By: Sergey Gigoyan | Updated: 2019-12-13 | Comments | Related: > Indexing
Problem
It is well-known that correctly designed indexes are key for SQL Server database performance. However, in order to fully derive the benefits of the indexes, it is important to maintain them periodically. Therefore, properly organized and regularly scheduled index maintenance operations play a crucial role in improving database performance. This article is devoted to one of the index maintenance tasks, Rebuild Index using SQL Server Maintenance Plans.
Solution
Usually, in transactional databases, data is regularly modified, which also changes how index data is stored. As a result, indexes get fragmented. In turn, the fragmentation affects the efficiency of indexes and therefore could impact performance. Thus, to make the usage of indexes more optimal, they should be defragmented regularly. To do so, we can either reorganize or rebuild the indexes.
As compared to rebuilding, reorganization is a more lightweight operation. It is an online operation and not only defragments the indexes, but also compacts them based on the existing fill factor settings.
Rebuilding indexes is a more resource-consuming process as it drops and recreates indexes. Additionally, a different value for fill factor can be set to optimize the index storage. This operation can be either online or offline depending on the index type and the version of SQL Server. The rebuild index operation automatically updates statistics as well, unlike the reorganize index operation.
Discussing the details of index architecture and the rebuild and reorganize operations is out of the scope of this article, but you can read more about rebuilding and reorganizing indexes.
Now we are going to illustrate how to design a rebuild index task via SQL Server Maintenance Plans.
Designing a SQL Server Maintenance Plan Rebuild Index Task
Let’s assume that we need to configure the Rebuild Index task for all indexes in all databases of our instance. We will use the Maintenance Plans Wizard to configure these tasks. The version of SQL Server used is SQL Server 2017.
In SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), we choose Management > Maintenance Plans and then right-click and select Maintenance Plan Wizard.

After clicking on Maintenance Plan Wizard, the following window will appear.

If we do not want to see this starting screen every time, we can click on the checkbox "Do not show this starting page again".
After clicking Next, the next window appears where we give a name and description to our task.

Additionally, we set the schedule for the task by clicking the Change button in the bottom right-hand corner.
Choosing the schedule of the Rebuild Index task depends on how quickly indexes get fragmented which is hard to say without creating a baseline for comparison. It is also desirable to run this task when the database is not busy as it is a resource-consuming operation. We will set it to run weekly, every Sunday at 1:30am, but this could be run more or less frequently depending on fragmentation levels.

Here we can click OK and then Next to move to the screen where we choose the tasks.
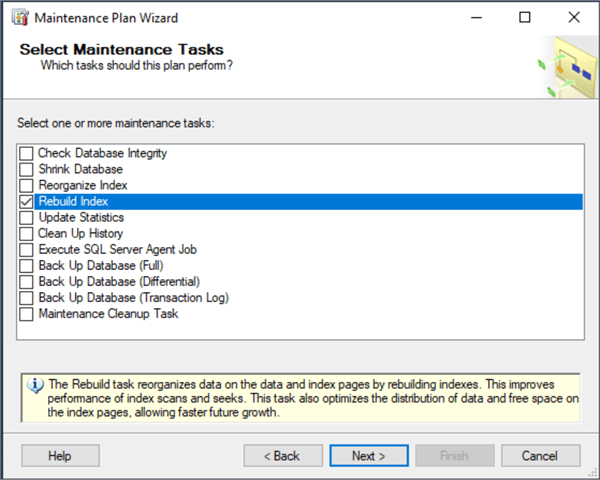
Above, we choose Rebuild Index and move forward by clicking Next.

As we have only one task here, we just click Next to continue.
In the screen below, we choose "All databases". It is also possible to choose specific databases and specific tables or views in the particular database. As mentioned earlier, we are using SQL Server 2017 to demonstrate our example and we can see that there are various options for the Index Rebuild operation.

To compare, the same screen in SQL Server 2014 has very limited options. In the picture below, on the left side is SQL Server 2017's Rebuild Index screen and on the right side is SQL Server 2014.

The difference is easily visible. For instance, in the Maintenance Plans of SQL Server 2017, it is possible to rebuild only those indexes where fragmentation level is higher than a specific percentage and has more pages than specified in "Page Count". Defining "Index Stats Options" as well has become available in SSMS. These options define how much resources should be used to gather index statistics. The faster the scan type, the lower the precision. We leave the default value of this option "Fast".
Even more, it is also possible to consider only those indexes that are used recently by setting the value of the "Used in last" option. This variety of options definitely makes the Rebuild Index task more flexible and optimal by rebuilding only the indexes which are really need to be rebuilt. In contrast, if we need to consider these options in older versions of SQL Server, we need to use T-SQL code as the Maintenance Plans wizard options are limited to only resetting the Fill Factor ("Change free space per page to"), choosing between sorting the result in the tempdb or not and keeping indexes online or offline during the rebuild process.
Microsoft recommends rebuilding indexes where the fragmentation level is more than 30%, so we will leave the above settings and click Next.

After choosing the report options, we click Next.
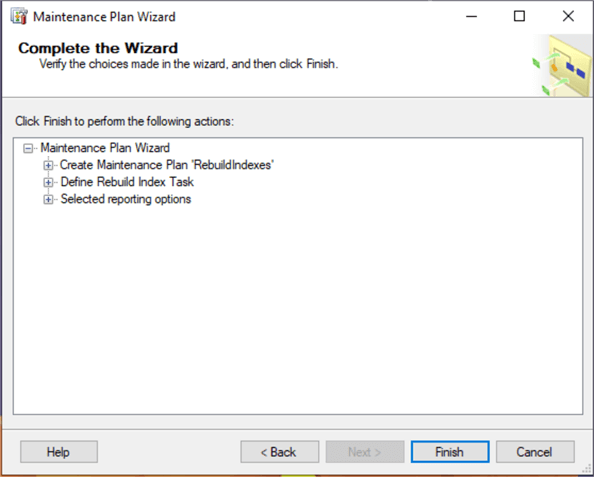
Then, we complete the configuration by clicking Finish.

Modifying an Existing SQL Server Maintenance Plan
Under the Maintenance Plans in SSMS, we can see our plan. If we want to edit it, we can right-click on it and choose Modify.

The Maintenance Plan Designer will open where we can modify the task.

Modifying a SQL Server Maintenance Plan
To execute our task, we can right-click on the plan and choose Execute.

We can also run the task by running the corresponding job in SQL Server Agent.

After it completes, we can see the job was successful.

Hence, we have configured and tested the Rebuild Index task. In the next article, we will learn about the Reorganize Index and Update Statistics tasks.
Conclusion
To sum up, by using Maintenance Plans it is possible to design powerful index maintenance tasks. Moreover, unlike older versions of SQL Server Maintenance Plans, in the newer versions, the Rebuild Index task includes more options. This, definitely, makes it possible to create more robust index maintenance tasks without using T-SQL code. Having said that, there are still some limitations in Maintenance Plans, and for creating much more complex, flexible index maintenance solutions the use of manually written T-SQL code is essential.
Next Steps
For more information about the discussed topic, please follow the links below:
- All SQL Server Indexing Tips
- Getting Started with SQL Server Maintenance Plans - Part 1
- SQL Server Maintenance Plan Index Rebuild and Reorganize Tasks
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/maintenance-plans/maintenance-plans?view=sql-server-2017
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/maintenance-plans/rebuild-index-task-maintenance-plan?view=sql-server-ver15
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/indexes/reorganize-and-rebuild-indexes?view=sql-server-ver15
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/indexes/specify-fill-factor-for-an-index?view=sql-server-ver15
About the author
 Sergey Gigoyan is a database professional with more than 10 years of experience, with a focus on database design, development, performance tuning, optimization, high availability, BI and DW design.
Sergey Gigoyan is a database professional with more than 10 years of experience, with a focus on database design, development, performance tuning, optimization, high availability, BI and DW design.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2019-12-13






