By: Greg Robidoux
Overview
The INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS view allows you to get information about all columns for all tables and views within a database. By default it will show you this information for every single table and view that is in the database.
Explanation
This view can be called from any of the databases in an instance of SQL Server and will return the results for the data within that particular database.
The columns that this view returns are as follows:
| Column name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TABLE_CATALOG | nvarchar(128) | Table qualifier. |
| TABLE_SCHEMA | nvarchar(128) | Name of schema that contains the table. |
| TABLE_NAME | nvarchar(128) | Table name. |
| COLUMN_NAME | nvarchar(128) | Column name. |
| ORDINAL_POSITION | int | Column identification number.
Note: In SQL Server 2005, these column IDs are consecutive numbers. |
| COLUMN_DEFAULT | nvarchar(4000) | Default value of the column. |
| IS_NULLABLE | varchar(3) | Nullability of the column. If this column allows for NULL, this column returns YES. Otherwise, NO is returned. |
| DATA_TYPE | nvarchar(128) | System-supplied data type. |
| CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH | int | Maximum length, in characters, for binary data, character data, or text and image data.
-1 for xml and large-value type data. Otherwise, NULL is returned. For more information, see Data Types (Transact-SQL). |
| CHARACTER_OCTET_LENGTH | int | Maximum length, in bytes, for binary data, character data, or text and image data.
-1 for xml and large-value type data. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| NUMERIC_PRECISION | tinyint | Precision of approximate numeric data, exact numeric data, integer data, or monetary data. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| NUMERIC_PRECISION_RADIX | smallint | Precision radix of approximate numeric data, exact numeric data, integer data, or monetary data. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| NUMERIC_SCALE | int | Scale of approximate numeric data, exact numeric data, integer data, or monetary data. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| DATETIME_PRECISION | smallint | Subtype code for datetime and SQL-92 interval data types. For other data types, NULL is returned. |
| CHARACTER_SET_CATALOG | nvarchar(128) | Returns master. This indicates the database in which the character set is located, if the column is character data or text data type. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| CHARACTER_SET_SCHEMA | nvarchar(128) | Always returns NULL. |
| CHARACTER_SET_NAME | nvarchar(128) | Returns the unique name for the character set if this column is character data or text data type. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| COLLATION_CATALOG | nvarchar(128) | Always returns NULL. |
| COLLATION_SCHEMA | nvarchar(128) | Always returns NULL. |
| COLLATION_NAME | nvarchar(128) | Returns the unique name for the collation if the column is character data or text data type. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| DOMAIN_CATALOG | nvarchar(128) | If the column is an alias data type, this column is the database name in which the user-defined data type was created. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| DOMAIN_SCHEMA | nvarchar(128) | If the column is a user-defined data type, this column returns the name of the schema of the user-defined data type. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
| DOMAIN_NAME | nvarchar(128) | If the column is a user-defined data type, this column is the name of the user-defined data type. Otherwise, NULL is returned. |
(Source: SQL Server 2005 Books Online)
Here is an example of data that was pulled from the AdventureWorks database. This data was pulled using this query:
| SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS |
To be able to show the output the results were broken into multiple pieces.
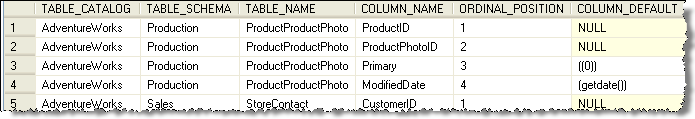
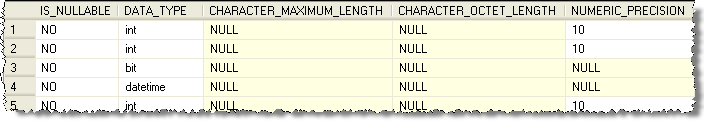
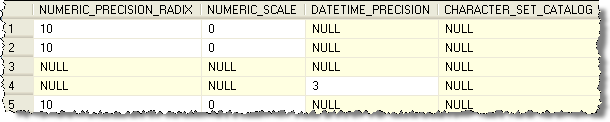
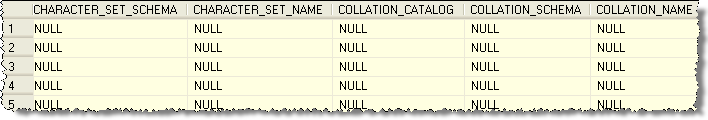
To query for just one table you can use a query like this:
| SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_NAME = 'Address' |
Last Update: 7/2/2009
