By: Jugal Shah | Updated: 2011-10-24 | Comments (11) | Related: > Install and Uninstall
Problem
If you have a requirement to install multiple SQL Server instances with the same settings, you most likely want to do it without following the numerous manual installation steps. The below tip will guide you through how to install a SQL Server instance with less effort.
Solution
SQL Server Setup generates a configuration file named ConfigurationFile.ini, based upon the system default and run-time inputs. The ConfigurationFile.ini file is a text file which contains the set of parameters in name/value pairs along with descriptive comments. Many of the parameter names correspond to the screens and options which you see while installing SQL Server through the wizard.
You can then use the configuration file to install SQL Server with the same configuration instead of going through each of the installation screens.
SQL Server generates the Configurationfile.ini file on the Ready to Install step. If you missed the Configuration.ini file path during the installation, you can find the configuration file in the C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\100\Setup Bootstrap\Log folder. There will a subfolder based on a timestampof when you went through the SQL Server 2008 installation.
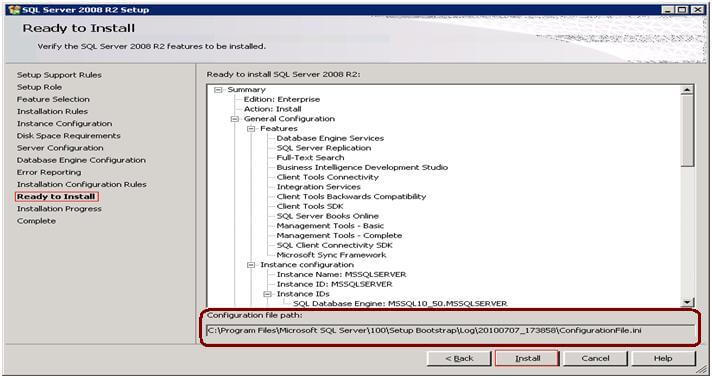
Sample ConfigurationFile.ini File
Here is a sample of what the configuration file looks like:
;SQLSERVER2008 Configuration File [SQLSERVER2008] ; Specify the Instance ID for the SQL Server features you have specified. SQL Server directory structure, registry structure, and service names will reflect the instance ID of the SQL Server instance. INSTANCEID="MSSQLSERVER" ; Specifies a Setup work flow, like INSTALL, UNINSTALL, or UPGRADE. This is a required parameter. ACTION="Install" ; Specifies features to install, uninstall, or upgrade. The list of top-level features include SQL, AS, RS, IS, and Tools. The SQL feature will install the database engine, replication, and full-text. The Tools feature will install Management Tools, Books online, Business Intelligence Development Studio, and other shared components. FEATURES=SQLENGINE,REPLICATION,FULLTEXT,CONN,IS,BC,SDK,SSMS,ADV_SSMS,OCS ; Displays the command line parameters usage HELP="False" ; Specifies that the detailed Setup log should be piped to the console. INDICATEPROGRESS="False" ; Setup will not display any user interface. QUIET="False" ; Setup will display progress only without any user interaction. QUIETSIMPLE="False" ; Specifies that Setup should install into WOW64. This command line argument is not supported on an IA64 or a 32-bit system. X86="False" ; Detailed help for command line argument ENU has not been defined yet. ENU="True" ; Parameter that controls the user interface behavior. Valid values are Normal for the full UI, and AutoAdvance for a implied UI. UIMODE="Normal" ; Specify if errors can be reported to Microsoft to improve future SQL Server releases. Specify 1 or True to enable and 0 or False to disable this feature. ERRORREPORTING="False" ; Specify the root installation directory for native shared components. INSTALLSHAREDDIR="D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server" ; Specify the root installation directory for the WOW64 shared components. INSTALLSHAREDWOWDIR="D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server" ; Specify the installation directory. INSTANCEDIR="D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server" ; Specify that SQL Server feature usage data can be collected and sent to Microsoft. Specify 1 or True to enable and 0 or False to disable this feature. SQMREPORTING="False" ; Specify a default or named instance. MSSQLSERVER is the default instance for non-Express editions and SQLExpress for Express editions. This parameter is required when installing the SQL Server Database Engine (SQL), Analysis Services (AS), or Reporting Services (RS). INSTANCENAME="MSSQLSERVER" ; Agent account name AGTSVCACCOUNT="NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE" ; Auto-start service after installation. AGTSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Automatic" ; Startup type for Integration Services. ISSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Automatic" ; Account for Integration Services: Domain\User or system account. ISSVCACCOUNT="NT AUTHORITY\NetworkService" ; Controls the service startup type setting after the service has been created. ASSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Automatic" ; The collation to be used by Analysis Services. ASCOLLATION="Latin1_General_CI_AS" ; The location for the Analysis Services data files. ASDATADIR="Data" ; The location for the Analysis Services log files. ASLOGDIR="Log" ; The location for the Analysis Services backup files. ASBACKUPDIR="Backup" ; The location for the Analysis Services temporary files. ASTEMPDIR="Temp" ; The location for the Analysis Services configuration files. ASCONFIGDIR="Config" ; Specifies whether or not the MSOLAP provider is allowed to run in process. ASPROVIDERMSOLAP="1" ; A port number used to connect to the SharePoint Central Administration web application. FARMADMINPORT="0" ; Startup type for the SQL Server service. SQLSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Automatic" ; Level to enable FILESTREAM feature at (0, 1, 2 or 3). FILESTREAMLEVEL="0" ; Set to "1" to enable RANU for SQL Server Express. ENABLERANU="False" ; Specifies a Windows collation or an SQL collation to use for the Database Engine. SQLCOLLATION="SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS" ; Account for SQL Server service: Domain\User or system account. SQLSVCACCOUNT="NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE" ; Windows account(s) to provision as SQL Server system administrators. SQLSYSADMINACCOUNTS="SQLDBPool\Jugal" ; The default is Windows Authentication. Use "SQL" for Mixed Mode Authentication. SECURITYMODE="SQL" ; The Database Engine root data directory. INSTALLSQLDATADIR="F:\" ; Default directory for the Database Engine user databases. SQLUSERDBDIR="F:\" ; Default directory for the Database Engine user database logs. SQLUSERDBLOGDIR="F:\" ; Directory for Database Engine TempDB files. SQLTEMPDBDIR="G:\" ; Provision current user as a Database Engine system administrator for SQL Server 2008 R2 Express. ADDCURRENTUSERASSQLADMIN="False" ; Specify 0 to disable or 1 to enable the TCP/IP protocol. TCPENABLED="1" ; Specify 0 to disable or 1 to enable the Named Pipes protocol. NPENABLED="0" ; Startup type for Browser Service. BROWSERSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Disabled" ; Specifies how the startup mode of the report server NT service. When ; Manual - Service startup is manual mode (default). ; Automatic - Service startup is automatic mode. ; Disabled - Service is disabled RSSVCSTARTUPTYPE="Automatic" ; Specifies which mode report server is installed in. ; Default value: "FilesOnly" RSINSTALLMODE="FilesOnlyMode" ; Add description of input argument FTSVCACCOUNT FTSVCACCOUNT="NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE"
Using the ConfigurationFile.ini
With the SQL Server 2008 installer, we can use the ConfigurationFile.ini file to install SQL Server using one of these methods:
- Using the Installer Wizard with options prefilled by the configuration file
- Using a fully automated and unattended installation from the command line
Installing Using Installer Wizard
Go to SQL Server Installation Center and click on the Advanced page. Click on Install based on configuration file, specify the location of the ConfigurationFile.ini file and the SQL Server setup.exe location. You can find setup.exe at the root level of the SQL Server installation media.
Like a normal installation you can see all the screens with the prefilled information and this gives you the advantage to review or make changes if needed.
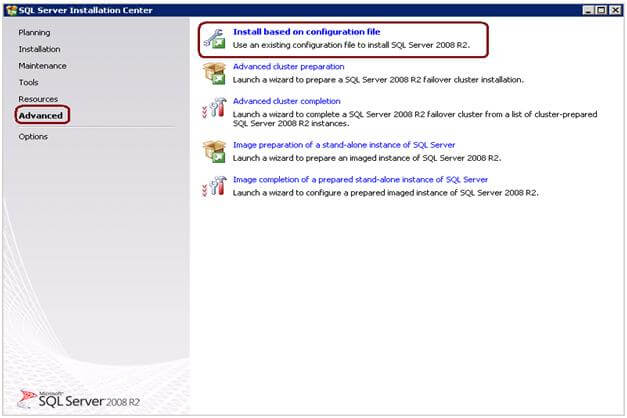
Installing Using Command Prompt
Go to the SQL Server installation media root from the command prompt and specify the ConfigurationFile.ini as a parameter as shown below.
Setup.exe /ConfigurationFile=ConfigurationFile.INI
You can override any of the values in the configuration file or add more values which are not specified in the configuration file by providing additional command line parameters to setup.exe as shown below.
Setup.exe /SQLSVCPASSWORD="password" /ASSVCPASSWORD="password" /AGTSVCPASSWORD="password" /ISSVCPASSWORD="password" /RSSVCPASSWORD="password" /SAPWD="password" /ConfigurationFile=ConfigurationFile.INI
You can also control the level of the installer interface while installing SQL Server from the command prompt. The installer interface level can be silent, basic or full interaction. You have to use the below switches for the installer interface level.
- /Q- specifies that setup runs in a quiet mode without any user interface. This is used for unattended installations.
- /QS - specifies that setup runs and shows progress through the UI, but does not accept any input or show any error messages.
Please note
- There is no configuration file template available on the installation media. To get the configuration file you have to run the SQL Server Installation wizard until you get to the Ready to Install page.
- Make sure you make a copy of the ConfigurationFile.inifile before modifying it
- Installer does not write passwords into the ConfigurationFile.inifile. You have to either specify the password through a parameter or you can specify during the installation screen prompt for the password.
- If you have chosen the authentication mode as Mixed Mode, you have to specify the SA password using the /SAPWDswitch.
- For any method of installation, you have to accept the software license terms agreement. For SQL Server 2008 R2 for a fully unattended installation you can specify it by using the /IACCEPTSQLSERVERLICENSETERMSswitch.
- Also, for SQL Server 2008 R2 you can use the /UIMODE switch instead of /Q or /QS switch.
Next Steps
- Generate a configuration file for the different kinds of installation (i.e. Client tools, Cluster and Standalone)
- Create a batch file for command prompt installation
- Check out MSDN http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms144259.aspx for more information about this topic
About the author
 Jugal Shah has 8+ years of extensive SQL Server experience and has worked on SQL Server 2000, 2005, 2008 and 2008 R2.
Jugal Shah has 8+ years of extensive SQL Server experience and has worked on SQL Server 2000, 2005, 2008 and 2008 R2.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2011-10-24






