By: Ron L'Esteve | Updated: 2021-07-06 | Comments (2) | Related: > Azure Data Factory
Problem
The need to load data from Excel spreadsheets into SQL Databases has been a long-standing requirement for many organizations for many years. Previously, tools such as VBA, SSIS, C# and more have been used to perform this data ingestion orchestration process. Recently, Microsoft introduced an Excel connector for Azure Data Factory. Based on this new Excel connector, how can we go about loading Excel files containing multiple tabs into Azure SQL Database Tables?
Solution
With the new addition of the Excel connector in Azure Data Factory, we now have the capability of leveraging dynamic and parameterized pipelines to load Excel spreadsheets into Azure SQL Database tables. In this article, we will explore how to dynamically load an Excel spreadsheet residing in ADLS gen2 containing multiple Sheets into a single Azure SQL Table and also into multiple tables for every sheet.
Pre-Requisites
Create an Excel Spreadsheet
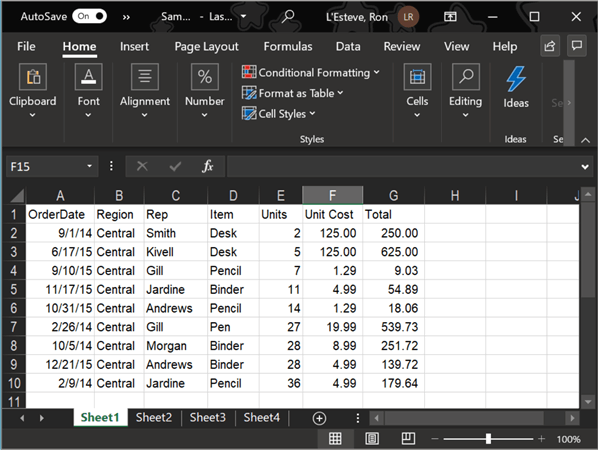
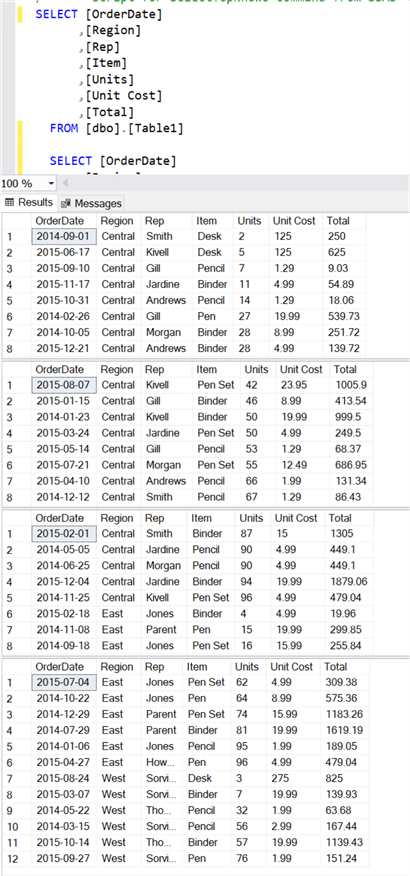
The image below shows a sample Excel spreadsheet containing four sheets containing the same headers and schema that we will use in our ADF Pipelines to load data in Azure SQL Tables.
Upload to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
This same Excel spreadsheet has been loaded to ADLS gen2.
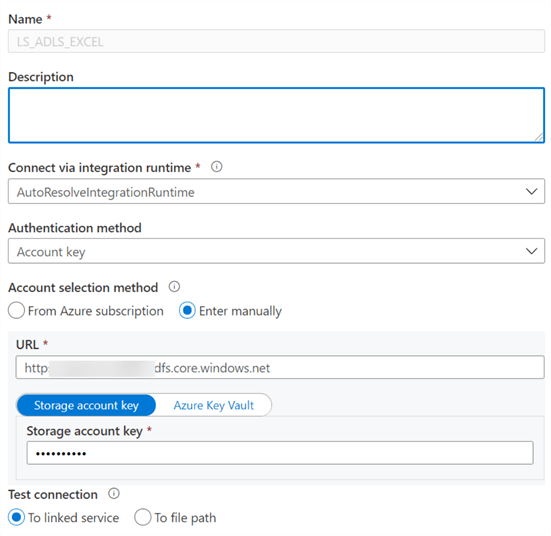
Within Data Factory, we can add an ADLS gen2 linked service for the location of the Excel spreadsheet.
Create Linked Services and Datasets

We'll need to ensure that the ADLS gen2 linked service credentials are configured accurately.
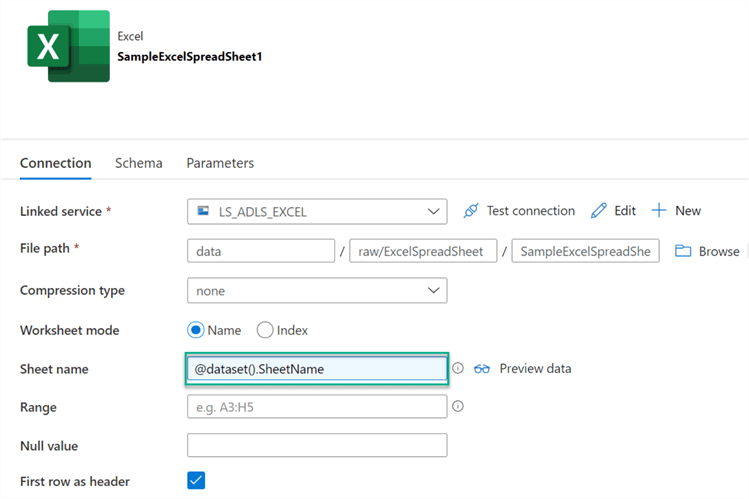
When creating a new dataset, notice that we have Excel format as an option which we can select.

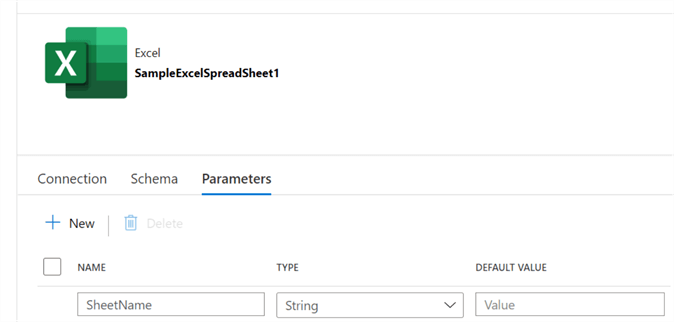
The connection configuration properties for the Excel dataset can be found below. Note that we will need to configure the Sheet Name property with the dynamic parameterized @dataset().SheetName value. Also, since we have headers in the file, we will need to check 'First row as header'.
Within the parameters tab, we'll need to add SheetName.
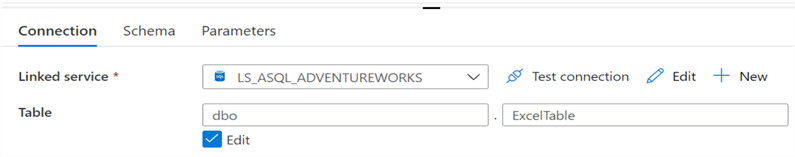
Next, a sink dataset to the target Azure SQL Table will also need to be created with a connection to the appropriate linked service.
Create a Pipeline to Load Multiple Excel Sheets in a Spreadsheet into a Single Azure SQL Table
In the following section, we'll create a pipeline to load multiple Excel sheets from a single spreadsheet file into a single Azure SQL Table.
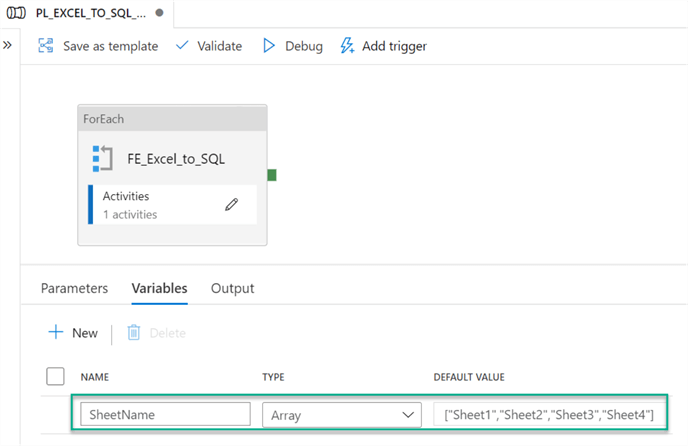
Within the ADF pane, we can next create a new pipeline and then add a ForEach loop activity to the pipeline canvas. Next, click on the white space of the canvas within the pipeline to add a new Array variable called SheetName containing default values of all the sheets in the spreadsheet from Sheet1 through Sheet4, as depicted in the image below.
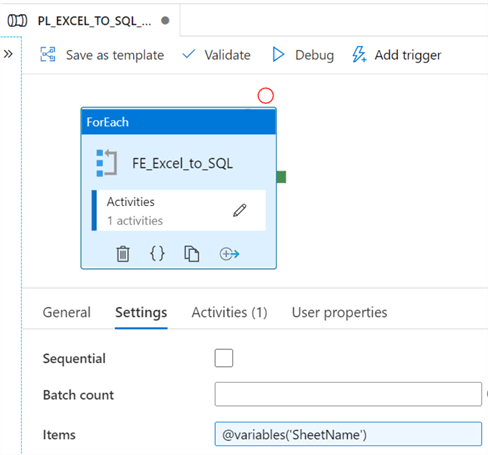
Next, add @variables('SheetName') to the items property of the ForEach Settings.
Next, navigate into the ForEach activity and add a CopyActivity with source configurations as follows.
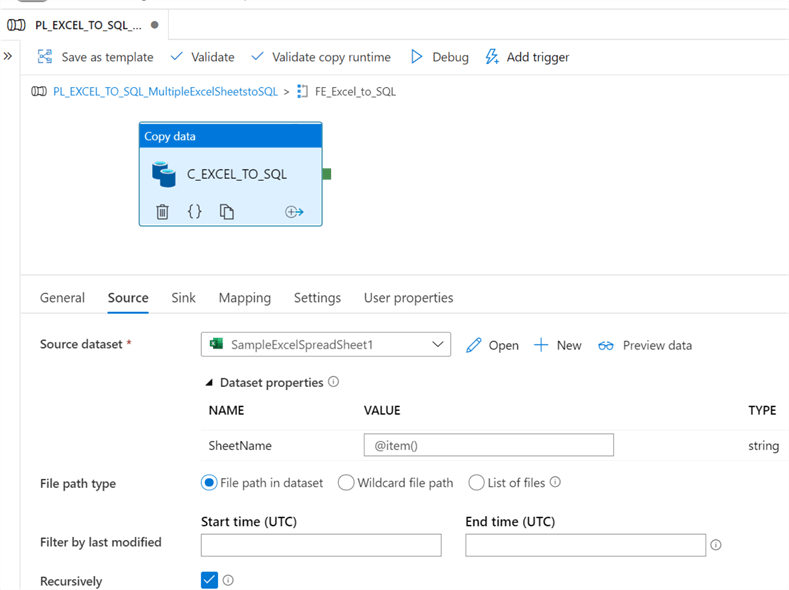
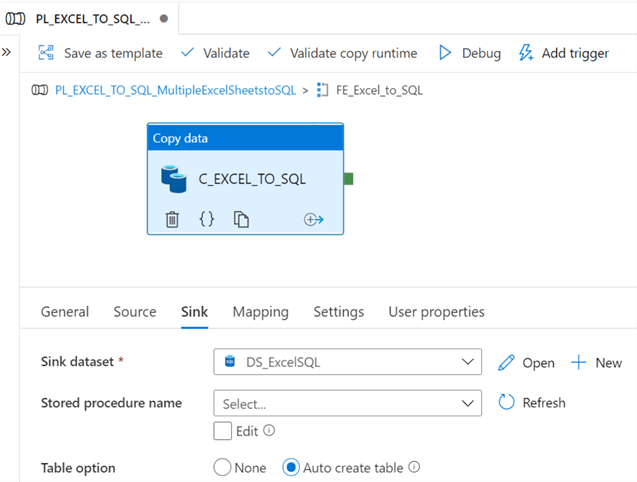
Within the sink configurations, we'll need to set the table option property to 'Auto Create Table' since we currently do not have a table created.
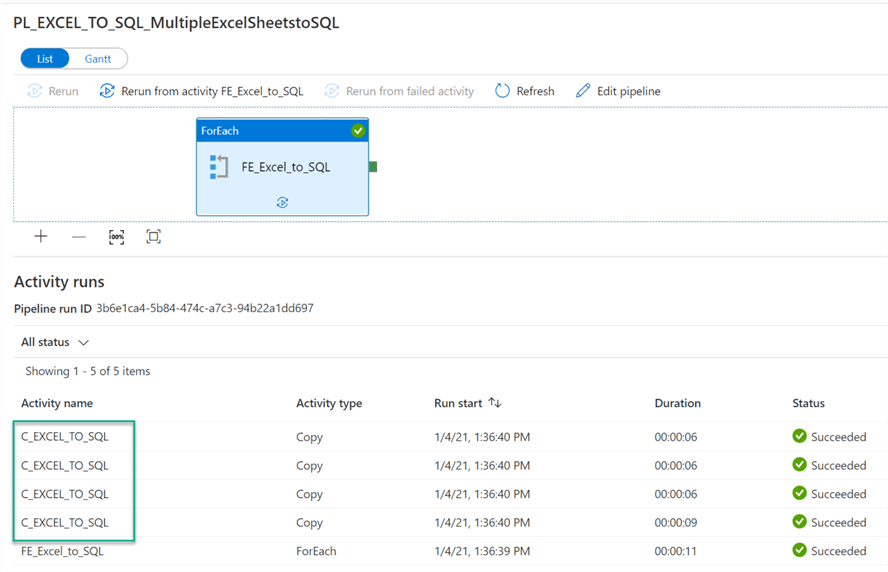
After executing the pipeline, we can see that the four Sheets have been loaded into the Azure SQL Table.
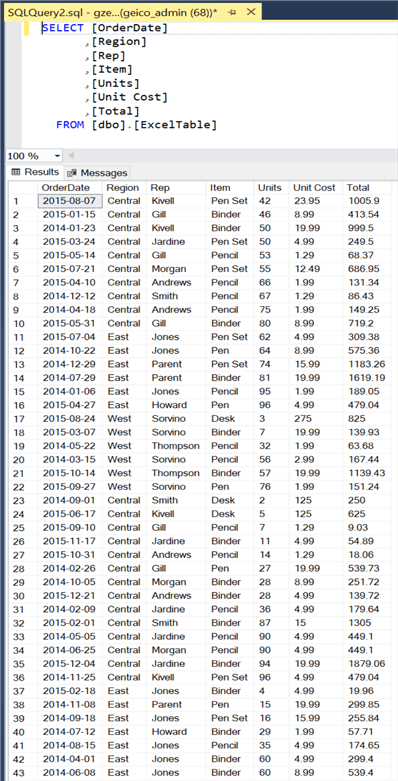
When we navigate to the Azure SQL Table and query it, we can see that the data from all the Excel Sheets were loaded into the single Azure SQL Table.
Create a Pipeline to Load Multiple Excel Sheets in a Spreadsheet into Multiple Azure SQL Tables
In this next example, we will test loading multiple Excel sheets from a spreadsheet into multiple Azure SQL Tables. To begin, we will need a new Excel lookup table that will contain the SheetName and TableName which will be used by the dynamic ADF pipeline parameters.
The following script can be used to create this lookup table.
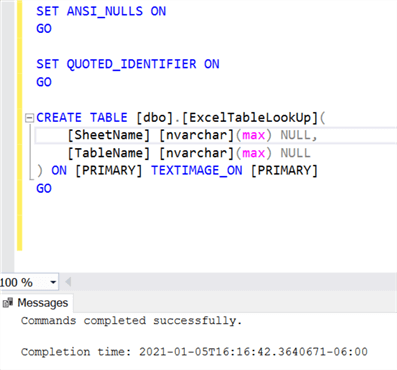
SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[ExcelTableLookUp]( [SheetName] [nvarchar](max) NULL, [TableName] [nvarchar](max) NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY] GO
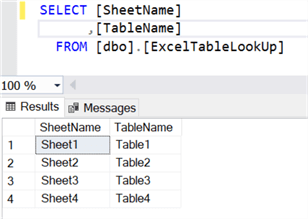
Once the table is created, we can insert the SheetNames and corresponding TableNames into the table:
Next, we will also need to create a new dataset with a connection to the Excel Look up table.
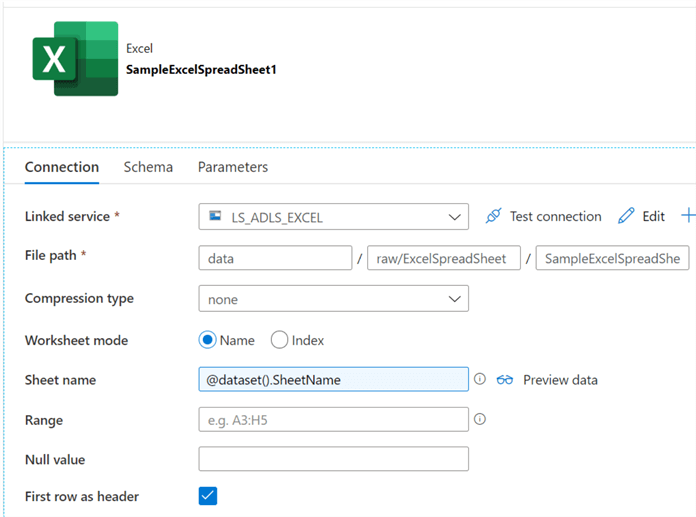
The connection properties of the Excel Spreadsheet will be similar to the previous pipeline where we parameterized SheetName as follows.
In this scenario, we will also need to add a parameter for the TableName in the Azure SQL Database dataset connection as follows.
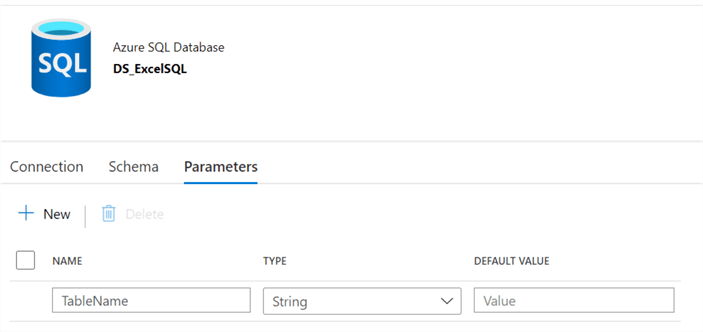
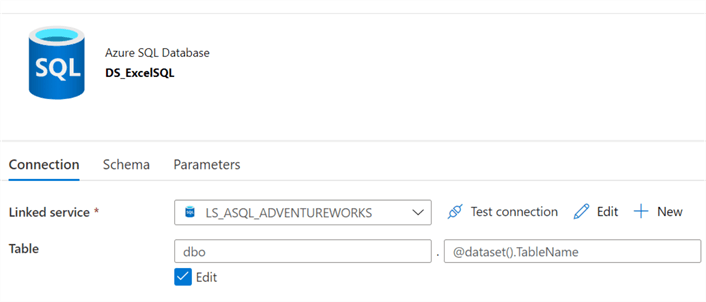
In the Azure SQL DB connection section, we'll leave the schema as hardcoded and would need to add the parameter for the TableName as follows.
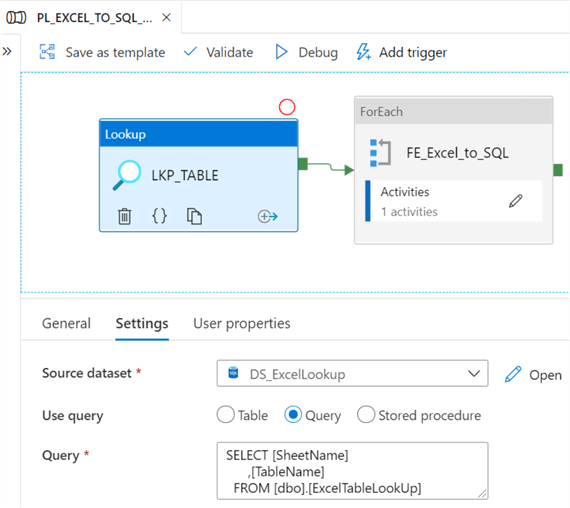
In this pipeline, we will also need a lookup table which will serve the purpose of looking up the values in the SQL lookup table through a select * lookup on the table.
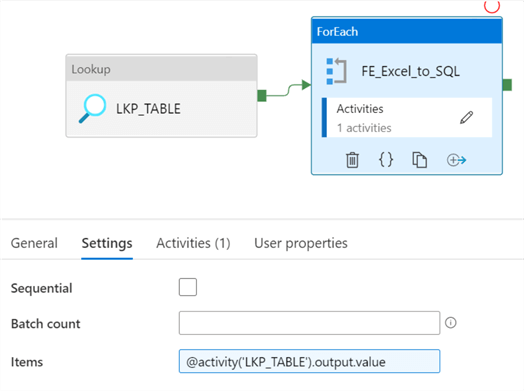
The values from the lookup can be passed to the ForEach loop activity's items property of the settings tab, as follows:
Next, within the ForEachLoop activity, we'll need a Copy Data activity with the source dataset properties containing the parameterized SheetName value, as follows.
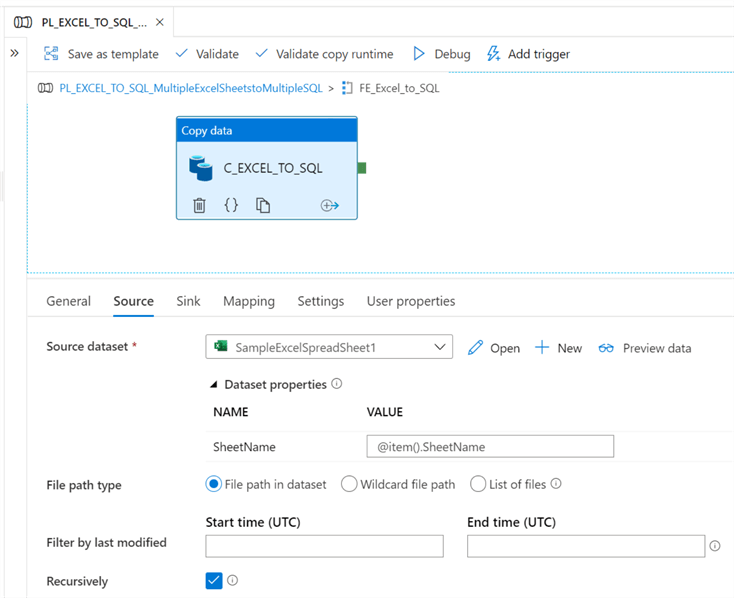
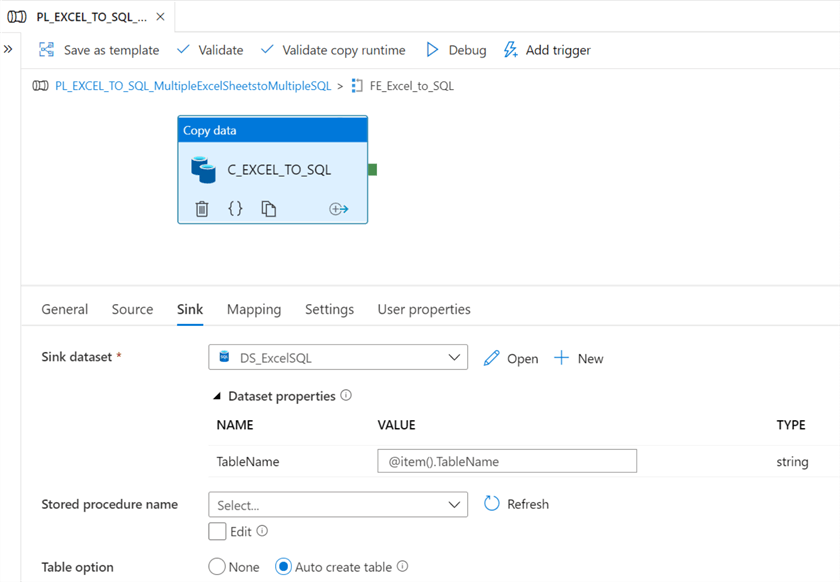
Next, the sink dataset properties will also need to contain the parameterized TableName value, as follows. Note that the table option is once again set to 'Auto Create Table'.
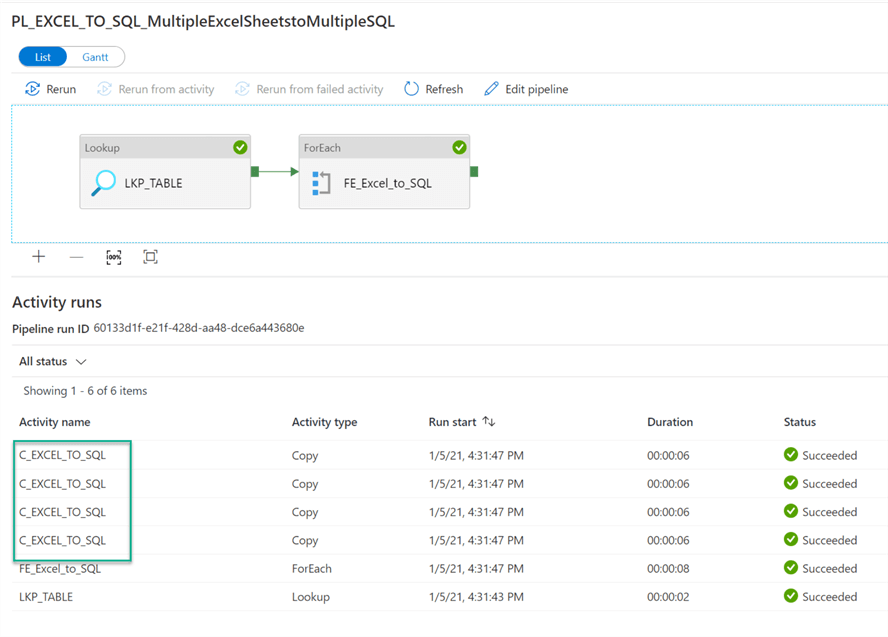
After we run this pipeline, we can see that the pipeline succeeded and four tables were created in the Azure SQL Database.
Upon navigating to the Azure SQL Database, we can see that all four table were created with the appropriate names based on the TableName values we defined in the SQL Lookup table.
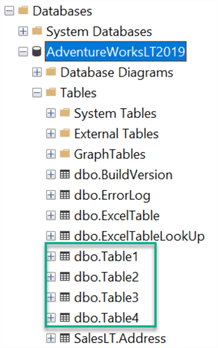
As a final check, when we query all four tables, we can see that they all contain the data from the Excel Sheets which confirms that the pipeline executed successfully and with the correct mappings of sheets to multiple tables which were defined in the lookup tables.
Next Steps
- For more details on the Excel Connector, read the Microsoft article - ADF Adds Connectors for Delta Lake and Excel.
- For a list of all the other Azure Data Factory Connectors, read Azure Data Factory Connector overview.
- Explore my article, Using SQL Server Integration Services to Generate Excel Files Based on Criteria which was built using SSIS and explore how to re-create this similar process in Azure Data Factory and also explore other capabilities and patterns to work with Excel files in ADF.
About the author
 Ron L'Esteve is a trusted information technology thought leader and professional Author residing in Illinois. He brings over 20 years of IT experience and is well-known for his impactful books and article publications on Data & AI Architecture, Engineering, and Cloud Leadership. Ron completed his Master�s in Business Administration and Finance from Loyola University in Chicago. Ron brings deep tec
Ron L'Esteve is a trusted information technology thought leader and professional Author residing in Illinois. He brings over 20 years of IT experience and is well-known for his impactful books and article publications on Data & AI Architecture, Engineering, and Cloud Leadership. Ron completed his Master�s in Business Administration and Finance from Loyola University in Chicago. Ron brings deep tecThis author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2021-07-06






