By: Ahmad Yaseen | Updated: 2017-08-16 | Comments (2) | Related: > Functions System
Problem
SQL Server provides different ways to get system-level information for a SQL Server instance. The SERVERPROPERTY system defined function is the easiest method that can be used to get descriptive information about system values of the current SQL Server instance. Starting with SQL Server 2016, eight new properties have been added to the SERVERPROPERTY system defined function that makes the SERVERPROPERTY function more powerful in describing the SQL Server instance characteristics. In this tip, we will go through these new properties.
Solution
SERVERPROPERTY is a system defined function that helps get property information about the current server instance. In SQL Server 2016, eight new properties were added to the SERVERPROPERTY system function that provides us with more information about the current SQL Server instance version, build and other useful information. The list of these new properties is shown below:
- InstanceDefaultDataPath
- InstanceDefaultLogPath
- ProductBuild
- ProductBuildType
- ProductMajorVersion
- ProductMinorVersion
- ProductUpdateLevel
- ProductUpdateReference
In order to understand the new properties, we will categorize it into groups depending on the type of information that this property returns.
SQL Server Database Default Locations
In SQL Server, you can get the default data and log files locations in many ways, such as reading the related system registry keys, which requires extra effort and server permissions to retrieve this information. Another way to get the default files location is from the Database Settings tab of the SQL Server instance Properties window, as shown below:
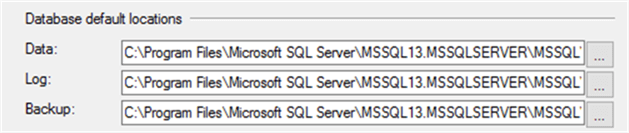
Two new properties have been added to the SERVERPROPERTY system function; InstanceDefaultDataPath property that specifies the default path for the current SQL Server instance data files and the InstanceDefaultLogPath property that specifies the default path for the current SQL Server instance log files.
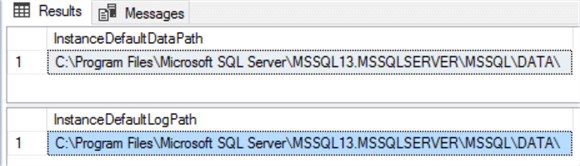
You can easily get the default location for the database data and log files using these new properties, without going through the registry keys complexity. The below T-SQL scripts can be used to get the default data and log files locations for the current SQL Server instance:
Select InstanceDefaultDataPath=SERVERPROPERTY('InstanceDefaultDataPath')
Select InstanceDefaultLogPath=SERVERPROPERTY('InstanceDefaultLogPath')
The result will present the same information retrieved from the Server Properties in the SSMS window as shown below:
SQL Server Version
The @@VERSION system function is widely used by most of SQL Server database administrators to get the system and build information for the current SQL Server installation. The @@VERSION system function has been modified starting with SQL Server 2014 SP1 CU3, by providing extra information about the current installation Service Pack and the Cumulative Update.
SELECT @@VERSION AS CurrentSQLVersion
If you call the @@VERSION system function from a SQL Server instance older than SQL Server 2014 SP1 CU3 you will get information as shown below:

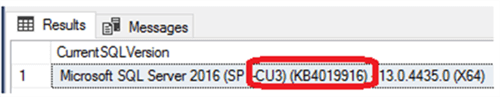
If you use the @@VERSION system function call from SQL Server 2014 SP1 CU3 or later, you will see an extra information that shows the service pack, cumulative update and the related KB article:

As you can see the results are returned as one nvarchar string. In order to get the results as individual property values you can use the SERVERPROPERTY system function.
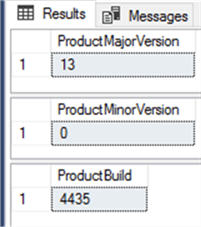
In SQL Server 2016, three new properties are added to the SERVERPROPERTY system function that provides information about the current SQL Server instance version: the ProductMajorVersion that specifies the major version of the current SQL Server instance, the ProductMinorVersion that specifies the minor version, if available, for the current SQL Server instance and the ProductBuild that shows the build number of the current SQL Server instance.
The below T-SQL script will use these three new properties to get the version of the current SQL Server instance:
Select ProductMajorVersion=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductMajorVersion')
Select ProductMinorVersion=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductMinorVersion')
Select ProductBuild=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductBuild')
The results are as follows:
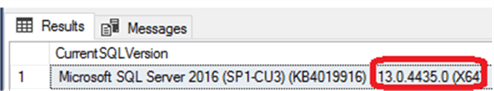
As you can see, the previous individual values are the same that we got when using @@VERSION above:
SQL Server Update
The SERVERPROPERTY function can be also used to provide information about the current SQL Server instance update. This can be achieved using three new properties that have been added to the SERVERPROPERTY function in the SQL Server 2016. The ProductUpdateLevel property specifies the update level for the current SQL Server build, where CU indicates a cumulative update. It returns the cumulative update number of the current build or NULL if not applicable. The ProductUpdateReference property specifies the KB article number for the installed release, and the ProductBuildType property specifies the type of the current build.
Valid build types returned from this property include OD that indicates On Demand release for a specific customer, and GDR that indicates General Distribution Release released through a Windows update. A NULL value indicates no type is applicable for the current instance.
The below T-SQL shows how we can use the SERVERPROPERTY system function to get information about the cumulative update and KB article of the current SQL Server instance:
Select ProductUpdateLevel=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductUpdateLevel')
Select ProductUpdateReference=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductUpdateReference')
The CU and KB for the current SQL Server installation are:
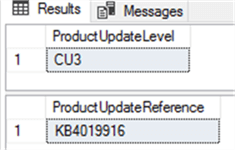
The previous values are the same as from the @@VERSION function output.
The below T-SQL query illustrates how to use the SERVERPROPERTY system function to get the build type for the current SQL Server installation:
Select ProductBuildType=SERVERPROPERTY('ProductBuildType')
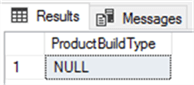
Here are the results. This is NULL for our install, so this is not applicable in our case:
Next Steps
- The new SERVERPROPERTY system function properties mentioned in this article are also available with the latest update of SQL Server 2012 and SQL Server 2014 versions.
- Read How to tell what SQL Server version you are running
- Also read Understanding the SQL Server SELECT @@VERSION command
- Check How to Change Default Data and Log file directory for SQL Server running on Linux
About the author
 Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.
Ahmad Yaseen is a SQL Server DBA with a bachelorís degree in computer engineering as well as .NET development experience.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2017-08-16






