By: Koen Verbeeck | Updated: 2019-11-26 | Comments (7) | Related: > Azure Data Factory
Problem
I’m orchestrating a data pipeline using Azure Data Factory. One of the activities the pipeline needs to execute is loading data into the Snowflake cloud data warehouse. Since Azure Data Factory currently doesn’t support a native connection to Snowflake, I’m thinking about using an Azure Function to accomplish this task. How can I integrate this in into my pipeline?
Solution
Snowflake is a database vendor who offer a cloud native data warehouse solution. This data warehouse can be hosted on all major cloud platforms (Azure, AWS and Google Cloud). For an introduction to Snowflake and their offerings, I refer to the Snowflake website.
In the two-part tip Using an Azure Function to execute SQL on a Snowflake Database (part 1 and part 2), an Azure Function was created which is able to take a SQL statement as a parameter and execute this on a Snowflake database. As output, the duration and the number of affected rows are returned. If you haven’t already, please read the tip about creating the function, as we will use it as an example in this tip. However, the explanation in this tip is useful for integrating any kind of Azure Function into Azure Data Factory (ADF), even if you’re not using Snowflake.
Integrating an Azure Function into ADF
Test Set-up
We’re going to execute two SQL statements in our ADF pipeline:
- A TRUNCATE TABLE statement to empty a staging table
- A COPY INTO statement to load the data from an XML file stored on Azure Blob Storage into the table. The COPY INTO statement is a powerful statement which is able to load multiple files in parallel into a table with great performance. It supports multiple types of compression and different file types. For more information, please check the documentation.
The data that is going to be loaded is an XML file of the StackOverflow sample database, stored in an Azure Blob container:
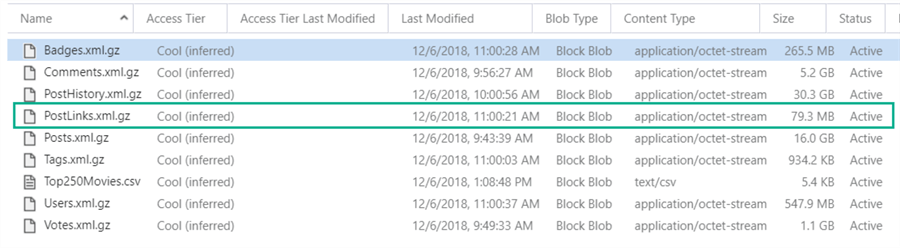
The PostLinks XML file is about 80MB large (compressed using the gzip format. Keep in mind the original files are in the 7z format which is currently not supported by the COPY INTO statement) and contains 5,292,624 lines. It will be loaded into a table named STAGE.DEMO_Postlinks_XML. It can be created with the following SQL:
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE STAGE.Demo_PostLinks_XML(src_xml VARIANT);
The XML is stored in one single column of the VARIANT data type. The COPY INTO statement takes the following format:
COPY INTO STAGE.Demo_PostLinks_XML FROM @AZURESTAGINGDEV/PostLinks.xml.gz FILE_FORMAT=(TYPE=XML STRIP_OUTER_ELEMENT = TRUE) ON_ERROR='CONTINUE';
The STRIP_OUTER_ELEMENT parameter tells the COPY INTO statement to drop the root node of the XML file and load each individual child node as a single row to the destination table. If you don’t enable this parameter, Snowflake will try to load the entire XML file into one row. However, there’s a 16MB size limit per row, so this will fail. By setting this parameter to True, 5 million lines will be loaded instead of one. This comes with a computational overhead since the XML has to be parsed.
Adding the Azure Function to ADF
The first step is to add a new Linked Service to your ADF environment:
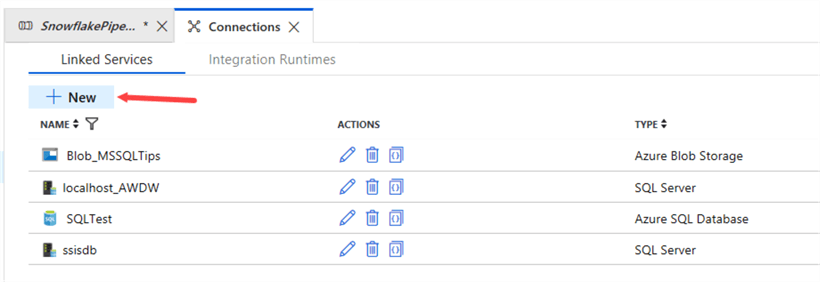
In the Compute tab, choose Azure Function.

Choose your Azure Function from your subscription:
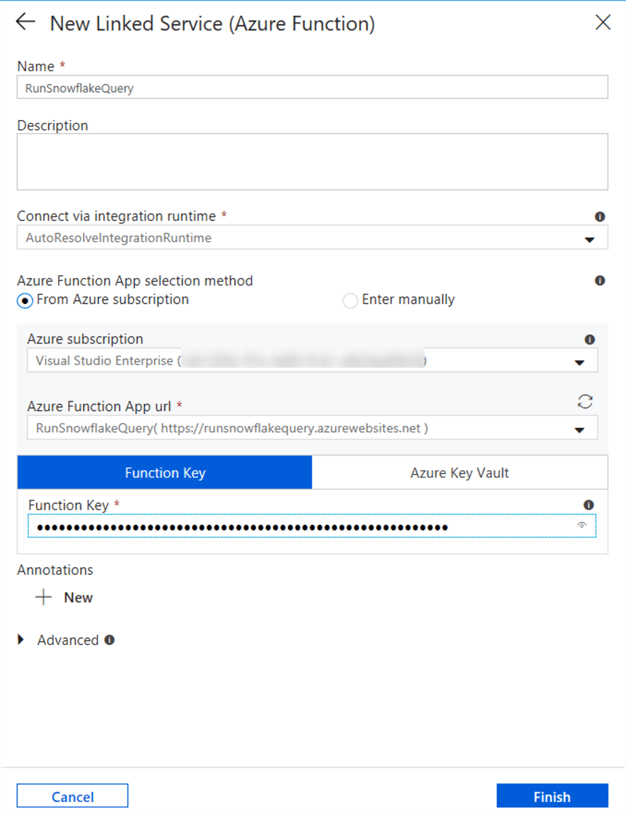
The Function Key can be found in the Azure Portal. In the Function App, search for the Function itself, and then go to the Manage page. There you can copy the Function Key to the clipboard or add new ones.
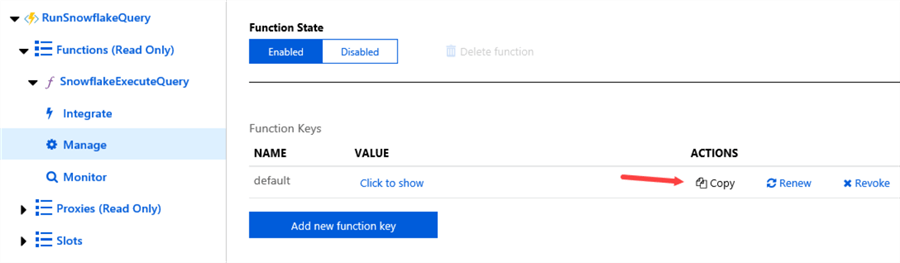
Once the Function Key is pasted to the configuration, the Linked Service can be created.
In your pipeline, drag the Azure Function activity to the canvas and give it a descriptive name.
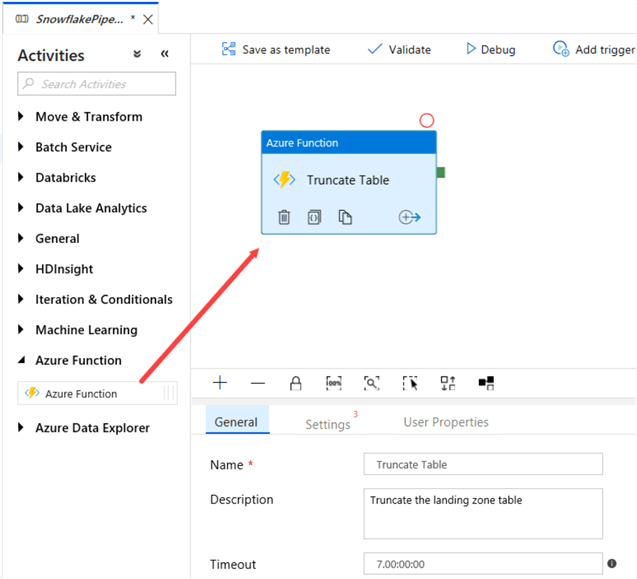
In the Settings, choose the Azure Function Linked Service we just created. Pick the Azure Function you want to use and select the POST method from the dropdown.
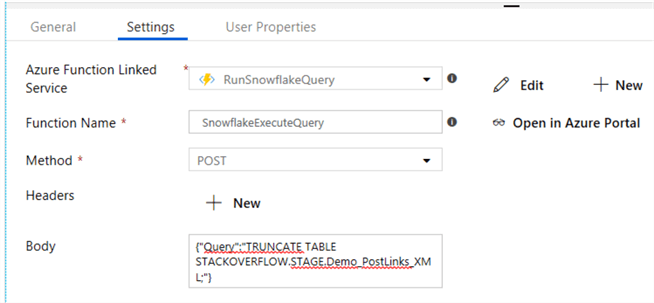
For the body, we pass along the SQL statement to the Query parameter using a JSON format:
{"Query":"TRUNCATE TABLE STACKOVERFLOW.STAGE.Demo_PostLinks_XML;"}
Repeat the same steps to add a new Azure Function activity to the canvas and configure it to execute the COPY INTO statement:
{"Query":"COPY INTO STACKOVERFLOW.STAGE.Demo_PostLinks_XML
FROM @AZURESTAGINGDEV/PostLinks.xml.gz
FILE_FORMAT=(TYPE=XML STRIP_OUTER_ELEMENT = TRUE)
ON_ERROR='CONTINUE';"}
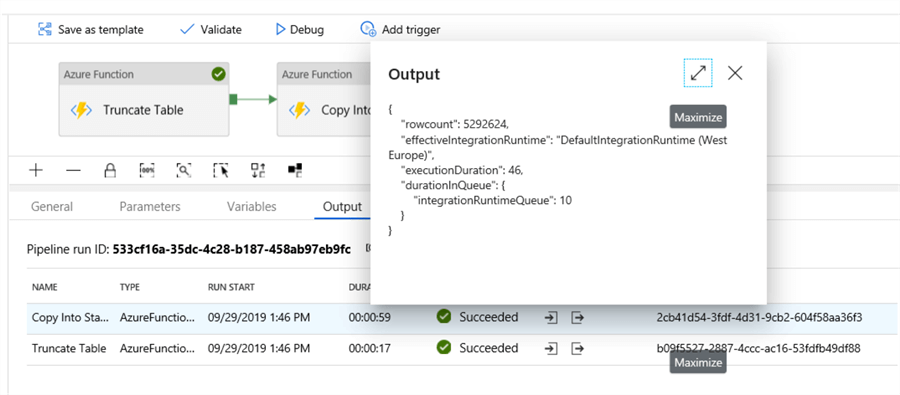
When the pipeline is executed, we can see in the output window the number of affected rows and the duration of the query:
In Snowflake, we can verify the data has actually been loaded:
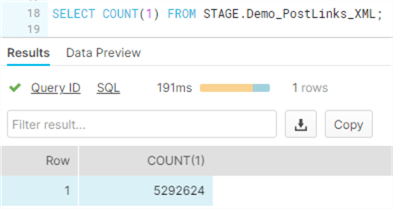
Each line of the XML file has been loaded to one row in the destination table:
Conclusion
In this tip, we saw how we can integrate an Azure Function into an Azure Data Factory pipeline using the native Linked Service and activity. Using an Azure Function, we’re able to execute SQL statement on a Snowflake database and return the output to ADF.
Next Steps
- Check out the tips Using an Azure Function to execute SQL on a Snowflake Database – Part 1 and Part 2 to create the Azure Function used in this tip.
- Official documentation on Azure Functions:
- For an overview of all the Azure Data Factory activities, check out the tip Azure Data Factory Control Flow Activities Overview.
- For more Azure tips, check out this overview.
About the author
 Koen Verbeeck is a seasoned business intelligence consultant at AE. He has over a decade of experience with the Microsoft Data Platform in numerous industries. He holds several certifications and is a prolific writer contributing content about SSIS, ADF, SSAS, SSRS, MDS, Power BI, Snowflake and Azure services. He has spoken at PASS, SQLBits, dataMinds Connect and delivers webinars on MSSQLTips.com. Koen has been awarded the Microsoft MVP data platform award for many years.
Koen Verbeeck is a seasoned business intelligence consultant at AE. He has over a decade of experience with the Microsoft Data Platform in numerous industries. He holds several certifications and is a prolific writer contributing content about SSIS, ADF, SSAS, SSRS, MDS, Power BI, Snowflake and Azure services. He has spoken at PASS, SQLBits, dataMinds Connect and delivers webinars on MSSQLTips.com. Koen has been awarded the Microsoft MVP data platform award for many years.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2019-11-26






