By: Ahmad Yaseen | Updated: 2017-01-27 | Comments (5) | Related: > TSQL
Problem
The SELECT…INTO T-SQL statement is used to copy data from one table to another by creating a new table in the default database filegroup of the destination database and inserting the data from the source table into the created one. With a large amount of data, the SELECT…INTO statement runs slowly as it runs under a single thread using a serial plan to copy the requested data. Are there any enhancements with the SELECT…INTO T-SQL statement in SQL Server that makes the statement run faster?
Solution
SQL Server 2014 and later comes with a valuable enhancement for the SELECT…INTO T-SQL statement, where it now runs with multiple threads using a parallel plan. The parallel execution for SELECT…INTO makes it faster compared with the old serial execution in previous SQL Server versions.
In this tip, we will demonstrate the results. We will try to run a standard SELECT…INTO command to copy data between two tables in the same database twice; the first time using SQL Server 2012 compatibility level 110 and then using SQL Server 2014 compatibility level 120.
Let’s first change the compatibility level of the MSSQLTipsDemo test database to 110 to force it to run as the SQL Server 2012 version:
ALTER DATABASE MSSQLTipsDemo SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 110; GO
Now we will run the SELECT…INTO statement. We will also set STATISTICS TIME ON, so we can see how long it took to complete.
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO SET STATISTICS TIME ON SELECT * INTO [Production].[TransactionHistory2] FROM [Production].[TransactionHistory] SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
The below execution plan shows us that the SELECT…INTO T-SQL statement executed using a serial plan:
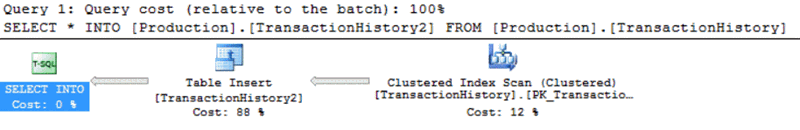
In our example, the statement took 132 ms to execute the query:

Let’s change the compatibility level of the MSSQLTipsDemo database to 120 to force the code to run as the SQL Server 2014 version:
ALTER DATABASE MSSQLTipsDemo SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 120; GO
Drop the table we created above, so we can run the statement again:
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO DROP TABLE TransactionHistory2
And again run the following standard SELECT…INTO command after enabling STATISTICS TIME:
USE MSSQLTipsDemo GO SET STATISTICS TIME ON SELECT * INTO [Production].[TransactionHistory2] FROM [Production].[TransactionHistory] SET STATISTICS TIME OFF
The generated execution plan shows us that the SELECT…INTO statement executed using SQL Server 2014 compatibility is using a parallel plan as shown below:
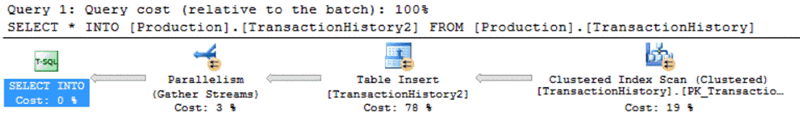
In our example, the statement took 87 ms to complete:
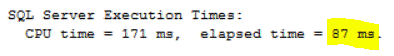
It is clear from our example that the SELECT…INTO T-SQL statement ran ~1.5X faster using a SQL Server 2014 compatibility level using a parallel plan rather than running with a serial plan.
Next Steps
- Read more about INSERT INTO new SQL table with SELECT INTO.
About the author
 Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelor’s degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.
Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelor’s degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-01-27






