unlike SQL Server Analysis Services, WEKA generates Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves, calculates the area under the ROC curve, and calculates precision and recall. In this tip we will step through the process of connecting WEKA 3.8.0 to SQL Server 2016 on Windows 10. The data in this tip is from a banking example provided by Bamshad Mobasher at DePaul University.
After installing WEKA 3.8.0 with the default settings, download and install the Microsoft JDBC 4 driver. Please remember the path and file name of the driver as it is needed in the next step. In this tip, the installation program was run with Administrator rights and the driver was installed in the directory C:\Program Files\Microsoft JDBC Driver 6.0 for SQL Server.
Next we need to add the full path and file name of the Microsoft JDBC 4 driver to the CLASSPATH system environment variable. In this example, the path and file name is C:\Program Files\Microsoft JDBC Driver 6.0 for SQL Server\sqljdbc_6.0\enu\sqljdbc4.jar.
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on System.
- Click on Advanced System Settings.
Click on Environment Variables...
Look for a CLASSPATH variable in the System Variables box.
If a CLASSPATH variable exists, click on CLASSPATH and then Edit. In the Variable Value box, append a semicolon and the full path to the JDBC jar file to the existing CLASSPATH value. Make sure to include the file name. Click on OK to close the Edit System Variable window.
If CLASSPATH does not exist click on New.
In the Variable Value box enter the full path and file name to the JDBC jar file. Click on OK to close the New System Variable window.
Now that the CLASSPATH is pointing to the JDBC driver, click on OK to close the Environment Variable window.
Click on OK to close the System Properties window.
With the CLASSPATH set we need to make modifications to the WEKA database utilities property file. You will need to have administrator rights to do the next series of steps. Go to the WEKA home directory. In this example it is C:\Program Files\Weka-3-8. Locate the weka.jar file.
From the weka.jar file, we want to extract the directory structure and files. The goal is to have the directory .\weka\experiment created and its files extracted to this directory. In this example the full path is C:\Program Files\Weka-3-8\weka\experiment. Notice the database utility property files at the bottom of the following image.
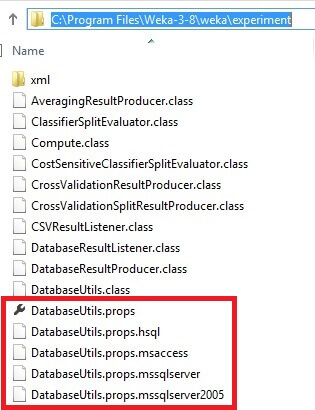
We need to make several changes to the DatabaseUtils.props file. Make a backup copy of DatabaseUtils.props. Open the file DatabaseUtils.props.mssqlserver2005 with a text editor and save as DatabaseUtils.props to overwrite the existing DatabaseUtils.props file. Make sure your entries for JDBC driver and database URL are similar to what are shown below. In this example the server is localhost, the port is 1433, and the database is named MSSQLTips. The # symbol denotes a comment.
# JDBC driver (comma-separated list) jdbcDriver=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver # database URL jdbcURL=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;databasename=MSSQLTips
Below the database URL entry there is a section that configures the data type mappings between WEKA and SQL Server. In the example below I have added comments to show the default mappings and I have added some more mappings.
# specific data types # string, getString() = 0; --> nominal # boolean, getBoolean() = 1; --> nominal # double, getDouble() = 2; --> numeric # byte, getByte() = 3; --> numeric # short, getByte()= 4; --> numeric # int, getInteger() = 5; --> numeric # long, getLong() = 6; --> numeric # float, getFloat() = 7; --> numeric # date, getDate() = 8; --> date # text, getString() = 9; --> string # time, getTime() = 10; --> date # timestamp, getTime() = 11; --> date # map SQL Server data type to WEKA data type # default mappings varchar=0 float=2 tinyint=3 int=5 # values added manually string=0 bigint=6 nvarchar=9 decimal=2 bit=1
Save the changes to this file.
Next, we will use the T-SQL examples below to create and then populate our example table. By default, WEKA will use the last column as the label used for the classification algorithms. In this example, the column DidBuyAPersonalEquityPlan will be the class label in WEKA.
create table dbo.tblBankData ( UniqueID int identity(1,1) Primary Key, AgeRange varchar(8) not null, Gender varchar(6) not null, Region varchar(10) not null, Income varchar(8) not null, Married varchar(3) not null, NumberOfChildren int not null, IsCarOwner varchar(3) not null, HasSavingsAccount varchar(3) not null, HasCurrentAccount varchar(3) not null, HasMortgage varchar(3) not null, DidBuyAPersonalEquityPlan varchar(3) not null )
Click here for the T-SQL code to insert 600 rows into the table.
Now let's start WEKA 3.8 (with console).
In the WEKA GUI Chooser window, select Explorer.
Click on Open DB...
Click on the button highlighted below to display the Database Connection Parameters window.
Enter the database login and password. Click on OK. Please note that I was only able to connect using SQL Server Authentication.
Click on the connect to the database button.
A successful database connection will appear as shown below with a warning message in the Info box. Any connection errors will also display in this box.
Enter a query and click on Execute.
The results will display in the Results box. If satisfied with the results click on OK.
We now see that our SQL Server database data has been loaded into WEKA.
Next Steps
Now that the data is loaded into WEKA, you can take advantage of all of the available machine learning algorithms available to classify and cluster your data. Also, please check out these tips on data mining in SQL Server Analysis Services on MSSQLTips.com.
- Classic Machine Learning Example In SQL Server Analysis Services
- Data Mining Clustering Example in SQL Server Analysis Services
- Microsoft Na´ve Bayes Data Mining Model in SQL Server Analysis Services
- SQL Server 2012 Analysis Services Association Rules Data Mining Example
- Introduction to the SQL Server Analysis Services Neural Network Data Mining Algorithm
About the author
 Dr. Dallas Snider is an Assistant Professor in the Computer Science Department at the University of West Florida and has 18+ years of SQL experience.
Dr. Dallas Snider is an Assistant Professor in the Computer Science Department at the University of West Florida and has 18+ years of SQL experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-01-09






