By: Sebastiao Pereira | Updated: 2024-06-04 | Comments (2) | Related: > Stored Procedures
Problem
When writing a Microsoft SQL Server store procedure, it is normal to have multiple stored procedures for each CRUD operation (Create, Read, Update, Delete) – SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE. However, is it possible to simplify this Transact-SQL logic into a single SQL Server stored procedure and include tracking changes? Can you please demonstrate a possible solution?
Solution
Let's create an example of a simple table to store a list of people in a SQL database with T-SQL code run in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
The first database table will store the data. As you can see, the only column that gets updated is the PersonName.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Persons]( [PersonId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [PersonName] [nvarchar](10) NOT NULL, [ModifiedDate] [datetime] NULL, [ModifiedBy] [sysname] NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GO
The second database table will track the changes:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[PersonsLog]( [ControlId] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [PersonId] [int] NULL, [PersonName] [nvarchar](10) NULL, [ModifiedDate] [datetime] NULL, [ModifiedBy] [sysname] NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GO
Rules to Call Stored Procedure
The main table PERSONS has a key column [PersonId], so if we want to:
- INSERT (Create Operation): Use 0 (zero) to indicate that it is new and pass the PersonName.
- SELECT (Read Operation): Use the [PersonId] number and leave the [PersonName] null.
- UPDATE (Update Operation): Use the [PersonId] number and pass the PersonName change.
- DELETE (Delete Operation): Use the [PersonId] number but pass as a negative number.
- TRACK CHANGES: This is done inside the stored procedure for the INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE.
This stored procedure takes 2 input parameters:
- @PersonId
- @PersonName
SQL Stored Procedure Syntax
USE [MsSqlTips]
GO
/****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[uspPerson] Script Date: 08/05/2024 14:31:01 ******/
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
-- =============================================
-- Author: SCP
-- Create date: 202400508
-- Description: General Stored Procedure
-- =============================================
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[uspPerson]
@PersonId int, -- input parameters
@PersonName nvarchar(70) -- variable name and data type
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
IF (@PersonName IS NULL OR LEN(@PersonName) = 0) AND (@PersonId > 0)
SELECT [PersonId]
,[PersonName]
,[ModifiedDate]
,[ModifiedBy]
FROM [MsSqlTips].[dbo].[Persons]
WHERE [PersonId] = @PersonId;
ELSE
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
DECLARE @ModifiedDate datetime = GETDATE();
DECLARE @ModifiedBy sysname = CURRENT_USER;
-- Updating a record
IF @PersonId > 0
UPDATE [dbo].[Persons]
SET [PersonName] = @PersonName
,[ModifiedDate] = @ModifiedDate
,[ModifiedBy] = @ModifiedBy
WHERE [PersonId] = @PersonId;
-- Inserting a record
IF (@PersonId = 0 AND
(@PersonName IS NOT NULL AND LEN(@PersonName) > 0))
BEGIN
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Persons]
([PersonName]
,[ModifiedDate]
,[ModifiedBy])
VALUES (@PersonName
,@ModifiedDate
,@ModifiedBy);
SET @PersonId = SCOPE_IDENTITY();
END
-- Deleting a record
IF @PersonId < 0
DELETE FROM [dbo].[Persons]
WHERE [PersonId] = ABS(@PersonId);
-- Tracking the changes
INSERT INTO [dbo].[PersonsLog]
([PersonId]
,[PersonName]
,[ModifiedDate]
,[ModifiedBy])
VALUES(@PersonId
,@PersonName
,@ModifiedDate
,@ModifiedBy)
COMMIT TRANSACTION;
-- Returning the changed record
SELECT [PersonId]
,[PersonName]
,[ModifiedDate]
,[ModifiedBy]
FROM [MsSqlTips].[dbo].[Persons]
WHERE [PersonId] = @PersonId;
RETURN;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
IF @@TRANCOUNT > 0
BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION;
END
-- Print error information.
PRINT 'Error: ' + CONVERT(varchar(50), ERROR_NUMBER()) +
', Severity: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_SEVERITY()) +
', State: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_STATE()) +
', Procedure: ' + ISNULL(ERROR_PROCEDURE(), '-') +
', Line: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), ERROR_LINE()) +
', User: ' + CONVERT(varchar(5), @ModifiedBy);
PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH;
END
END
SQL Statements when Working with the Stored Procedure
Inserting
Inserting a record for a person named John:
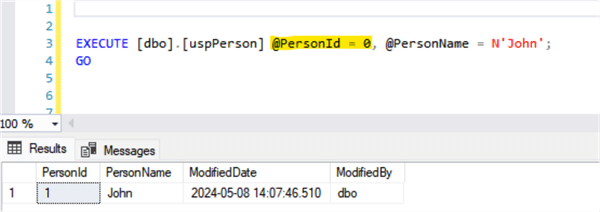
Inserting a record for a person named Mary:
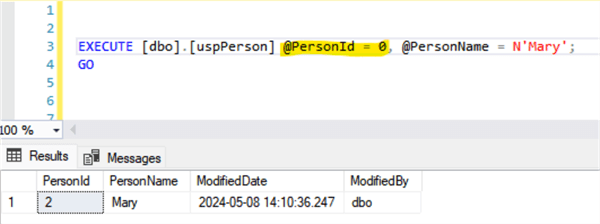
Select Statement
Select the record with a PersonId = 1:
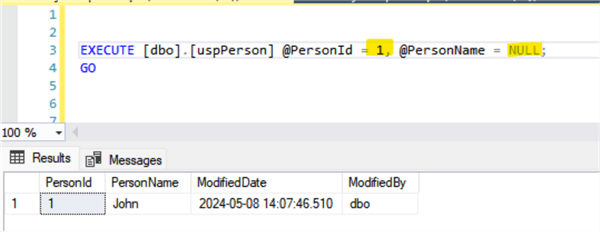
Updating
Changing the record for PersonId = 2 from "Mary" to "Mary Jane":
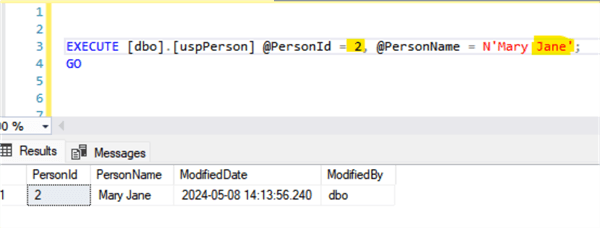
Deleting
Delete the record with PersonId = 1. For this example, any value for PersonName could have been used since the delete just needs the PersonId value.
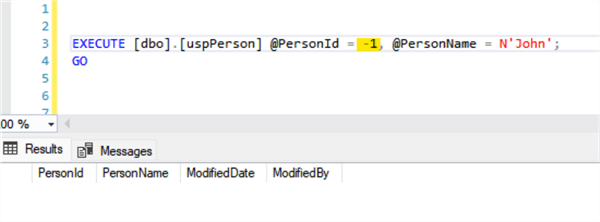
Error Handling
If we try to insert a name with more than 10 characters, the store procedure shows the message below:
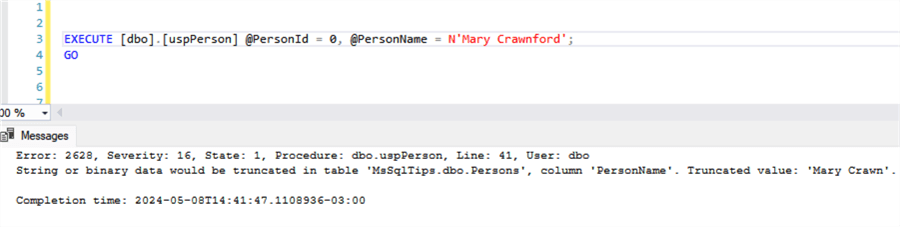
Tracking Changes
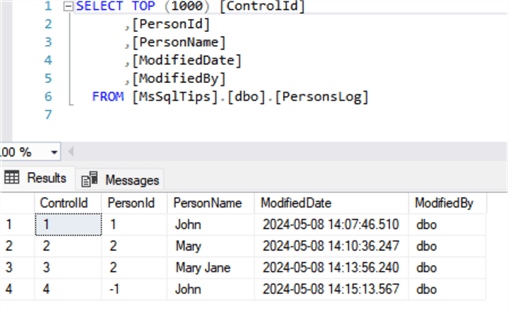
When listing the content of the Table [PersonsLog], we can check for all the of modifications completed in the main [Persons] table. Here is an explanation of the data:
- ControlId 1 and 2 below are inserted records
- ControlId 3 was the name change for the PersonId = 2
- ControlId 4 was a deletion of the PersonId = 1
Summary
As you can see, this is a way to create one stored procedure to handle multiple tasks. This can definitely be made more robust and add additional code for handling record updates and also for the logging table, but hopefully this gives you an idea of how you might accomplish something like this.
Next Steps
- Check out the following MSSQLTips.com resources:
About the author
 Sebastiao Pereira has over 38 years of healthcare experience, including software development expertise with databases.
Sebastiao Pereira has over 38 years of healthcare experience, including software development expertise with databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2024-06-04






