By: Daniel Farina | Updated: 2017-06-16 | Comments (1) | Related: > Install and Uninstall
Problem
You are a SQL Server Database Administrator (DBA) and your company is starting a new project. Since the project needs a SQL Server instance you ask the sysadmins for a new database server and they tell you that they will give you a new server with SQL Server already installed. When you hear that, you totally disagree and think you should install SQL Server as the DBA. In this tip I will expose a few points about why SQL Server should be installed by a specialist.
Solution
Over the years, SQL Server has evolved from being a simple relational database management system to becoming an entire data platform. Ten to twenty years ago it wasn’t uncommon to find companies running SQL Server without a SQL Server DBA. In those days, I heard from developers and system analysts that if they need a database system for high performance they would use Oracle and leave SQL Server for small and non-critical systems. Those were the days of SQL Server 7.0 and Oracle 8i, and Oracle had an advantage with a more robust platform yet it was hard to administer and use.
Nowadays both database systems offer the same functionality, but at different costs. If you want to have the same functionality on Oracle that SQL Server offers you'll have to pay much more because most of the things you get with SQL Server come at an additional cost with Oracle.
We as SQL Server DBA’s know how much SQL Server has changed. Unfortunately SQL Server has been thought as lesser than Oracle amongst the rest of the IT community, especially those close to Linux. That may be one of the reasons why SQL Server is entering the Linux community.
Installing SQL Server
If you ever had a chance to install SQL Server 7.0 or 2000, you know the installation process has increased in its complexity on newer versions. But with increased complexity, it maintains the ease of use that Microsoft has offered. What I mean is that you can still install SQL Server by pressing the next button on each screen, something that with Oracle is almost impossible. But the fact that you can install SQL Server and get it running with just a few clicks doesn’t mean that the installation was done properly.
Setting up The Storage
Storage is one of the key components that will affect the database performance on production servers. Besides provisioning of disk space, the person in charge of installing SQL Server must select how many drives to use according to the project’s budget. According to the number of disks available they must decide the proper configuration for those disks like discussed in this tip Hard Drive Configurations for SQL Server.
After selecting a proper disk configuration, the person that installs SQL Server must format the disks with the proper allocation unit size depending on if the disk is used for data files or log files, like discussed in this tip: Format drives with correct allocation and offset for maximum SQL Server performance.
When the disks are properly formatted the person that installs SQL Server must run some tests in order to know the disk response times. One way to do this is by using the SQLIO tool like in this tip: Benchmarking SQL Server IO with SQLIO.
The final step regarding storage configuration is to enable Instant File Initialization. If this feature is not enabled, when a database file needs to grow, SQL Server will spend more time to fill the file with zeros for the allocated space. You can see the effects of Instant File Initialization in this tip Effect of Instant File Initialization within SQL Server, and also you can see how to enable Instant File Initialization in this tip Configuring Windows Instant File Initialization for SQL Server 2005.
Default Instance or Named Instance
This may seem trivial, but it is not; especially for sysadmins who don’t have an in depth knowledge of SQL Server. There are applications that run on SQL Server that need to be on the default instance, so the connection to the database uses only the machine name. I have seen servers with an already installed version of SQL Server because of a monitoring tool that uses SQL Server Express.
On the other hand, there are applications that require the SQL Server instance to have a specific name, so if the person in charge of the installation just presses the “Next” button, the DBA will have to do the whole installation again.
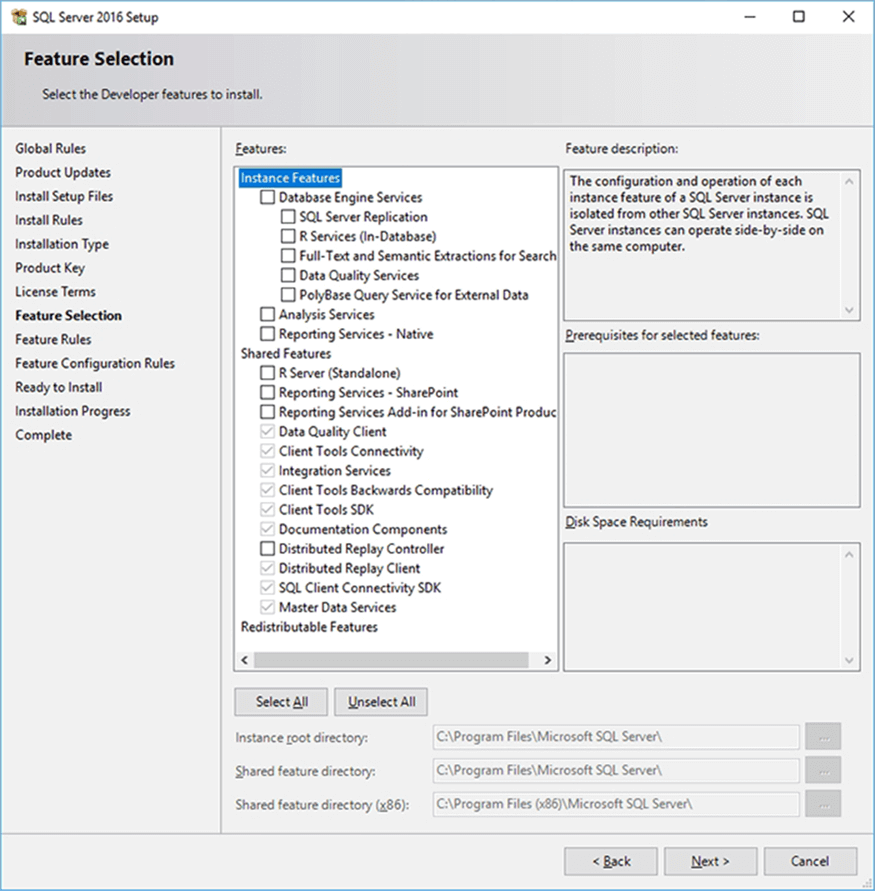
SQL Server Feature Selection
Who of us haven’t seen a server that only uses the database engine, but has Reporting Services, Integration Services and even Analysis Services installed? That happens even when a SQL Server specialist is the one who has installed the instance.
The problem with installing features that you won’t use relies on the fact that most of these features are services that automatically start and use system resources. When you are installing on a production server you must install only the features you will use, there isn’t a just in case.
Service Accounts
When someone installs SQL Server with the default setup, it will install with the default service accounts. Almost all mid-sized companies and especially large enterprises use Active Directory or a similar tool to handle user accounts. If SQL Server is installed with local service accounts there is a chance that SQL Server doesn’t recognize the domain accounts as trusted domain accounts, because SQL Server will not be able to register the SPN in the domain.
On the other hand, there are people that use a domain admin account as the service account. This is a serious problem and as an example, if xp_cmdshell is enabled a malicious user can shut down all the computers of the entire organization.
Authentication Mode
SQL Server provides two authentication modes, Windows authentication mode on which you can login to the database instance directly with an authorized Windows login and Mixed mode, that includes the possibility to use SQL Server logins.
By default SQL Server uses Windows authentication mode, but to use this security mode the instance usually must be part of a domain, something that happens when you select a domain account as a service account which as I discussed above, is not the default option.
If the person in charge of installing SQL Server decides to use Mixed mode, he should be aware of security issues that are exposed in these two tips: Best Practices to Secure the SQL Server sa Account and Different ways to secure the SQL Server SA Login.
Specifying SQL Server Administrators
SQL Server setup asks for users or groups to be the administrators of the instance, in other words those who will have unrestricted access. Someone that doesn’t know about SQL Server security may add the Administrator group, or even worse the Domain Administrators group. On the following tip you will find the issues of committing such a mistake: Security Issues with the SQL Server BUILTIN Administrators Group.
Selection of Data Directories
This is one of the steps that if you made all the previous steps correctly, makes all those steps worthless. You may have done a great job of selecting the proper storage and cluster size, but if you choose the default options when you are asked for the directories to be used by data files, log files and backups, all that work was done in vain.
The reason why you must set up the storage properly before installing SQL Server is that data files and log files need to be treated differently. It is a bad practice to use the same drive to store both data and log files.
Configuring TempDB
Selecting the right location for TempDB is crucial for a SQL Server installation.
Previous to SQL Server 2016, the installer only allowed the creation of one data file for TempDB, now you are allowed to add as many files as you need. There is a misconception that TempDB must have one file per core, but as exposed in this tip SQL Server tempdb one or multiple data files, there are some issues to consider about having one file per core.

Also there are other best practices regarding TempDB configuration that you may find in the following tip: Tempdb Configuration Best Practices in SQL Server.
Choosing the Proper Collation
I told you that a wrong selection of data directories was one of the reasons that will make the whole installation a failure and this is the other. Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties. If your organization is deploying a production server for a new application, the person in charge of the installation must know what collation is used by the application. Otherwise the application will not run properly or may not run at all.
If you as a DBA face a situation like this, you have to change the server collation by using any of the methods described in these two tips: Changing SQL Server Collation After Installation and How to change server level collation for a SQL Server Instance.
Next Steps
- If you are a sysadmin who needs to install a SQL Server instance, I suggest you take a look at the SQL Server DBA Best Practices Tips category.
- Also you should review the SQL Server Install and Uninstall Tips category.
- Another section you should look at is SQL Server Security Tips category.
- Are you a First Timer on SQL Server? Welcome to MSSQLTips.com!
- If you are a sysadmin that wants to become a SQL Server DBA, take a look at the SQL Server Professional Development Tips and Tricks category.
About the author
 Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.
Daniel Farina was born in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Self-educated, since childhood he showed a passion for learning.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-06-16






