By: Daniel Calbimonte
The SYSDATETIME() function returns the server date time stamp using the datetime2 format. This function has a better precision than the GETDATE() or GETUTCDATE(). The data type returned by this function is datetime2(7).
Syntax
SYSDATETIME()
Parameters
- No parameters required
Simple SYSDATETIME Example
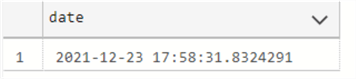
The following example will show the output for SYSDATETIME.
SELECT SYSDATETIME() as date
As you can see, there are 7 positions for nanoseconds (8324291).
Difference between GETDATE and SYSDATETIME
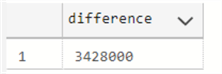
The following example shows the difference in nanoseconds between the GETDATE function and SYSDATETIME.
SELECT DATEDIFF(NANOSECOND, GETDATE(), SYSDATETIME()) as difference
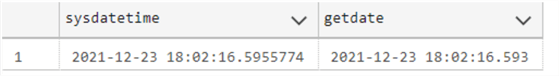
As you can see, the SYSDATETIME function is more precise.
SELECT DATEDIFF(NANOSECOND,GETDATE(),SYSDATETIME()) as difference
GETDATE has 3 positions for nanoseconds and SYSDATETIME has 7 positions.
How to set the SYSDATETIME in a custom format
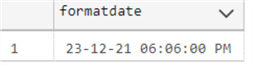
The following example shows the SYSDATETIME in the dd-MM-yyyy hh:mm:ss tt format.
SELECT FORMAT(SYSDATETIME(),'dd-MM-yy hh:mm:ss tt') as formatdate
How to set the SYSDATETIME in a different cultural format
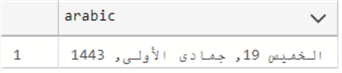
The following example will set the SYSDATETIME in Arabic date format.
SELECT FORMAT(SYSDATETIME(), 'dddd dd, MMMM, yyyy','AR-ar') as arabic
Use SYSDATETIME with Data from a Table
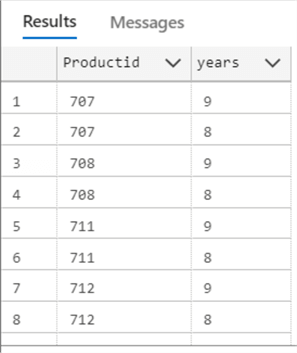
The following example will show the products with a StartDate between 8 and 9 years ago.
SELECT Productid, DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, SYSDATETIME()) as years FROM Production.ProductCostHistory WHERE DATEDIFF(YEAR, StartDate, SYSDATETIME()) BETWEEN 8 AND 9
Related Articles
- SQL CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
- SQL GETDATE
- SQL GETUTCDATE
- SQL DATEDIFF
- SQL YEAR
- Mimic timestamp behavior of other database platforms to store last modified date
- SQL Convert Date to YYYYMMDD
- SQL Server DIFFERENCE Function
Last Update: 1/5/2022
