By: Svetlana Golovko | Updated: 2018-07-24 | Comments | Related: > Monitoring
Problem
SQL Server Audit can be used to monitor numerous security events, but it requires audit logs review which could be time consuming. We would like to get real-time alerts every time when Server Scope Permissions or Server Objects Permissions are changed. How do we setup alerts and jobs responding to these alerts?
Solution
In one of our previous tips, we explained how to setup WMI alerts for database changes monitoring. The setup consists of SQL Server Agent configuration steps, Database Mail configuration, and creation of the alert and SQL Server job.
In this tip we will provide steps and scripts for setting up WMI alerts to monitor the Server Scope or Server Objects Permissions changes and jobs responding to these alerts. Here are some of the examples of these permissions:
- Login granted "CONTROL SERVER"
- Login granted SQL Server Access ("CONNECT SQL")
- "CREATE ANY DATABASE" permission granted
- "VIEW ANY DEFINITION" permission granted
- Login granted permissions to alter another login
- Login granted permissions to alter server role (permission can be granted only to a custom Server Role)
A "Server" Type Securable permission is available by to any login who has access to SQL Server. This is when a login has "CONNECT SQL" permission. The login could be granted additional Server Scope permissions (for example, "ALTER ANY DATABASE"):

The same permissions are accessible through the "Server Properties" in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
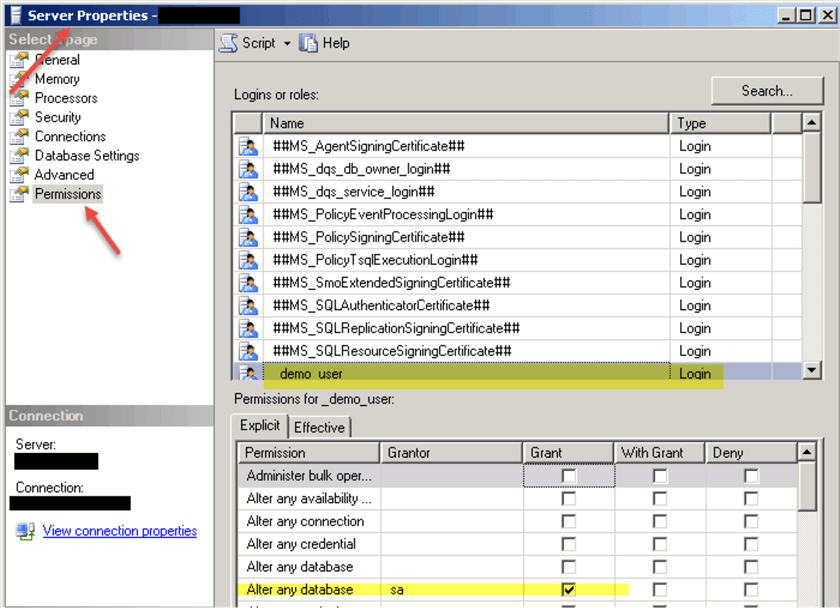
There are other Securables (Object Types) available in addition to the "Server". We can see available Object Types by clicking "Search..." button in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) when we open a login's property (the "Securables" page):

Here is the list of available Objects Types through the SSMS on our test SQL Server:

Note: If Availability Groups are not configured on SQL Server then the "Availability Groups" Object Type won't be available.
Setting permissions on the "Server" Object Type triggers alerts (if they were setup) using AUDIT_SERVER_SCOPE_GDR_EVENT WMI Class. The rest of the Object Types permissions use AUDIT_SERVER_OBJECT_GDR_EVENT WMI Class.
An example of the "Server" type Securable permission is already covered in the previous tip when we provided the steps to monitor login's permission to access SQL Server.
In this tip we will provide more examples to monitor the "Server" type Securable permissions and steps and scripts to get alerts on Server Objects Permissions changes.
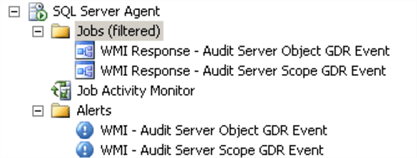
Here are the jobs and alerts that will be created:
Make sure that the Database Mail is configured and SQL Server Agent is setup to allow replacing tokens as per this tip.
We will provide the jobs' steps and alerts screenshots and a complete script at the end of the tip for all of the jobs and alerts.
Note, that the jobs are not scheduled and cannot be run manually or on schedule.
Create SQL Server Agent Job that will Respond to the Server Scope Permissions Changes
The following job ("WMI Response - Audit Server Scope GDR Event") will be responding to the WMI event every time when a Server Scope Permission is granted/denied/revoked to/from a login.
Here is the documentation about granting the Server Permissions.
The image below displays the job's step. You will need to update @profile_name and @recipients parameters with your values (@profile_name will be the "Mail profile" that you created during Database Mail configuration):

Here is the script for the job step above (you will need to update @profile and @recipients parameters with your values):
DECLARE @p_subject NVARCHAR(255), @p_action INT, @p_importance VARCHAR (6) ,
@p_action_desc NVARCHAR(10), @p_permission NVARCHAR(255), @TextData NVARCHAR(500)
SELECT @p_action = $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(EventSubClass))),
@p_importance = CASE WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(Success))) = 0 THEN 'High' ELSE 'Normal' END,
@p_action_desc = CASE WHEN @p_action = 1 THEN 'GRANT'
WHEN @p_action = 3 THEN 'DENY'
WHEN @p_action = 2 THEN 'REVOKE' END,
@TextData = LTRIM(RTRIM(REPLACE('$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TextData)))', char(9), ' ')))
SELECT @p_permission =
LTRIM(RTRIM(SUBSTRING(@TextData,
CHARINDEX(@p_action_desc, @TextData, 0)+ LEN(@p_action_desc),
CHARINDEX(CASE WHEN @p_action = 2 THEN ' FROM ' ELSE ' TO ' END,
@TextData, 0) - CHARINDEX(@p_action_desc, @TextData, 0) - LEN(@p_action_desc)) ))
SELECT @p_subject = N'WMI Alert: Login [$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TargetLoginName)))] ' +
' - [' + @p_permission + '] ' +
' SQL Server Permission ' + CASE WHEN @p_action = 1 THEN 'granted'
WHEN @p_action = 2 THEN 'revoked'
WHEN @p_action = 3 THEN 'denied'
ELSE '' END + ' on [$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ComputerName)))\$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SQLInstance)))].' ;
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'DBServerAlerts', -- update with your values
@recipients = '[email protected]', -- update with your values
@importance = @p_importance ,
@subject = @p_subject,
@body = N'Time: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(StartTime)));
ComputerName: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ComputerName)));
SQL Instance: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SQLInstance)));
Target Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TargetLoginName)));
Source Application Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ApplicationName)));
Source Host Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(HostName)));
Source Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(LoginName)));
Source Session Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SessionLoginName)));
EventSubClass: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(EventSubClass)));
TextData: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TextData)));
Success: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(Success)));
';
Setting up WMI Alert to Respond to the Server Scope Permissions Changes
Now we will setup the WMI alert:
- set the alert type to "WMI event alert"
- make sure you use correct WMI namespace:

Note: the namespace will be different for the default instance and for the named instance:
-- DEFAULT instance's namespace ("DEMOSQL1" SQL Server):
\\.\root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ServerEvents\MSSQLSERVER
-- NAMED instance's namespace ("DEMOSQL1\SQLINSTANCE1" SQL Server):
\\.\root\Microsoft\SqlServer\ServerEvents\SQLINSTANCE1
Here is the WMI query for this alert:
select * from AUDIT_SERVER_SCOPE_GDR_EVENT
Read more about the Audit Server Scope GDR Event Class here.
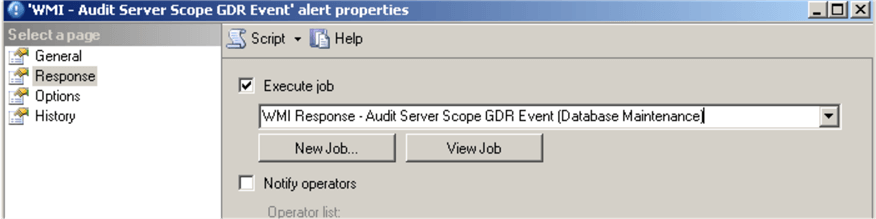
Set the response in alert's properties to execute the job we created earlier:
If you use the alert covered in our previous WMI tip to monitor "CONNECT SQL" permission:
select * from AUDIT_SERVER_SCOPE_GDR_EVENT where Permissions='1'
then you can add another alert with a query like this (to avoid duplicate alerts) or just remove the filter completely:
select * from AUDIT_SERVER_SCOPE_GDR_EVENT where Permissions <> '1'
If you want to monitor only specific permissions you can adjust the WMI query above to something like this:
select * from AUDIT_SERVER_SCOPE_GDR_EVENT where Permissions='1' or Permissions='4294967296' or Permissions='4194304'
Note, that you can't use the "IN" operator in WMI (WQL) queries:
...where Permission in ('1', '4294967296', '4194304')
Refer to this resource for the WQL (SQL for WMI) overview.
You can find a list of supported WQL operators to use in the WHERE clause here.
The following table has a list of all permissions IDs starting with SQL Server 2008. The column "Is New" specifies a permission that was introduced in a "SQL Server Version" column. Note, that two permissions were introduced in SQL Server 2014 and then removed (not available in the later versions):
| Permission ID | SQL Server Version | Permission Name | Is New | Is Removed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65536 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ADMINISTER BULK OPERATIONS | ||
| 4 | SQL SERVER 2012 | ALTER ANY AVAILABILITY GROUP | Yes | |
| 2048 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY CONNECTION | ||
| 256 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL | ||
| 4096 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY DATABASE | ||
| 512 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY ENDPOINT | ||
| 33554432 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY EVENT NOTIFICATION | ||
| 2147483648 | SQL SERVER 2012 | ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION | Yes | |
| 68719476736 | SQL SERVER 2014 | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE | Yes | Yes |
| 137438953472 | SQL SERVER 2014 | ALTER ANY EXTERNAL FILE FORMAT | Yes | Yes |
| 1024 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY LINKED SERVER | ||
| 128 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY LOGIN | ||
| 268435456 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER ANY SERVER AUDIT | ||
| 1073741824 | SQL SERVER 2012 | ALTER ANY SERVER ROLE | Yes | |
| 8192 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER RESOURCES | ||
| 67108864 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER SERVER STATE | ||
| 16384 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER SETTINGS | ||
| 32768 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | ALTER TRACE | ||
| 131072 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | AUTHENTICATE SERVER | ||
| 8589934592 | SQL SERVER 2014 | CONNECT ANY DATABASE | Yes | |
| 1 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CONNECT SQL | ||
| 4294967296 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CONTROL SERVER | ||
| 64 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CREATE ANY DATABASE | ||
| 8 | SQL SERVER 2012 | CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP | Yes | |
| 8388608 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CREATE DDL EVENT NOTIFICATION | ||
| 32 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CREATE ENDPOINT | ||
| 536870912 | SQL SERVER 2012 | CREATE SERVER ROLE | Yes | |
| 16777216 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | CREATE TRACE EVENT NOTIFICATION | ||
| 262144 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | EXTERNAL ACCESS ASSEMBLY | ||
| 17179869184 | SQL SERVER 2014 | IMPERSONATE ANY LOGIN | Yes | |
| 34359738368 | SQL SERVER 2014 | SELECT ALL USER SECURABLES | Yes | |
| 2 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | SHUTDOWN | ||
| 134217728 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | UNSAFE ASSEMBLY | ||
| 1048576 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | VIEW ANY DATABASE | ||
| 2097152 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | VIEW ANY DEFINITION | ||
| 4194304 | SQL SERVER 2008 R2 | VIEW SERVER STATE |
Create SQL Server Agent Job that will Respond to the Server Objects Permissions Changes
Here is the "WMI Response - Audit Server Object GDR Event" job's step for the Server Objects GDR (grant/deny/revoke) events response:

Here is the script for the job step:
DECLARE @p_subject NVARCHAR(255), @p_action INT, @p_importance VARCHAR (6)
SELECT @p_action = $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(EventSubClass))),
@p_importance = CASE WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(Success))) = 0 THEN 'High' ELSE 'Normal' END
SELECT @p_subject = N'WMI Alert: SQL Server - [$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ComputerName)))\$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SQLInstance)))]. Permissions ' +
CASE WHEN @p_action = 1 THEN 'granted'
WHEN @p_action = 2 THEN 'revoked'
WHEN @p_action = 3 THEN 'denied'
ELSE '' END + ' on [' +
CASE WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 19539 THEN 'SQL Login'
WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 19543 THEN 'Windows Login'
WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 18263 THEN 'Microsoft Windows Group'
WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 18259 THEN 'Server Role'
WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 20549 THEN 'Endpoint'
WHEN $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectType))) = 18241 THEN 'Availability Group'
ELSE 'Other Server Object' END +
']:[$(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectName)))].' ;
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'DBServerAlerts', -- update with your values
@recipients = '[email protected]', -- update with your values
@importance = @p_importance,
@subject = @p_subject,
@body = N'Time: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(StartTime)));
ComputerName: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ComputerName)));
SQL Instance: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SQLInstance)));
Database: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(DatabaseName)));
Target Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TargetLoginName)));
Target Object Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ObjectName)));
Source Application Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(ApplicationName)));
Source Host Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(HostName)));
Source Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(LoginName)));
Source Session Login Name: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(SessionLoginName)));
EventSubClass: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(EventSubClass)));
Text Data: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(TextData)));
Success: $(ESCAPE_SQUOTE(WMI(Success)));
'
Object Types and IDs could be found here, but we only use in email subject the following (that are available through the SSMS):
| Permission ID | Permission Name |
|---|---|
| 20549 | Endpoint |
| 19539 | SQL Login |
| 19543 | Windows Login |
| 18263 | Microsoft Windows Group |
| 18259 | Server Role |
| 18241 | Availability Group |
The rest of the Object Types will be classified in the email subject as "Other Server objects".
Setting up WMI Alert to Respond to the Server Objects GDR Events
Now we will create the WMI alert as the following:

Here is the WMI query for this alert:
select * from AUDIT_SERVER_OBJECT_GDR_EVENT
Read more about the Audit Server Object GDR Event Class here.
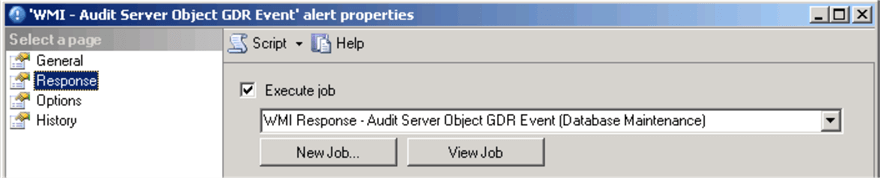
Set the response in alert's properties to execute the job we have created earlier:
Testing the Alerts
Now we should be able to receive email notifications every time when the Server Scope Permissions or the Server Objects Permissions are changed.
Let's create test Logins and a custom Server Role for our tests:
USE [master] GO CREATE LOGIN [_demo_user] WITH PASSWORD=N'AlwaysStr0ngP@ssword', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON; GO CREATE LOGIN [WMITest] WITH PASSWORD=N'AlwaysStr0ngP@ssword', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON; GO CREATE LOGIN [Test] WITH PASSWORD=N'AlwaysStr0ngP@ssword', DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON; GO CREATE SERVER ROLE [custom_srv_role]; GO ALTER SERVER ROLE [bulkadmin] ADD MEMBER [custom_srv_role]; GO ALTER SERVER ROLE [dbcreator] ADD MEMBER [custom_srv_role]; GO ALTER SERVER ROLE [custom_srv_role] ADD MEMBER [WMITest]; GO GRANT ALTER ON LOGIN::[ Test] TO [custom_srv_role]; GO GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO [custom_srv_role]; GO
Now we will grant to this login permissions to View any Definition on SQL Server:
USE [master] GO GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO LOGIN [_demo_user]; GO
You should get an email as the following one:

Let's test granting to the "_demo_user" login permissions to other Securables.
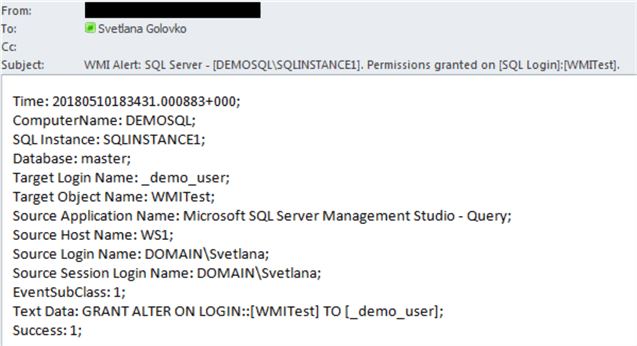
use [master] GO GRANT ALTER ON LOGIN::[WMITest] TO [_demo_user] GO
Here is the email that was sent for this event:
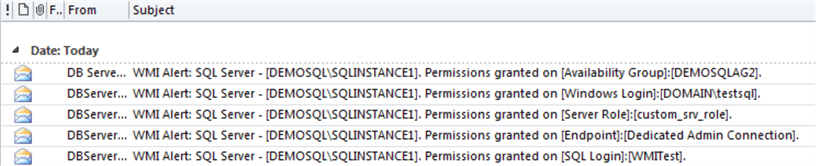
Here are other permissions that could be granted and all of the emails received:
use [master] GO -- permissions on LOGIN Object Type GRANT IMPERSONATE ON LOGIN::[CORP\sql_test] TO [_demo_user] GO -- permissions on ENDPOINT Object Type use [master] GO GRANT CONNECT ON ENDPOINT::[Dedicated Admin Connection] TO [_demo_user] GO -- permissions on SERVER ROLE Object Type use [master] GO GRANT ALTER ON SERVER ROLE::[custom_srv_role] TO [_demo_user] GO -- permissions on AVAILABILITY GROUP Object Type use [master] GO GRANT ALTER ON AVAILABILITY GROUP::[DEMOSQLAG2] TO [_demo_user_sg] GO
Troubleshooting Tips
Note, that in our tip we have tried to replace some additional (hidden) characters in the "GRANT" statement (extra spaces, TAB etc.). If you get an email with subject "SQL Server Message" (without details) it means that there are some hidden characters in the "GRANT" statement and they are not covered in our script:

This is only issue with the subject. You can still get enough details from the email's body.
use msdb GO GRANT ALTER ON AVAILABILITY GROUP::[DEMOSQLAG21] TO [_demo_user_sg] GO
Complete Script
The script for all of the jobs and alerts could be downloaded from here.
Please note, that you may need to update some of the sections in the script:
- @wmi_namespace for the alerts (see the examples above)
- @profile_name and @recipients parameters with your values (@profile_name will be the "Mail profile" that you created during Database Mail configuration)
- replace a job owner if "sa" login is renamed on your SQL Server:
@owner_login_name=N'sa'
Next Steps
- Refer to the previous tip #1, tip #2, tip #3, tip #4, tip #5 and tip #6 about setting up other WMI alerts.
- Read this tip about How to Automate SQL Server Monitoring with Email Alerts.
- Read this tip about How to setup SQL Server alerts and email operator notifications.
- Read these tips about Audit and Compliance.
- Get familiar with "WMI Provider for Server Events Concepts".
- Use other classes for your SQL Server events monitoring.
- Get a list of columns that are available for a given WMI event XML schema.
About the author
 Svetlana Golovko is a DBA with 13 years of the IT experience (including SQL Server and Oracle) with main focus on performance.
Svetlana Golovko is a DBA with 13 years of the IT experience (including SQL Server and Oracle) with main focus on performance. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2018-07-24






