By: Rajendra Gupta | Updated: 2023-07-26 | Comments | Related: > Tools
Problem
In the previous tip, Overview of the Go-SqlCmd command line tool, we explored the features of the new Go-SqlCmd (preview) tool, its Windows installation, and ways to connect to SQL Server. The Go-SqlCmd provides additional features for deploying and using the containers with great flexibility which we will explore in this tip.
Solution
Docker provides a standard for developers to deploy applications without environmental dependencies. It gives the flexibility to install a package to run the application. Therefore, deploying and testing code quickly without preparing an environment is beneficial. For example, to deploy SQL Server, you need to prepare the VM and run the SQL Server installation. This provides the following benefits:
- Quick deployments
- Resources scalability
- Portability
- Efficient Resource Utilization
The Go-SqlCmd tool enables you to deploy SQL Server using containers quickly. You can create multiple container environments, switch between them, and create a container with a database.
Install Go-SqlCmd on Ubuntu
Before moving further, let's install the Go-SqlCmd tool on Ubuntu.
Update the package index:
#mssqltips.com Sudo apt-get update

Install the CA certificates that allow apt to use the repository over HTTPS:
#mssqltips.com Sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg

Add Docker's official GPG key:
#mssqltips.com sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg

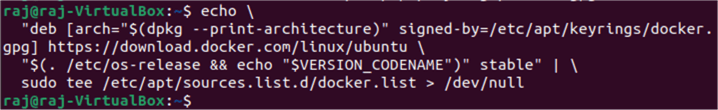
Setup the Docker repository on Ubuntu:
#mssqltips.com echo "deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu "$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Update the apt repository and install the Docker container:
#mssqltips.com sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin


Test the installation by running the hello-world docker container. Its output "Hello from Docker!" indicates that the docker installation works correctly.

Install Go-SqlCmd on Ubuntu
In the previous tip, we installed the Go-Sqlcmd on Windows. For this article, we will use the Ubuntu Linux version. However, you can use the Windows version as well.
Launch the terminal in Ubuntu and import the public repository GPG keys.
#mssqltips.com curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -

We are using Ubuntu 20.04 version. Therefore, add the Microsoft repository with the following code.
#mssqltips.com add-apt-repository "$(wget -qO- https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/20.04/prod.list)"

Update the apt repository:
#mssqltips.com Sudo apt-get update

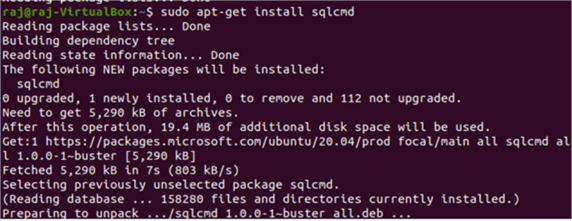
Install Go-SqlCmd with apt utility:
#mssqltips.com apt-get install sqlcmd
Create a Container Using the Go-SqlCmd
The Go-SqlCmd can quickly create a SQL Server container with or without the user database. The requirement here is that you should have Docker or Podman container environments available. We already installed Docker in this tip.
Run the command below to create a mssql container with the latest SQL version. The --accept-eula specifies that you accept the end user license agreement.
#mssqltips.com sqlcmd create mssql --accept-eula
If there is an access issue, you get the below error.

You can run the command using the sudo access as shown below. The command returns the following comments:
- It starts downloading the latest SQL Server release from the Microsoft registry mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:latest
- It disables the SA account and creates the user root for connection on port 1433.
- It gives specific examples of working with the SQL Server container using Go-SqlCmd.

To connect to the deployed container and run a query, use the following syntax:
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd query "SELECT @@VERSION"
As shown below, the Go-SqlCmd deployed SQL Server 2022 RTM-CU4 16.0.4035.4 Developer Edition on Ubuntu 20.04

As shown below, the container has no user databases. It has master, model, msdb, and tempdb system databases.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd query "SELECT Name from sys.databases"

You can start an interactive session with Go-Sqlcmd to execute the queries similar to using SqlCmd.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd query

Create Docker Container with the AdventureWorksLT Database
Above, we deployed a SQL Server container without a user database. The Go-SqlCmd provides functionality to restore a database while creating the container.
The following command creates the SQL Server container and restores the database using the backup file available on https://aka.ms/AdventureWorksLT.bak.
#mssqltips.com sqlcmd create mssql --accept-eula --using https://aka.ms/AdventureWorksLT.bak
The command output shows:
- It downloaded the AdventureWorksLT.bak from the specified URL
- It restores the database on the newly created container.

You can get the database list and verify that AdventureWorksLT is available in the SQL Server container.

Working with Contexts in Go-SqlCmd Containers
You can implement multiple containers with SQL instances using the Go-SqlCmd. The query you execute using SqlCmd runs under a specific container context.
For example, the below code lists all contexts available in the local machine. For example, two SQL instance containers are running on the test setup. These contexts are mssql and mssql2.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd config get-contexts

You should always check the context where you run the query in case there are multiple container contexts. To check the current context, run the following code. As shown below, my current context is mssql2.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd config current-context

You can switch the contexts easily with Go-SqlCmd. The following code switches the user context from mssql2 to mssql.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd config use mssql
As shown below, the code displays a message: Switched to context "mssql".

If you list the containers in the VM, you will find individual contexts.
#mssqltips.com Docker container ls

How do we delete the contexts not in use? First, list all the contexts available, as shown below.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd config get-contexts

You get different examples of deleting the current contexts using Go-Sqlcmd with the following command.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd delete mssql

Run the command sqlcmd delete to uninstall the
current context. It verifies the database files, removes contexts, and stops the
Docker image.

Alternatively, you can remove a specific context using the
delete-context command. For example, the below command
deletes the mssql2 context.
#mssqltips.com Sqlcmd config delete-context mssql2
Next Steps
- Go through the Go-SqlCmd documentation on Microsoft Docs.
- The Go-SqlCmd is in the preview phase and might change significantly over time. Keep an eye on the documentation.
- Explore existing tips on SQLCMD.
About the author
 Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.
Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2023-07-26






