By: Joe Gavin | Updated: 2022-06-15 | Comments (4) | Related: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | > SQL Server Management Studio
Problem
Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is a feature rich environment to manage and / or develop on SQL Servers. There are two related features that save you from having to reenter connection information every time you connect to a SQL Server. The first is SSMS automatically stores SQL Server connections you've successfully made and are accessible from the Server name dropdown in the Connect to Server box. The other way is a very handy feature called Registered Servers where you have the ability to create organized groups and lists of SQL Servers.
You use SSMS and make use of one or possibly both of these features and would like to know where the connection info is stored and how to back it up or migrate it to another installation of SSMS.
Solution
Each of these features are closely related function-wise, but work quite differently so we're going to look at each, one at a time.
Connect to Server Box Dropdown
SSMS automatically stores the connection info for any SQL Server instances you've connected to. When you start SSMS or click Connect in Object Explorer you're presented with the Connect to Server box.
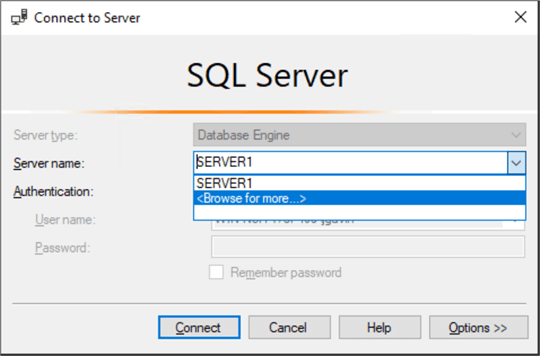
The list of SQL Servers are visible by clicking the Server Name dropdown.
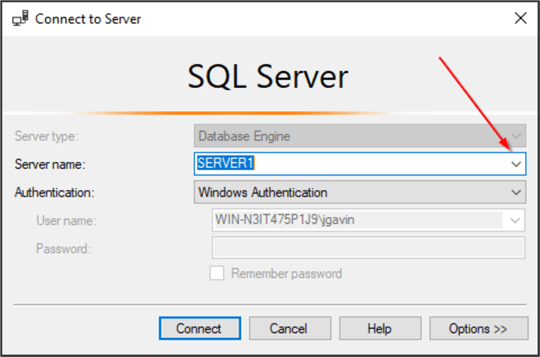
And here we see two SQL Server names, SERVER1 and SERVER2.
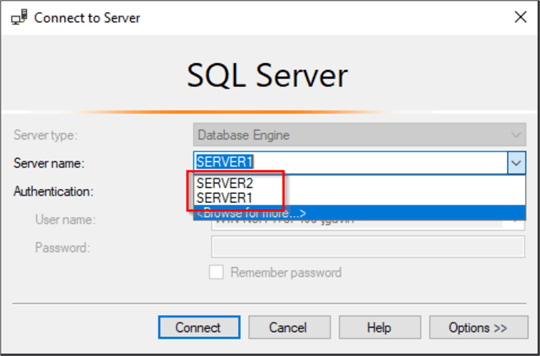
The connection info is stored locally in a file. The location and file format of where it's stored is different based on what version of SSMS you're using. This table shows the file name and location for each version.
| SSMS Version | File |
|---|---|
| 18 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\18.0\UserSettings.xml |
| 17 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\14.0\SqlStudio.bin |
| 16 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\13.0\SqlStudio.bin |
| 2014 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\12.0\SqlStudio.bin |
| 2012 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\11.0\SqlStudio.bin |
| 2008 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\100\Tools\Shell\SqlStudio.bin |
| 2005 | %APPDATA%\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\90\Tools\Shell\mru.dat |
Note: If you're simply trying to delete all the server names from the list you can just delete the file in the folder that matches your corresponding SSMS version. It will be recreated with an empty list when SSMS starts.
SSMS 18 x supports all supported SQL Server versions of SQL Server so that's what is used in this tip. The following examples were created using SSMS 18.11.1 which is the latest version as of this writing.
When you successfully connect to a SQL Server with SSMS 18.x the connection info is stored in the file %APPDATA%\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\18.0\UserSettings.xml. If we open the file, we'll see SERVER1 and SERVER1 between the <Instance> tags. Note, this is only applicable to SSMS 18.x and up. Connection info in earlier SSMS version isn't stored in text files.
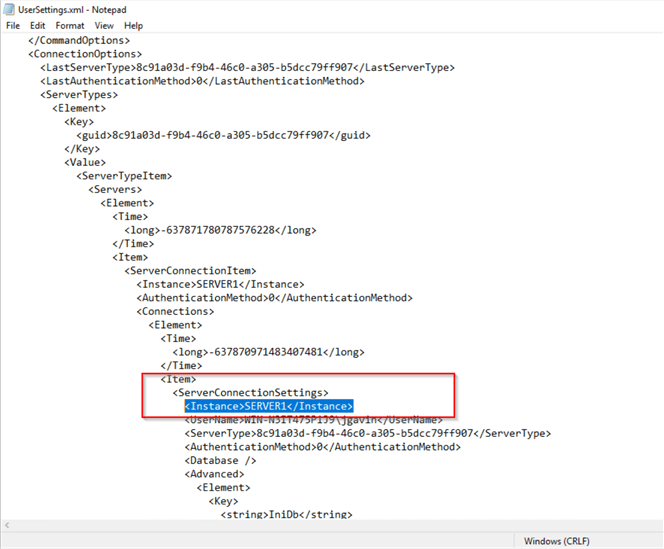
This file could be used to migrate the server list to another machine if you wanted to. However, if you are connecting to more than a couple of SQL Servers, it would be much more practical to use Registered Servers and export out a list that can be imported elsewhere. We'll look at how to do that in the next section.
Delete Unwanted Servers in List
You may be tempted to edit this file to clean up any old or unwanted entries in the list. Here's an easier way to do it.
Simply hover over the SQL Server name you want to delete with your mouse pointer and hit the Del key. I was able to test successfully going back as far as SSMS 2012.
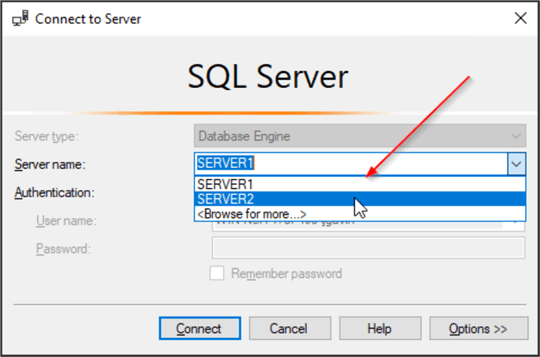
And the highlighted server entry is gone.
Register Servers
What are Registered Servers? If you're unfamiliar with this very useful piece of functionality in SSMS, it's simply an organized list of SQL Server connection information stored in SSMS. It lets you organize SQL Servers by group and run a query against every member of a group. Unlike the automatic saving of connection info when you successfully connect, you need to enter your info under Registered Servers.
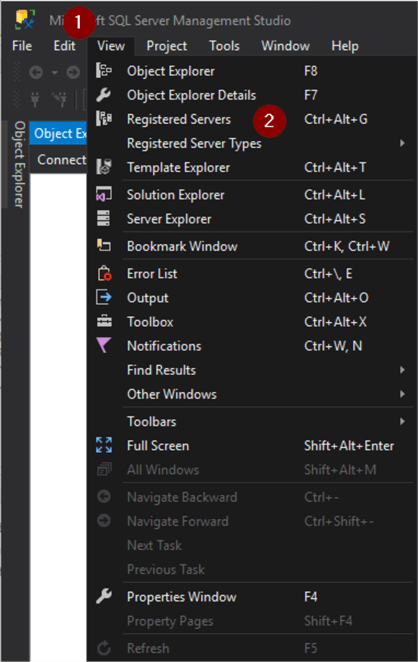
To open Registered Servers
- View
- Registered Servers
Or alternatively use the Ctrl+Alt+G keyboard shortcut.
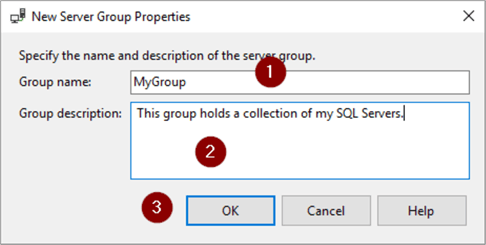
To illustrate, we'll create a Registered Server group.
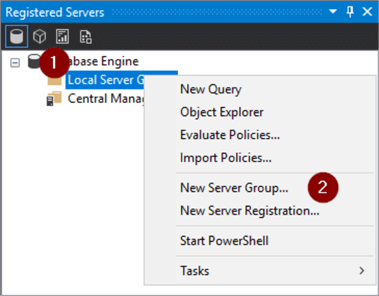
- Expand Database Engine and right click on Local Server Groups
- New Server Group…
- Name Group
- Enter a description (optional)
- OK
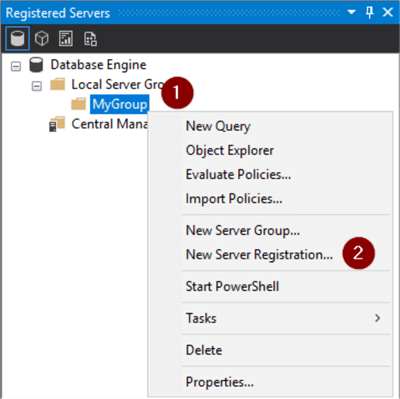
Next, we'll add a new Registration.
- Right click on group
- Click New Server Registration…
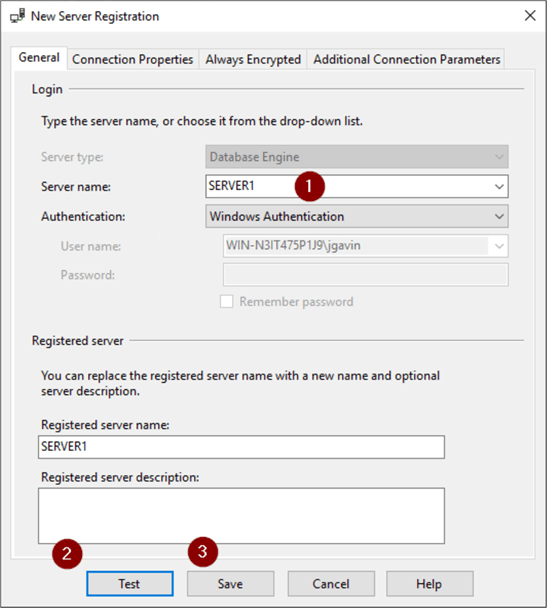
- Enter server name in Server name box
- Test to test connection
- Save
Repeat steps to add more servers.
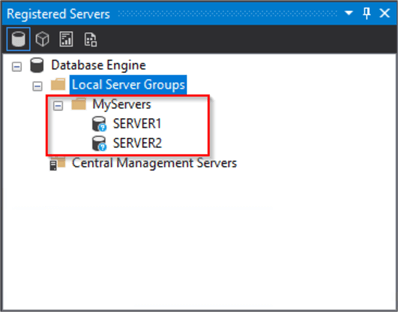
Here is my MyServers group with SERVER1 and SERVER2.
Export Registered Servers
If you only had two Registered Server like here in our example it would be easy enough to just re-enter them. But what if you have an extensive list of every SQL Server you work with, and it's organized just the way you want it? It would be inconvenient, time consuming and just plain annoying to have to re-enter them all in the event of a failure or just to move it to another machine.
Not to worry, this problem is easily solved with the built in Export and Import Registered Server Tasks.
- Right click on the top group to export all items
- Tasks
- Export…
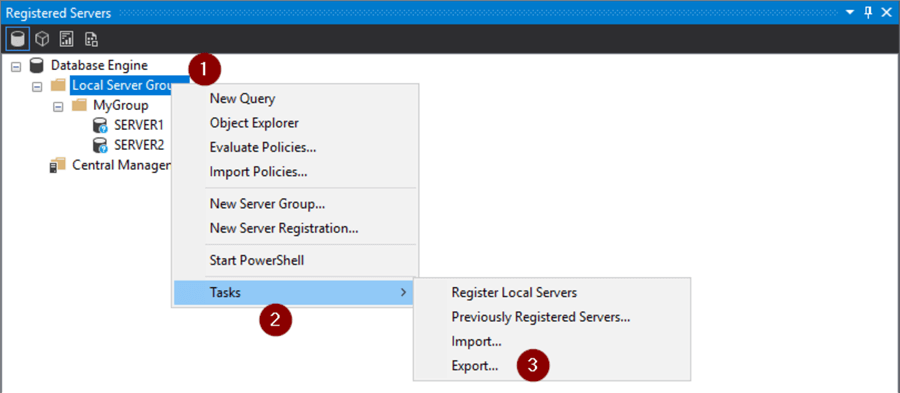
- Ellipse (…)
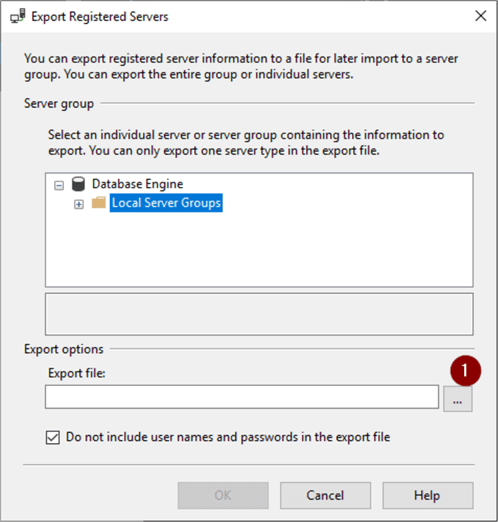
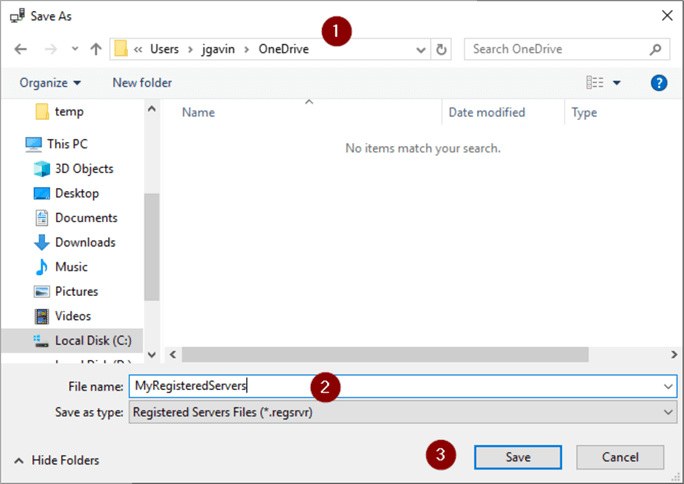
- Choose folder to export to (I chose OneDrive just so it's backed up)
- Name file
- Save
- OK
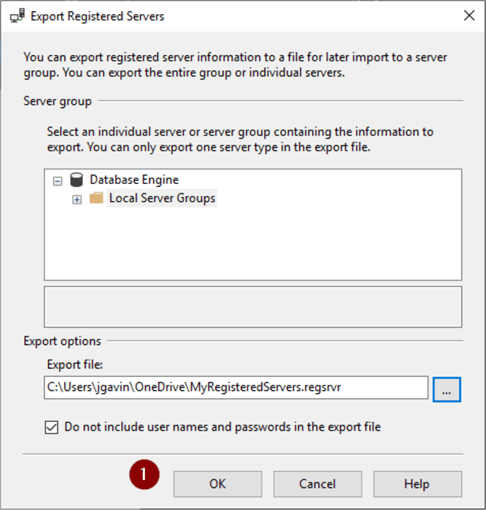
Note: "Do not include user names and passwords in the export file" is enabled by default and refers to SQL Authentication logins and passwords. Unchecking the box will save the login and password with the password encrypted. However, anyone who could import the file would have access with the saved credentials.
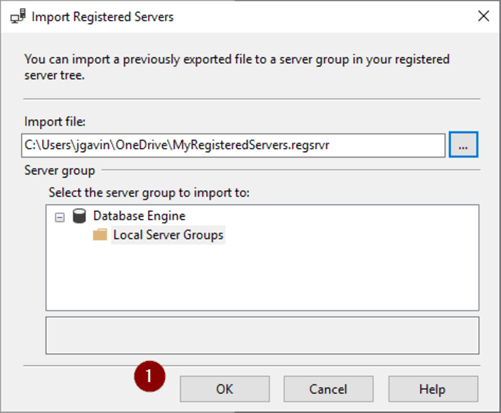
Import Registered Servers
To simulate reinstalling SSMS after a failure or to move migrate the Registers Servers to another machine, I've deleted the group and here we see it's gone.
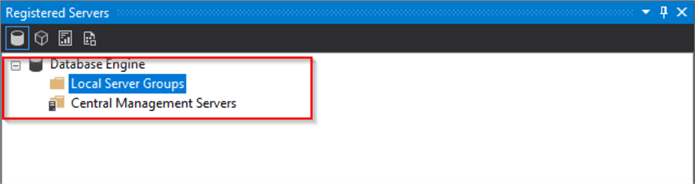
To restore
- Right click on the top group
- Tasks
- Import…
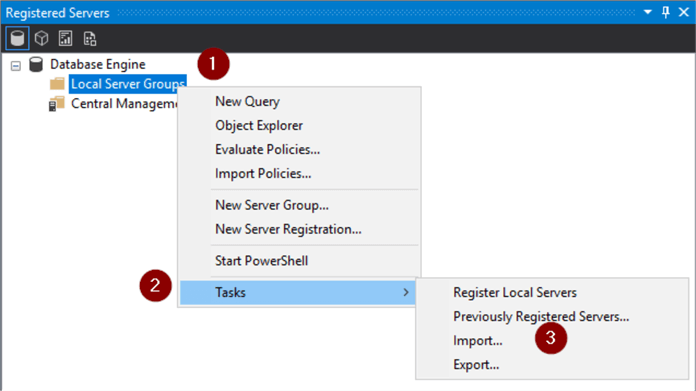
- Ellipse(…)
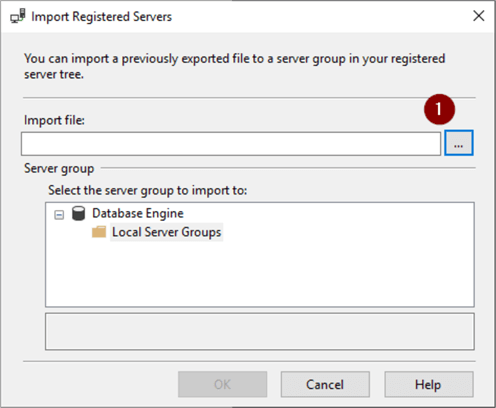
- Navigate to folder
- Select .regsrvr file to import
- Open
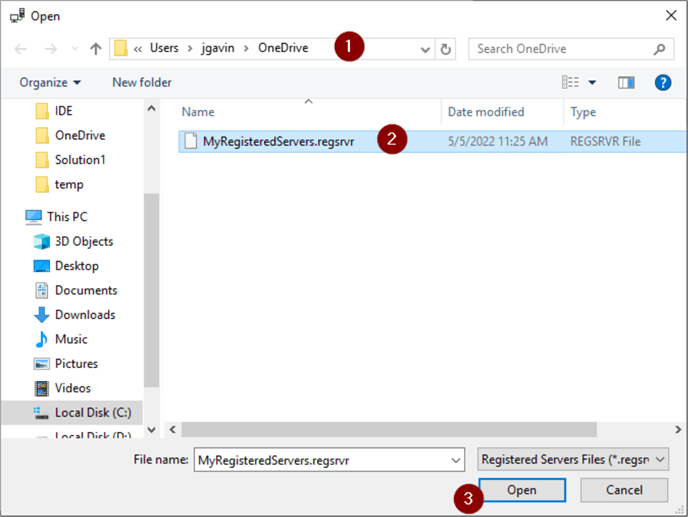
- OK
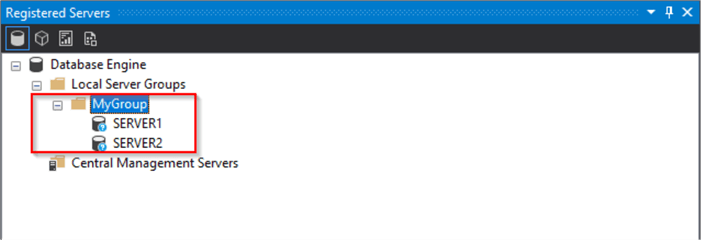
And your Groups and Servers are back.
Next Steps
- We've seen how to work with the list of server names in the Server name dropdown in the Connect to Server box and how to export and import a list of Registered Servers in SSMS.
- This link will bring you to an extensive list of SSMS Tips: SQL Server Management Studio Tips
About the author
 Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events.
Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2022-06-15






