By: Kun Lee | Updated: 2017-05-08 | Comments (7) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | > Security
Problem
Ben Snaidero wrote a nice tip about how to Register a SPN for SQL Server Authentication with Kerberos. I want to make sure SPNs are registered for all SQL Servers that I manage, however I manage hundreds of SQL Servers and I need an easy way to check and generate SPN commands without worry about making mistakes or forgetting to register SPNs.
Solution
I wrote a SQL script to use a combination of xp_cmdshell (yes, I know it is not preferred, but you can change the script to enable it right before running the script and disable it once the script is done) and other DMV queries to check and generate SPN commands so you can provide the script to your system's team to run.
NOTE: Depending on your environment, this query may take 15+ seconds to run so please be patient.
Here is the code. You can also download here.
/*
== Description ==
This script will check SPN and generate script like below if missed
SETSPN –S MSSQLSvc/YOURSERVERNAME:1604 mydomain\svcAcct
SETSPN –S MSSQLSvc/YOURSERVERNAME.mydomain.com:1433 mydomain\svcAcct
== LIMITATION ==
- Make sure your sql server is not using DynamicPort
- If the server is part of AG group, this script won't check AG Listner
*/
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- service account
DECLARE @DBEngineLogin VARCHAR(100)
EXECUTE master.dbo.xp_instance_regread
@rootkey = N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE',
@key = N'SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSSQLServer',
@value_name = N'ObjectName',
@value = @DBEngineLogin OUTPUT
-- SELECT [DBEngineLogin] = @DBEngineLogin
DECLARE @physicalServerName varchar(128) = '%' + cast(serverproperty('ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS') as varchar(64))+ '%'
DECLARE @ServerName varchar(128) = '%' + cast(SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName') as varchar(64)) + '%'
DECLARE @spnCmd varchar(265)
SET @spnCmd = 'setspn -L ' + @DBEngineLogin
CREATE TABLE #spnResult (output varchar(1024) null)
INSERT #spnResult exec xp_cmdshell @spnCmd
CREATE TABLE #spnLIst (output varchar(1024) null)
INSERT #spnLIst
SELECT output as 'SPN List for Service Account' FROM #spnResult
WHERE output like @physicalServerName or output like @ServerName
Declare @NodeName VARCHAR(128)
DECLARE db_cursor CURSOR FOR
SELECT '%' + NodeName + '%' AS NodeName FROM fn_virtualservernodes()
OPEN db_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @NodeName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
INSERT #spnLIst
SELECT output as 'SPN List for Service Account' FROM #spnResult
WHERE output like @NodeName
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @NodeName
END
CLOSE db_cursor
DEALLOCATE db_cursor
SELECT DISTINCT output as CurrentSPNRegisterStatus INTO #spnListCurrent FROM #spnLIst
TRUNCATE TABLE #spnLIst
-- GET Port Number
DECLARE @PortNumber varchar(10)
SELECT @PortNumber = cast(local_tcp_port as varchar(10))
FROM sys.dm_exec_connections WHERE session_id = @@SPID
-- GET FQDN
DECLARE @Domain NVARCHAR(100)
EXEC master.dbo.xp_regread 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', 'SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters', N'Domain',@Domain OUTPUT
INSERT #spnLIst
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + cast(serverproperty('ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS') as varchar(64)) + ':' + @PortNumber
UNION ALL
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + cast(serverproperty('ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS') as varchar(64)) + '.' + @Domain + ':' + @PortNumber
UNION ALL
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + cast(SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName') as varchar(64)) + ':' + @PortNumber
UNION ALL
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + cast(SERVERPROPERTY('MachineName') as varchar(64)) + '.' + @Domain + ':' + @PortNumber
-- If this serve is clusterd, need to check for all Physical nodes
IF SERVERPROPERTY('IsClustered') = 1
BEGIN
INSERT #spnLIst
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + NodeName + ':' + @PortNumber
FROM fn_virtualservernodes()
INSERT #spnLIst
SELECT 'MSSQLSvc/' + NodeName + '.' + @Domain + ':' + @PortNumber
FROM fn_virtualservernodes()
END
IF NOT EXISTS(SELECT CurrentSPNRegisterStatus FROM #spnListCurrent)
SELECT 'NO SPN has been registered' as CurrentSPNRegisterStatus
ELSE
SELECT CurrentSPNRegisterStatus FROM #spnListCurrent
SELECT
CASE
WHEN A.CurrentSPNRegisterStatus is NULL THEN '*Missing SPN - See SPNGenerateCommandLine'
ELSE A.CurrentSPNRegisterStatus END AS 'CurrentSPNRegisterStatus',
CASE
WHEN B.output IS NULL THEN '*** Review for Remove or you have multiple instance ***'
ELSE B.output end as SuggestSPNList,
CASE
WHEN B.output is null THEN
'SETSPN -D ' + A.CurrentSPNRegisterStatus + ' ' + @DBEngineLogin
ELSE 'SETSPN –S ' + output + ' ' + @DBEngineLogin END as SPNGenerateCommandLine
FROM #spnListCurrent A
FULL OUTER JOIN #spnLIst B on REPLACE(A.CurrentSPNRegisterStatus,CHAR(9),'') = B.output
WHERE CurrentSPNRegisterStatus is NULL OR B.output IS NULL
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0
SELECT 'All SPN has been registered correctly. If you are running for AG Group, this script does not check so please check manually' as SPNStatus
DROP TABLE #spnResult
DROP TABLE #spnLIst
DROP TABLE #spnListCurrent
GO
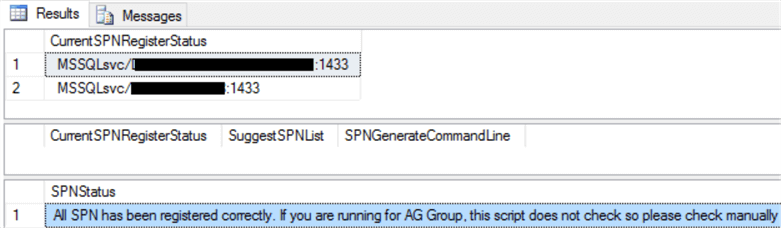
Example Result 1 - Good Case
This is a sample result for a standalone server with a single instance running. As you can see two SPNs have been registered currently and nothing new is suggested, so the SPNStatus is good.
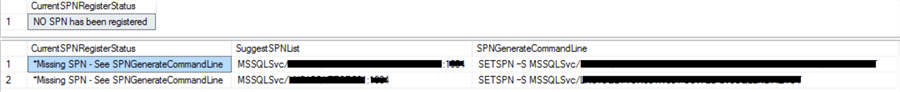
Example Result 2 – Missing SPN on a Standalone Server
This is sample result that you will get if the SPN has not been registered. You can just take the code from the third column “SPNGenerateCommandLine” and run the T-SQL (if you have the correct permissions to register) and it will register the SPN.
Example Result 3 – Wrong SPN Registered (Missing SQLPorts)
Here is an example of the wrong SPN being registered. As you can see, the SPN has been registered without a SQL port like 1433, so in this case the script will generate "SETSPN - D" to remove the existing SPN and also generate another SPN script to register the SPN.

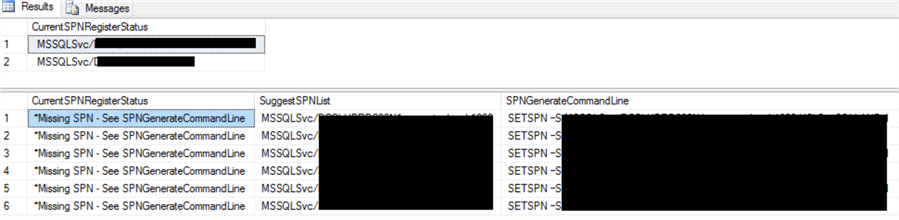
Example Result 4 – Cluster Servers
Don’t be surprised to see results like below if you are running on a clustered node. We found it is much better to register the actual cluster node to reduce errors in the event log, so this script will also check the physical node names and check if those are registered and if not it will generate the recommended scripts. I will leave up to you how you want to use this information. (Note: I hid a bunch of the sensitive information from my machine in the below image.)
Summary
This version of the script is meant and tested for SQL Server 2008 or later and this script is also meant for most general needs. Special cases like connecting SQL Server via a different CNAME or different paths like F5, AlwaysOn Listener, etc. you will need to manually handle these items.
Next Steps
- Enhance the script to handle for an AlwaysOn Listener
- Add detection for Dynamic Ports
About the author
 Kun Lee is a database administrator and his areas of interest are database administration, architecture, data modeling and development.
Kun Lee is a database administrator and his areas of interest are database administration, architecture, data modeling and development.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-05-08






