By: Edwin Sarmiento | Updated: 2017-08-01 | Comments (4) | Related: > Availability Groups
Problem
In a previous tip on Configure SQL Server Database Mirroring Using SSMS, we have seen how we can configure Database Mirroring to achieve local high availability for SQL Server databases. We need to upgrade our SQL Server 2008 R2 databases before extended support ends. However, we can only upgrade to Standard Edition due to licensing cost restrictions. And Database Mirroring has been deprecated since SQL Server 2012. What is our next best course of action?
Solution

When the Availability Group feature was introduced in SQL Server 2012, it was only available in Enterprise Edition. It made upgrading databases configured with Database Mirroring a challenge, especially when the principal and the mirror SQL Server instances are running Standard Edition. The only other option for providing high availability to databases running in Standard Edition is to implement a 2-node SQL Server failover clustered instance. But this requires shared storage and other external dependencies like Active Directory and DNS. So, even in SQL Server 2014, customers still use Database Mirroring.
SQL Server 2016 made it possible to run Availability Groups in Standard Edition. Although Availability Groups still required Active Directory and DNS as requirements for running Windows Server Failover Clusters (WSFC), it didnít take long for Windows Server 2016 to be released to the public, thereby, allowing creation of WSFC without Active Directory. Refer to this tip on how to deploy a Windows Server 2016 Failover Cluster without Active Directory. This made Availability Group a true viable replacement for Database Mirroring.
Setup and Implement SQL Server Always On Basic Availability Groups
The prerequisites for deploying Basic Availability Groups are the same as what they have been since their introduction in SQL Server 2012. But because they are on Standard Edition, there are some limitations. I will highlight those limitations as we go along the process of setting up and configuring Basic Availability Groups. Also, the WSFC has already been created and the Always On High Availability feature enabled on the instances that I will use as replicas.
Earlier releases of SQL Server 2016 and SQL Server Management Studio have an explicit option to specifically create Basic Availability Groups, like the one shown below. This is no longer the case.
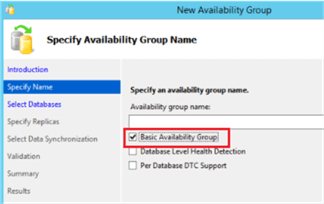
At the moment, there is no option to explicitly create a Basic Availability Group using SQL Server Management Studio (I hope the product team will bring that option back). But if you are creating an Availability Group with a Standard Edition instance using SQL Server Management Studio, the wizard will automatically detect it and create it as a Basic Availability Group.
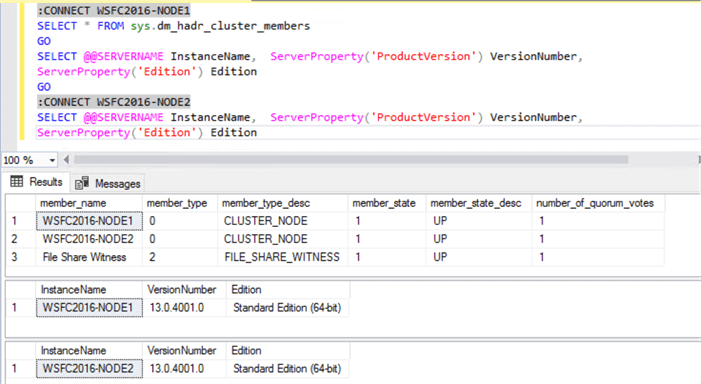
The environment that I am using in this tip is as follows:
- A 2-node WSFC joined to an Active Directory domain
- Uses a file share as a witness type
- SQL Server 2016 with Service Pack 1 Standard Edition
- SQL Server uses Active Directory domain accounts as service accounts
Launch the New Availability Group Wizard to create the Basic Availability Group.
- From within Object Explorer, expand the AlwaysOn High Availability node and the Availability Groups node
- Right-click the Availability Group node and select the New Availability Group Wizard command. This opens the New Availability Group Wizard dialog box
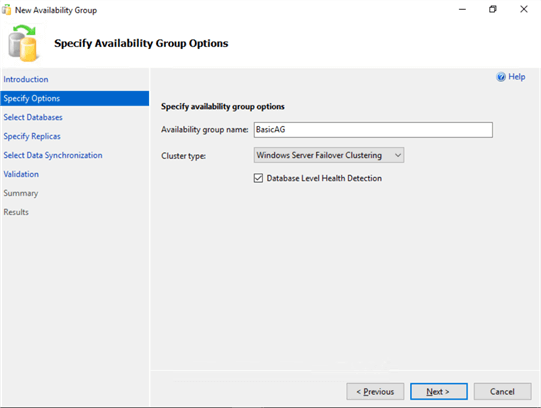
- In the Specify Availability Group Options dialog box, type the name of the Availability Group in the Availability group name: textbox. Notice the difference between this dialog box and the one I mentioned earlier Ė the Basic Availability Group checkbox is no longer there.
- In the Select Databases dialog box, select the database that you want to include in your Availability Group.
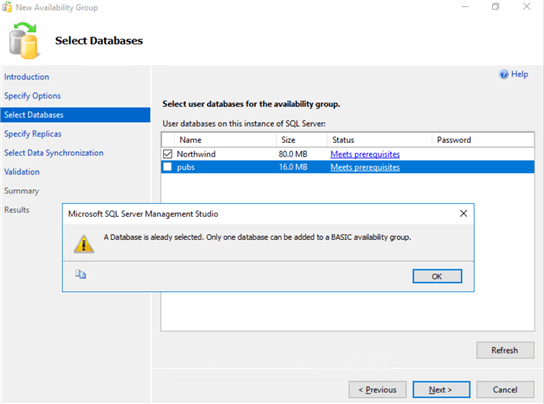
Limitation #1: You can only join one database per Basic Availability Group. You will get this warning message should you choose more than one database.
Click Next.
- In the Specify Replicas dialog box,
- In the Replicas tab, click on the Add Replica button to add the SQL Server instance that you want to configure as a secondary replica. Unlike Database Mirroring in Standard Edition, you can configure a secondary replica in a Basic Availability Group in Asynchronous mode.
Also, notice the following.
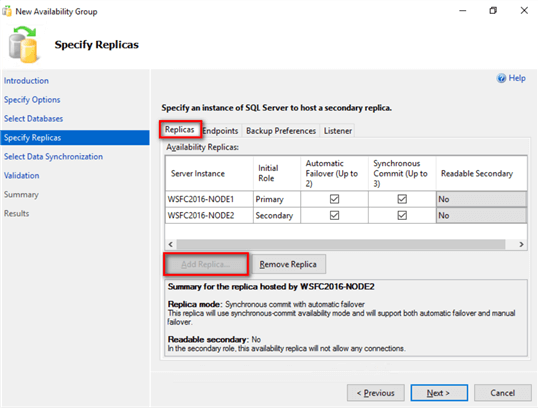
Limitation #2: You can only have two replicas Ė primary and secondary - per Basic Availability Group. The Add Replica button will automatically get disabled after adding the second replica.
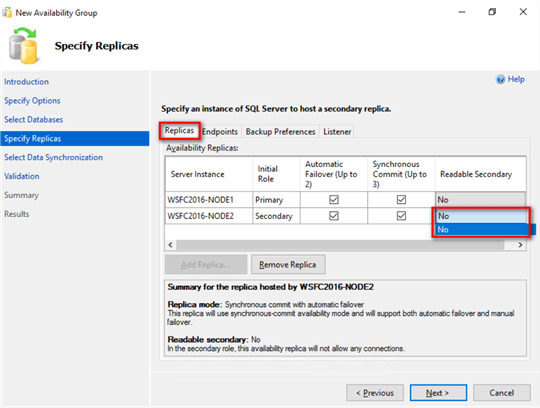
Limitation #3: You cannot enable the secondary replica as a readable secondary. No is the only option when you click on the drop-down list under Readable Secondary.
- In the Backup Preferences tab, notice how everything is disabled. I do wish that they also grayed out the Exclude Replica checkboxes.
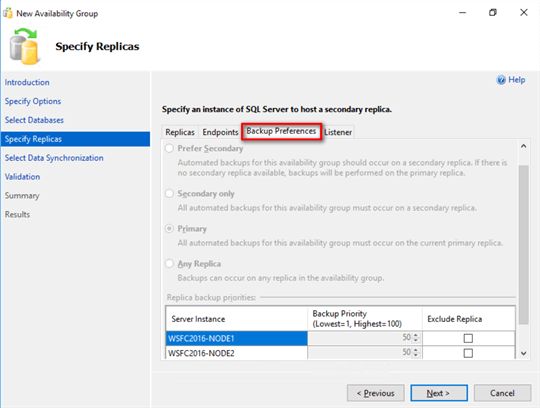
Limitation #4: You cannot run backups on the secondary replica.
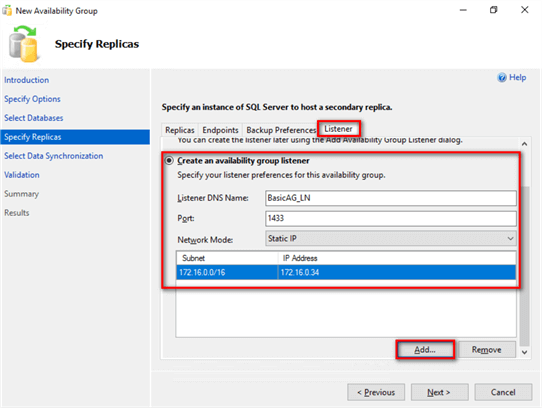
- Proceed to create the Listener name in the Listener tab.
- Select the Create an availability group listener option
- Type the Listener DNS name and Port number
- Select Static IP in the Network Mode: drop-down list
- Provide the virtual IP address by clicking the Add Ö button
This is another benefit of Basic Availability Group over Database Mirroring. In the past, you would need to add the Failover Partner attribute in the database connection string to automatically redirect client applications to the Database Mirroring partner after a failover. Another workaround is creating a DNS alias and assigning the IP address of the principal database server to it. Because the Availability Group listener name moves together with the primary replica, there is no need to create a DNS alias (since the listener name is technically a DNS alias) nor use the Failover Partner attribute in the database connection string. The client application will automatically get redirected to the current primary replica.
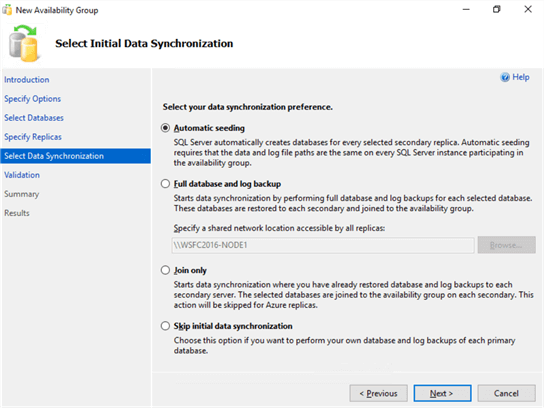
- In the Select Initial Data Synchronization dialog box, you can choose to either use the new Automatic Seeding feature, the usual Full database and log backup option, Join only option or Skip the initial data synchronization option. This example uses Automatic Seeding since the database is relatively small. Refer to this tip for more information about Automatic Seeding.
Click Next.
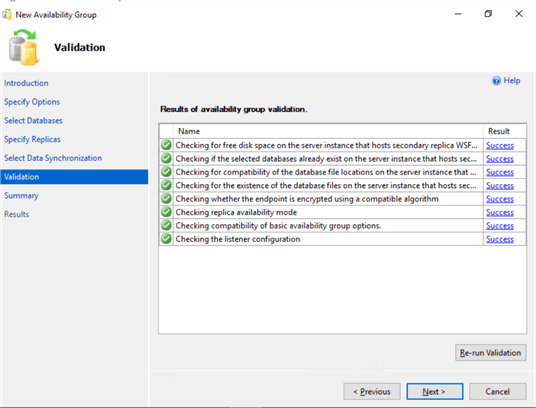
- In the Validation dialog box, make sure that all checks return successful results. Click Next.
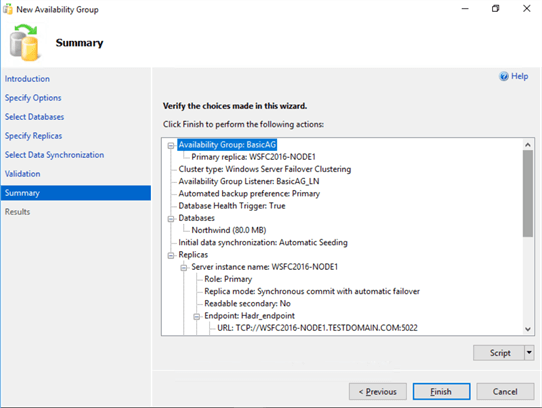
- In the Summary dialog box, verify that all the configuration settings are correct. Click Finish to create the Availability Group.
Summary
You can view the Availability Group dashboard for the state and configuration information.
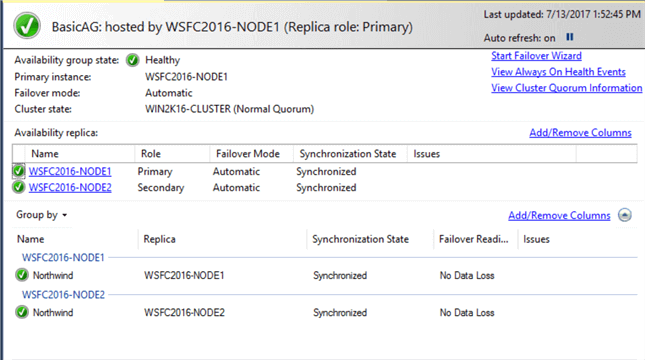
There really isnít that much difference in setting up and configuring Basic Availability Group when you compare it with the way it has been done since SQL Server 2012. The main thing here is that the setup and configuration experience is driven by the limitations. After all, you are working with Standard Edition with limited features. The best thing about it is there is now a viable replacement for Database Mirroring in SQL Server 2016.
Next Steps
- Review the previous tips on SQL Server AlwaysOn Availability Group Configuration
- Review the previous tip on Configure SQL Server Database Mirroring Using SSMS
- Review the previous tips on Deploying Windows Server 2016 Failover Cluster without Active Directory
About the author
 Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.
Edwin M Sarmiento is a Microsoft SQL Server MVP and Microsoft Certified Master from Ottawa, Canada specializing in high availability, disaster recovery and system infrastructures.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-08-01






