By: Sergey Gigoyan | Updated: 2021-05-10 | Comments (1) | Related: 1 | 2 | More > System Databases
Problem
Sometimes we need to move the SQL Server system databases' files to a new location. In this tutorial, we are going to illustrate the process for moving tempdb, msdb, and model system databases to a different location. Moving the master database is a different process, so this will be discussed in the second part of this series. It is also important to mention that the resource database files cannot be moved.
Solution
Let's start defining our task.
Suppose we have a new location for system database files and need to relocate these files from the default location to this new location. It is worth mentioning that we are just going to change the location of the system databases' files within the same instance.
Step 1 - Check File Location of System Databases
First, let's see the current location of these files:
SELECT name AS FileLogicalName, physical_name AS FileLocation FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id BETWEEN 1 AND 4
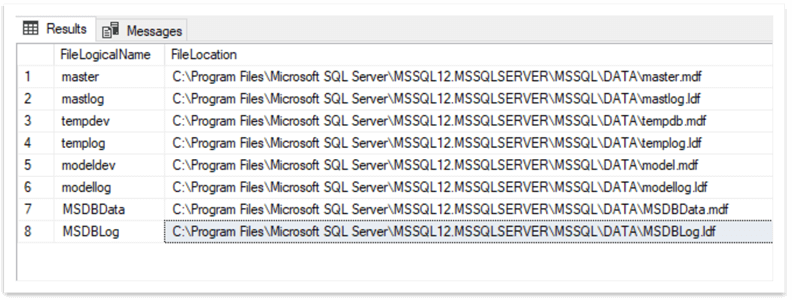
We can see that our system databases' files are in their default location:
Step 2 - Update System Database File Location
Let's assume that the new path of these files will be "C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases", but this can be any path SQL Server can access.
Using the following T-SQL code, we will set the new path for the data and log files of the tempdb, model, and msdb databases (we do not run this code for the master database as the process of relocating the master database files will be discussed separately):
USE master GO --tempdb ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE( NAME = tempdev, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\tempdb.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE tempdb MODIFY FILE( NAME = templog, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\templog.ldf') --model ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE( NAME = modeldev, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\model.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE( NAME = modellog, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\modellog.ldf') --msdb ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE( NAME = MSDBData, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\MSDBData.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE( NAME = MSDBLog, FILENAME = 'C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases\MSDBLog.ldf')
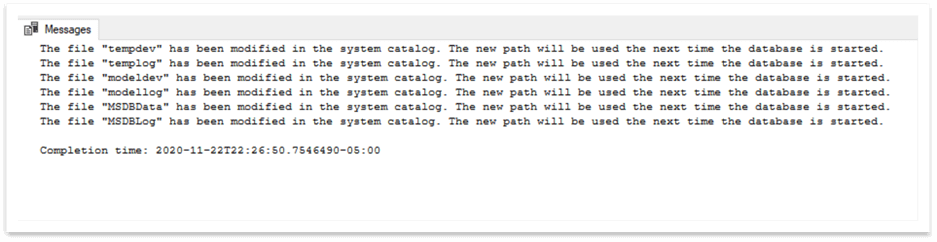
As the message shows, the new path will be used the next time the database is started:
We run the code below one more time to be sure that the new path of these files are set:
SELECT name AS FileLogicalName, physical_name AS FileLocation FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id BETWEEN 1 AND 4
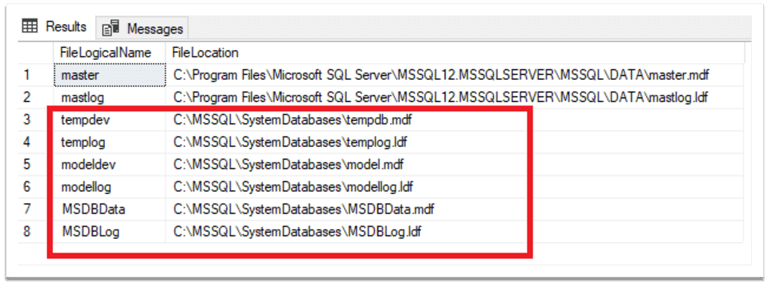
The result shows that the path of the data and log files of the tempdb, model, and msdb databases now is "C:\MSSQL\SystemDatabases" folder:
Step 3 - Physically Move System Database Files
Our system database files are still in the old location. Therefore, we need to move all these files to the new location.
In the case of relocating user database files, we take databases offline and then move files which is not possible in the case of the system databases (it is impossible to take system databases offline).
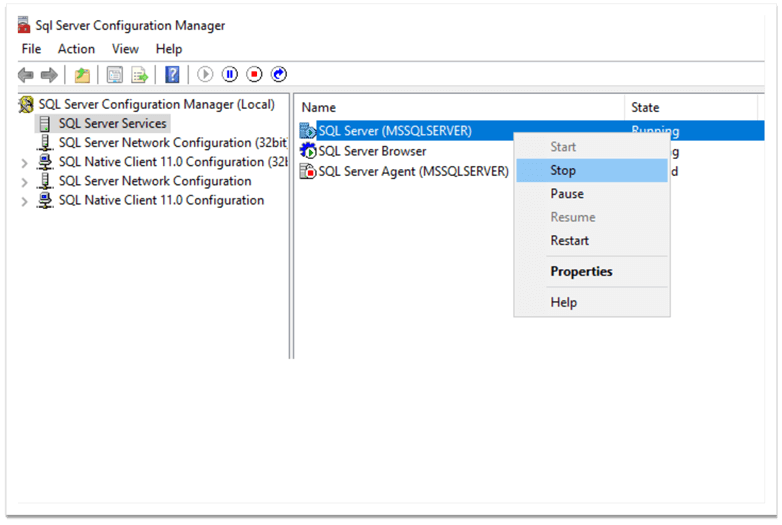
To copy files to the new location, we need to stop the SQL Server instance. We can do it using SQL Server Configuration Manager by right-clicking on the instance name and choosing "Stop":
After it stops, it will be possible to move the files to the new location (we will leave the master database files in the old location as their paths have not been changed):
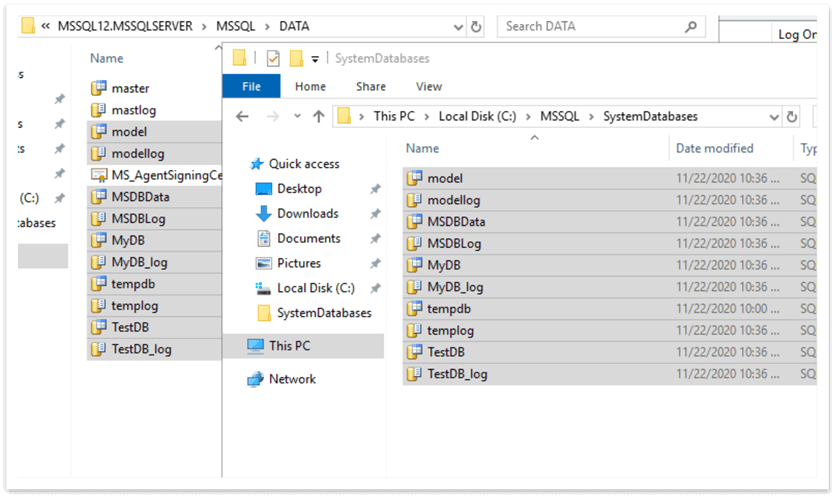
After we have copied the files to the new folder, we can start the instance by right clicking on the instance name and selecting Start.
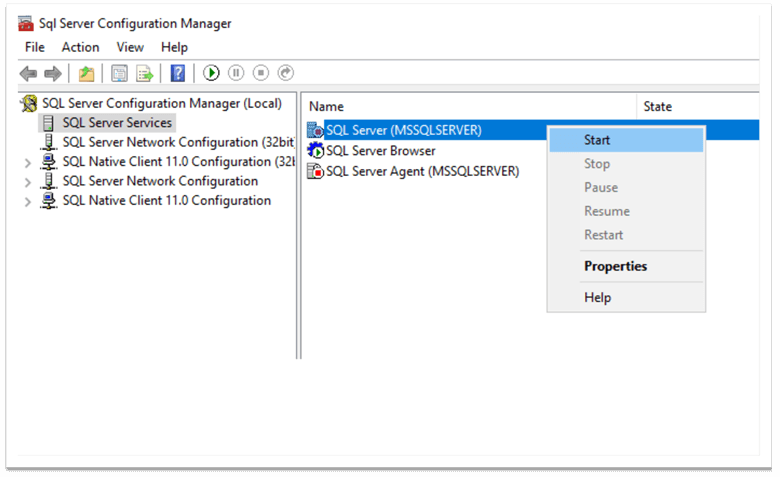
The instance should start successfully.
Step 4 - Check Database Mail and Service Broker
If "Database Mail" is configured on the instance, after moving the msdb database, it is important to check that Database Mail works properly. We should also check that Service Broker is enabled. That can be done by the following query:
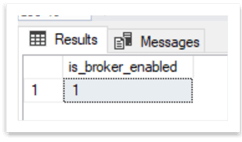
USE master GO SELECT is_broker_enabled FROM sys.databases WHERE name = N'msdb'
In our case, is_broker_enabled is 1, which means that it is enabled:
Then, we can send test emails to verify the functionality of Database Mail.
Checking Database File Location with SSMS
Previously, we checked a database files' locations using T-SQL, but we can also check the path in SQL Server Management Studio as well.
To do so, right-click on the database name, choose "Properties" and then "Files" and we can see the location below.
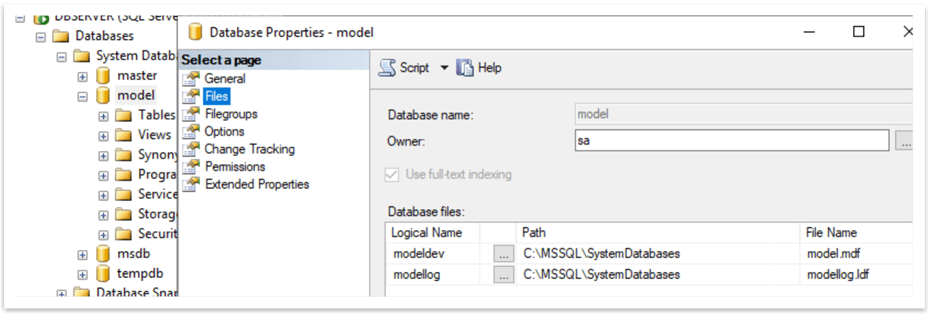
ResourceDB Settings
As mentioned above, the resource database files' locations cannot be changed. The data and log files of the resource database are mssqlsystemresource.mdf and mssqlsystemresource.ldf.
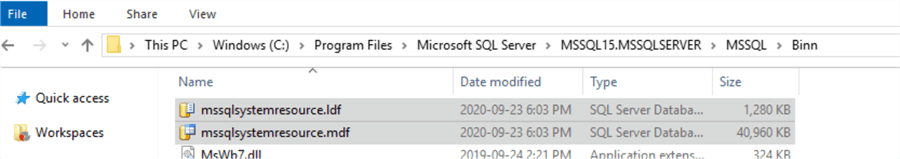
The location of these files is: <drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL<version>.<instance_name>\MSSQL\Binn
So, in our case, it will be "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Binn" and we can see the resource database's data and log files there:
Conclusion
Overall, the process of relocation of the msdb, model and tempdb files has many similarities with the process of moving user database files. Nevertheless, unlike the user databases case, when it is possible to physically move the databases' files after taking the databases offline, it is needed to stop the instance to move system databases' files.
Next Steps
For more information, please follow the links below:
- System Databases
- Move System Databases
- Move Database Files
- Move User Databases
- System view sys.master_files
About the author
 Sergey Gigoyan is a database professional with more than 10 years of experience, with a focus on database design, development, performance tuning, optimization, high availability, BI and DW design.
Sergey Gigoyan is a database professional with more than 10 years of experience, with a focus on database design, development, performance tuning, optimization, high availability, BI and DW design.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2021-05-10






