By: Joe Gavin | Updated: 2024-05-28 | Comments (1) | Related: > Functions System
Problem
A common task while working with data in Microsoft SQL Server is converting from one data type to another. Most often, it's done to change the way data is presented, but sometimes it is needed to make sure the right data types are being used for comparisons, joins, or sorting.
The SQL CONVERT function, which has long been part of the SQL language, and as the name implies, can be used to convert a value of one data type into a specified data type with optional formatting attributes. CONVERT gives you the ability to format, whereas the ISO Compliant CAST function does not.
Solution
We'll look at several examples of using the SQL CONVERT function to convert and optionally format date, datetime, string, and integer data types.
Here are some reasons you might use the CONVERT function:
- Display dates in a different format
- Display numbers in a different format
- Convert integers or dates to strings to concatenate with text data
- Change the data type for sorting purposes
- Align mismatched data types for comparisons or joins
In theory, the best solution is to always make sure you use the correct data type when storing data in the SQL database. Sometimes this was not done when a table was created, so the CONVERT function can be useful to change data types. Also, note that when using a function, like CONVERT, in the WHERE clause or for joining tales, SQL Server will need to perform the function on all of the data, so it negates the benefits of indexing and could impact performance. If you are solely using this for SELECTing data and changing what the output looks like for a column, the CONVERT function is pretty fast for SQL queries or stored procedures.
The following SQL Server CONVERT examples were run on SQL Server 2022 Developer Edition.
Basic CONVERT Syntax
The SQL Server CONVERT command can take three parameters:
- data_type - the target data type
- expression - what is being converted
- style - (optional) - this is used for different data formatting options (see list of styles at end of the article)
CONVERT(data_type(length), expression, style)
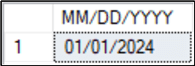
SQL CONVERT mm/dd/yyyy
This example creates a variable called @Date of datatype DATE, which is set to equal '2024-01-01'.
To display it in the form mm/dd/yyyy as 01/01/2024, we CONVERT the value in @Date to a VARCHAR(10) with a style of 101 to get the desired output.
DECLARE @Date DATE = '2024-01-01' -- date value SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@Date,101) AS [MM/DD/YYYY]; GO
SQL CONVERT Date to mm/dd/yy
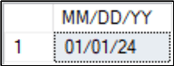
The following example is the same as above, except it uses a style of 1 to convert the default format yyyy-mm-dd to mm/dd/yy.
DECLARE @Date DATE = '2024-01-01' -- current date example SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@Date,1) AS [MM/DD/YY]; GO
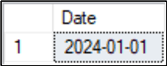
SQL CONVERT Datetime to Date
The style number is optional. This example removes the time by converting DATETIME to DATE and retaining the default yyyy-mm-dd format.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00:00.000' -- alternatively GETDATE() SELECT CONVERT (DATE,@DateAndTime) AS [Date]; GO
SQL CONVERT String to Date
This will convert the string '2024-01-01' to type DATE. There is no style parameter specified, so the default format, yyyy-mm-dd, is retained.
DECLARE @Date VARCHAR(10) = '2024-01-01' -- character string SELECT CONVERT (DATE, @Date) AS [Date]; GO

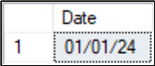
SQL CONVERT Date Format
Here, we're converting DATETIME to DATE and using style number 1 to display it in the mm/dd/yy format.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00:00.000' SELECT CONVERT (VARCHAR,@DateAndTime,1) AS [Date]; GO
SQL CONVERT Datetime
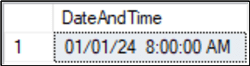
Style 22 is used to change the default 'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss' to a more easily read U.S. date format with a 12-hour clock in the form mm/dd/yy hh:mm am/pm.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00:000' SELECT CONVERT (VARCHAR,@DateAndTime,22) AS [DateAndTime]; GO
SQL CONVERT to String
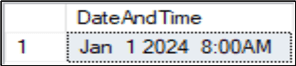
This converts DATETIME to a string of type VARCHAR(25) in the format mon dd yyyy hh:ss am/pm.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(25), @DateAndTime) AS [DateAndTime]; GO
Convert as Decimal in SQL
We can convert more than dates and times with CONVERT.
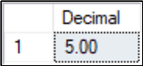
Here, we'll convert the integer 5 to a decimal value with a precision of 3 (total digits) and carry it out to two decimal places (x.xx).
DECLARE @Num INT = 5 SELECT CONVERT(DECIMAL(3,2), @Num) AS [Decimal]; GO
Convert the Date Format in SQL
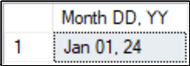
This query will convert the default format yyyy-mm-dd to mon dd, yy using style 7.
DECLARE @Date DATE = '2024-01-01' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR,@Date,7) AS [Month DD, YY]; GO
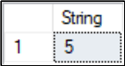
SQL CONVERT INT to String
This converts the integer 5 to a string.
DECLARE @Num INT = 5 SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), @Num) as [String]; GO
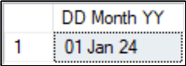
Convert Date Format in SQL
Here, we can convert the default date format to dd mon yy with style 6.
DECLARE @Date DATE = '2024-01-01' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR,@Date,6) AS [DD Mon YY]; GO
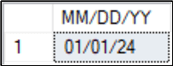
Convert Datetime in SQL Server to MM/DD/YY
Convert a datetime value to MM/DD/YY in SQL Server.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00:00.000' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @DateAndTime, 1) AS [MM/DD/YY]; GO
Convert Integer to String in SQL
Below is an example to convert an integer to a string.
DECLARE @MyInt INT = 1 SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @MyInt) AS [Varchar]; GO

Convert SQL String to INT
We saw how to convert an integer to a string. Now, we'll convert a string to an integer.
DECLARE @MyString VARCHAR(10) = '123' SELECT CONVERT(INT, @MyString) AS [Integer]; GO

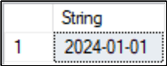
SQL CONVERT Date to String
Here, the DATE type variable value is converted to a string.
DECLARE @Date DATE = '2024-01-01' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Date) AS [String]; GO
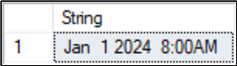
SQL CONVERT Datetime to String
We can do the same for a DATETIME variable type. The output is in the format month dd yyyy hh:mm am/pm.
DECLARE @DateAndTime DATETIME = '2024-01-01 08:00:00.000' SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(30), @DateAndTime) AS [String]; GO
Different Date Formats using CONVERT in SQL
A common use of the CONVERT function is to convert dates to different formats using a style code.
The following chart shows the style codes and descriptions that can be used to reformat date and time output.
| Style_Code | Style_Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Default |
| 1 | mon dd yyyy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 2 | mm/dd/yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 3 | dd/mm/yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 4 | dd.mm.yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 5 | dd-mm-yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 6 | dd mon yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 7 | Mon dd, yy hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 8 | hh:miAM (or PM) |
| 9 | mon dd yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM (or PM) |
| 10 | mm-dd-yy |
| 11 | yyyy/mm/dd |
| 12 | yymmdd |
| 13 | dd mon yyyy hh:mm:ss:mmm |
| 14 | hh:mi:ss:mmm (24h) |
| 20 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss (24h) |
| 21 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss.mmm (24h) |
| 22 | mm/dd/yy hh:mi:ss AM (or PM) |
| 23 | yyyy/mm/dd hh:mi:ss.mmm (24h) |
| 24 | hh:mi:ss (24h) |
| 25 | mon dd yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM |
| 100 | mon dd yyyy hh:miAM (or PM) with century |
| 101 | mm/dd/yyyy |
| 102 | yyyy.mm.dd |
| 103 | dd/mm/yyyy |
| 104 | dd.mm.yyyy |
| 105 | dd-mm-yyyy |
| 106 | dd mon yyyy |
| 107 | Mon dd, yyyy |
| 108 | hh:mi:ss |
| 109 | mon dd yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM (or PM) |
| 110 | mm-dd-yyyy |
| 111 | yyyy/mm/dd |
| 112 | yyyymmdd |
| 113 | dd mon yyyy hh:mm:ss:mmm |
| 114 | hh:mi:ss:mmm (24h) |
| 120 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss (24h) |
| 121 | yyyy-mm-dd hh:mi:ss.mmm (24h) |
| 126 | yyyy-mm-ddThh:mi:ss.mmm (no spaces) |
| 130 | dd mon yyyy hh:mi:ss:mmmAM (or PM) (HH:mi:ss:mmmAM for 24h format) |
Next Steps
So far, we've seen how to convert date data types (date, smalldatetime, etc.), and optionally convert the output format, as well as convert integers, bigint, decimals and numeric data types. The following are links to more tips and tutorials on SQL CONVERT primarily used for date functions:
- SQL Date Format Options with SQL CONVERT Function
- Convert Problematic Data in SQL Server
- SQL Convert Date to YYYYMMDD
- Different Ways to Convert a SQL INT Value Into a String Value
- Convert Implicit and the Related Performance Issues with SQL Server
- New Data Type Conversion Functions in SQL Server 2012
- Convert SQL Server DateTime Data Type to DateTimeOffset Data Type
- SQL Server Function to Convert Integer Date to Datetime Format
- Build a Cheat Sheet for SQL Server Date and Time Formats
- Handle Conversion Between Time Zones in SQL Server - Part 1
- Handle Conversion Between Time Zones in SQL Server - Part 2
- Handle Conversion Between Time Zones in SQL Server - Part 3
About the author
 Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events.
Joe Gavin is from the Greater Boston area. He started working with SQL Server and Sybase in 1998 in the financial services industry and has been a SQL Server Database Administrator for a dairy cooperative since 2011. He graduated from Northeastern University in Boston with a Bachelor of Science in Engineering Technology (BSET) degree in Computer Technology. Joe has spoken at the Boston and Providence SQL Saturday events. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2024-05-28






