By: Rajendra Gupta | Updated: 2023-11-07 | Comments | Related: > Amazon AWS
Problem
Previous tips have explored how Amazon Athena can help interact with S3 bucket data using standard SQL queries. Various Amazon services generate the logs in text or JSON format. Similarly, you need to go through the text-based records to audit the AWS account. This tip covers using Amazon Athena to query the Amazon CloudTrail logs for auditing your AWS account.
Solution
Amazon CloudTrail service helps to audit the AWS account by recording the user, role, or service level events. It captures the events from the AWS management console, command line interface (CLI), APIs, or AWS SDKs. These events can help perform audits, governance, and compliance. AWS automatically enables the CloudTrain once the AWS account is created.
The AWS CloudTrail records events in the following ways:
- Event History: Users can view the past 90 days of recorded management events in the AWS region using the Event History. To view the event history, navigate to the CloudTrail Console and Event History page. You can search for the specific event as well. AWS does not charge for viewing events from the Event history.
- CloudTrail Lake: CloudTrail Lake is useful for audit and security purposes. It is a managed data lake that captures and converts the events in a columnar format for faster retrieval and analysis. This columnar storage format is Apache ORC standard. You can view data for up to seven years using the CloudTrail lake. This service has a fee, go to AWS CloudTrail pricing for more details.
- Trails: S3 storage can be used to store AWS events. Optionally, you can also deliver these events to Amazon CloudWatch and EventBridge. The benefit of trails is that you can configure Amazon Athena and query the logs using the standard SQLs. Delivery of one ongoing event to the AWS S3 bucket is free. You need to pay for the S3 bucket standard storage charges.
This article will configure the trails to store events into the S3 bucket and query using Amazon Athena.
Create a Trail for the AWS Account
Once you sign in to the AWS Management Console, go to Services and launch the CloudTrail console.
In the AWS CloudTrail console, click Create a trail.

In the trails configuration page, enter the trail name. By default, AWS creates the S3 bucket that will store the events. As shown below, it creates the S3 bucket and folder aws-cloudtrail-logs-147081669821-91ab9629 for this demo instance.
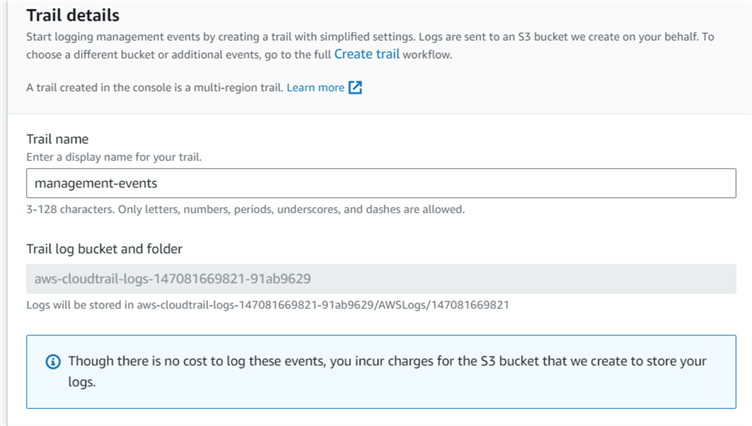
We can use advanced event selectors for creating a trail with custom events and an S3 bucket. Click on Create trail to use the advanced event selectors.
Create a trail with an auto-created S3 bucket and default logging management events. As shown below, there is a trail "management-events." Trails created from the management console use the multi-region trails.
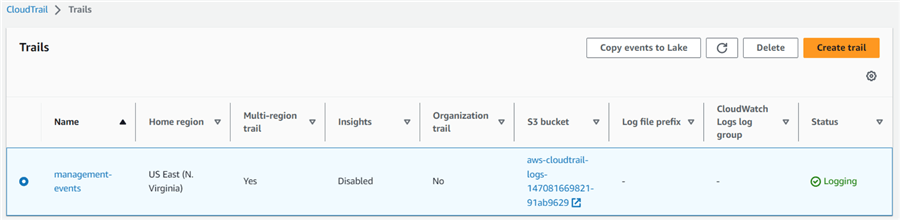
Click on the S3 bucket for a CloudTrail folder that records all audit events.
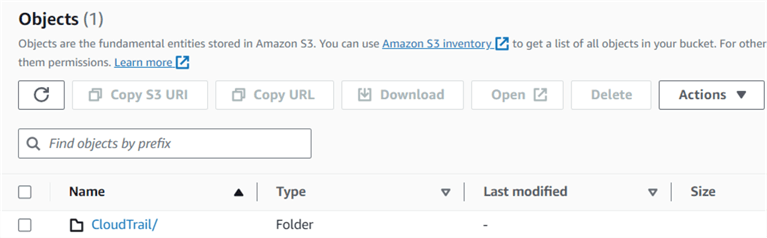
It will create subfolders inside the CloudTrail for the region and log date. For example, for this demo, you can see folders Amazon S3 > Buckets > aws-cloudtrail-logs-147081669821-91ab9629 > AWSLogs/ > 147081669821/ > CloudTrail/ > us-east-1/ > 2023/ > 09/ > 26/
The logs are uploaded in gz compression format, as shown below.
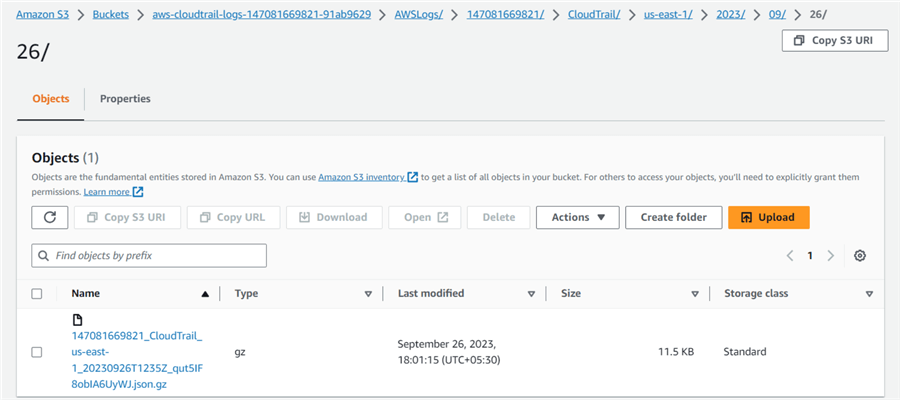
Create an Amazon Athena Table for CloudTrail
Click on the Event history tab in the CloudTrail console to view and filter all the events.
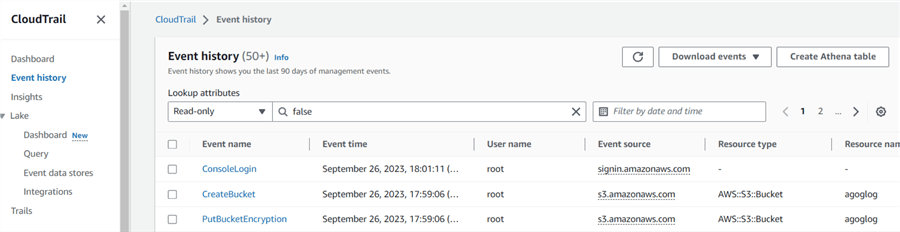
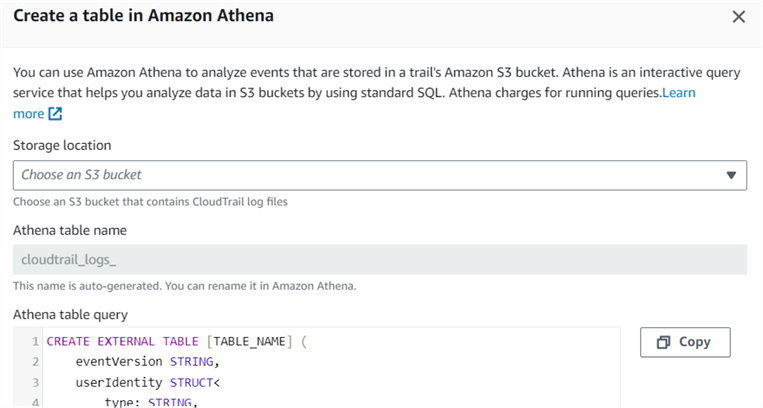
On the Event history page, click the Create Athena table option. It gives you a query to create the Athena table.
You can choose the S3 bucket name from the drop-down. By default, the table name is the same as your S3 bucket name. For example, my S3 bucket and Athena table name is cloudtrail_logs_aws_cloudtrail_logs_147081669821_91ab9629.
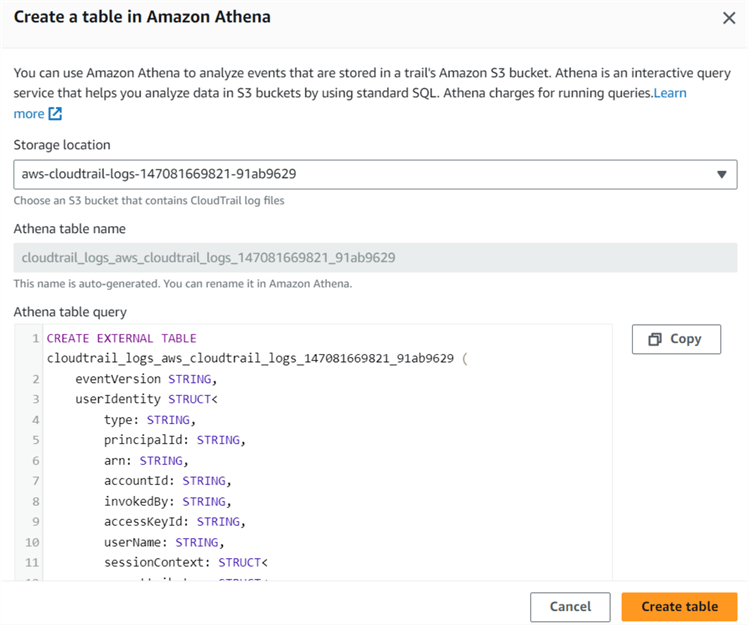
Click Create table, and it creates the table in Amazon Athena.

You can view this table by navigating to the Athena service or clicking the table name, redirecting you to launch the query editor.

Athena allows you to query your data using Trino SQL or PySpark and Spark SQL. For this demo, choose Query your data with Trino SQL and click Launch query editor.
As shown below, it creates the table in the default database.
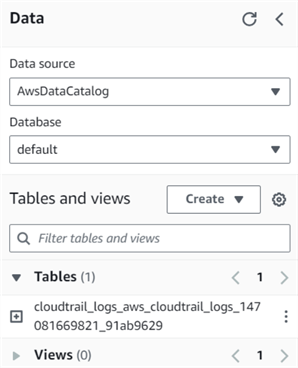
Query CloudTrail Data Using Amazon Athena Query
Before we run queries in Amazon Athena, let's perform the following task to generate some events.
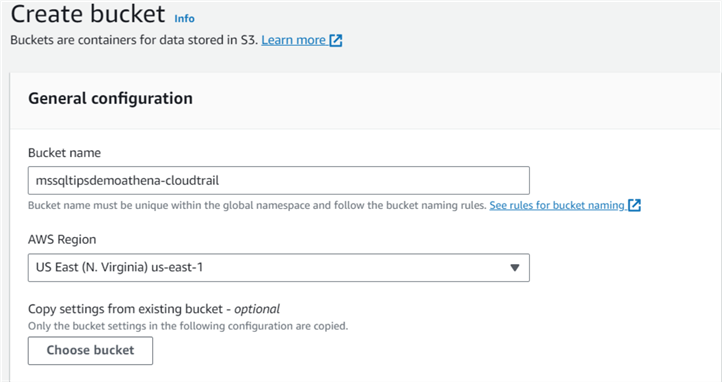
Task 1
Create a S3 bucket named mssqltipsdemoathena-cloudtrail.
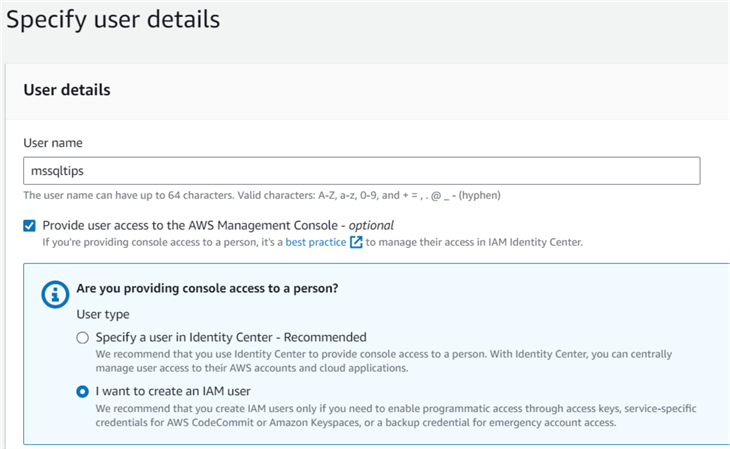
Task 2
Create an IAM User - mssqltips and provide user access to the AWS management console.
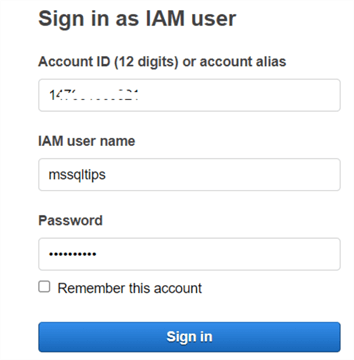
Task 3
Once the user is created, sign in using IAM credentials.
Task 4
After signing in from IAM credentials, delete the S3 bucket named mymssqlbucket.
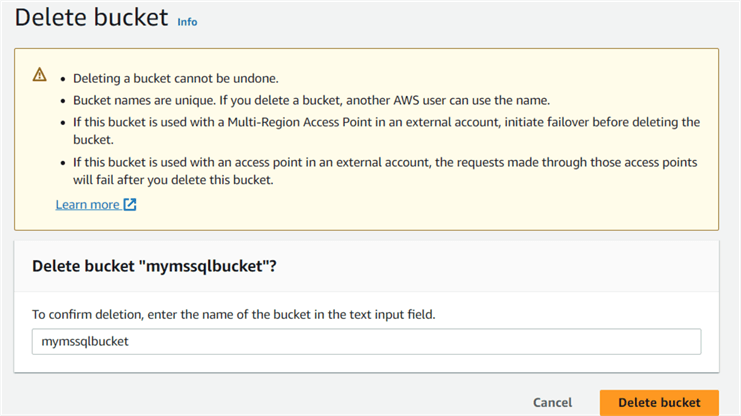
Let's query the Amazon Athena table that retrieves data from the Amazon CloudTrail.
Query 1: Get All Records from the CloudTrail
You can use the query below to get all records from the CloudTrail:
Select * from cloudtrail_logs_aws_cloudtrail_logs_147081669821_91ab9629
However, be careful while retrieving all records from CloudTrail, as you might need to pay a higher price for running an Amazon Athena query depending upon the data scanned.
Query 2: Get Events for S3 Bucket Creation
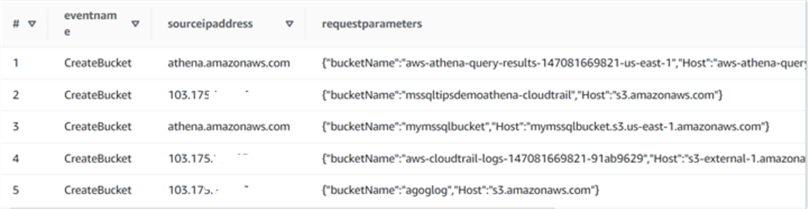
In this query, we want to see all events where an S3 bucket was created. You can get the source IP address requested parameters for the S3 bucket, such as the bucket name region.
Select eventname, sourceipaddress, requestparameters from cloudtrail_logs_aws_cloudtrail_logs_147081669821_91ab9629 where eventName = 'CreateBucket';
As you can see, we have five records of the CreateBucket event in the S3 bucket. Before running the query, we created a bucket -mssqltipsdemoathena-cloudtrail. You can see the entry for that bucket as row number 2.
Query 3: Get Events for S3 Bucket Deletion
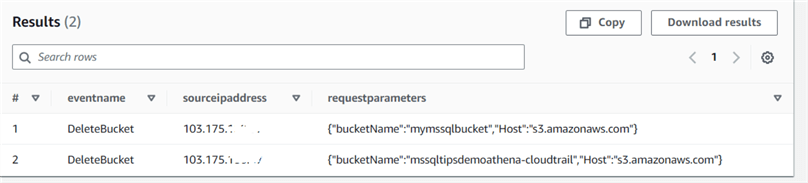
Suppose someone deleted the S3 bucket in your AWS account. You can use CloudTrail and Athena to query the deletebucket events and get all relevant records.
Select eventname, sourceipaddress, requestparameters from cloudtrail_logs_aws_cloudtrail_logs_147081669821_91ab9629 where eventName = 'DeleteBucket';
You can see two delete bucket events in my CloudTrail for mymssqlbucket and mssqldemoathena-cloudtrail.
Query 4: Find All Users Who Signed into the Console
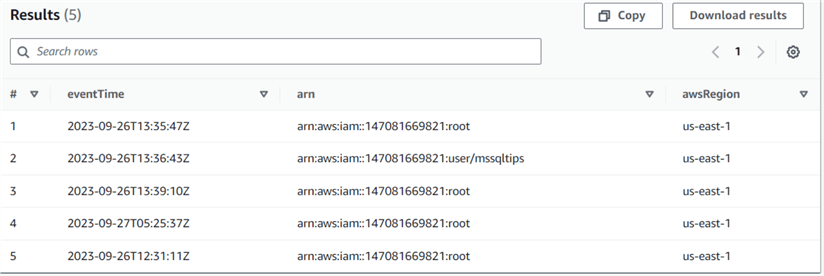
Suppose you want a list of users who have signed into the AWS Web Console. For this purpose, you can filter events for the event named ConsoleLogin.
SELECT eventTime, useridentity.arn, awsRegion FROM cloudtrail_logs_aws_cloudtrail_logs_147081669821_91ab9629 where eventName = 'ConsoleLogin';
Next Steps
- Read AWS Athena documentation on the AWS blog - https://aws.amazon.com/athena/
- Read existing AWS tips on MSSQLTips.
About the author
 Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.
Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2023-11-07






