By: Svetlana Golovko | Updated: 2014-03-28 | Comments (5) | Related: > Monitoring
Problem
We have quite a large number of databases and user connections to our SQL Server and we suspect that one application does not close connections properly. We need an automated way to monitor when this happens in order to contact developers to fix this issue.
Solution
In order to collect connection information, we will setup a SQL Server Agent alert that will execute a job every time there is more than N number of connections. We will use 50 connections in our example to simplify the test. The job then will populate a table with information about applications and connections.
Create a table to store monitoring data
First, we will create the table that will be populated by the job:
CREATE TABLE perf_warehouse.dbo._demo_sessions_alert( [host_name] nvarchar(128) NULL, [program_name] nvarchar(128) NULL, login_name nvarchar(128) NULL, num_sessions int NULL, capture_time datetime NULL ) ON [PRIMARY] GO
Create the SQL Server Agent Job
Create the SQL Server job with the following script as a step:
INSERT INTO perf_warehouse.dbo._demo_sessions_alert
SELECT [host_name],
[program_name],
login_name,
count(c.session_id ) num_sessions,
getdate()
FROM sys.dm_exec_connections c JOIN
sys.dm_exec_sessions s on c.session_id = s.session_id
GROUP BY host_name, program_name, login_name ORDER BY 4 DESC
You can capture all connections or only the top N ("SELECT TOP 10 [host_name],...").
Here is the complete script that you can use to create the job:
BEGIN TRANSACTION
DECLARE @ReturnCode INT
SELECT @ReturnCode = 0
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT name FROM msdb.dbo.syscategories
WHERE name=N'DBA' AND category_class=1)
BEGIN
EXEC @ReturnCode = msdb.dbo.sp_add_category @class=N'JOB', @type=N'LOCAL', @name=N'DBA'
IF (@@ERROR <> 0 OR @ReturnCode <> 0) GOTO QuitWithRollback
END
DECLARE @jobId BINARY(16)
EXEC @ReturnCode = msdb.dbo.sp_add_job @job_name=N'Sessions Monitoring',
@enabled=1,
@notify_level_eventlog=0,
@notify_level_email=2,
@notify_level_netsend=0,
@notify_level_page=0,
@delete_level=0,
@description=N'Inserts log records when number of connections is higher than 50',
@category_name=N'DBA',
@owner_login_name=N'sa',
@job_id = @jobId OUTPUT
IF (@@ERROR <> 0 OR @ReturnCode <> 0) GOTO QuitWithRollback
EXEC @ReturnCode = msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep @job_id=@jobId, @step_name=N'Log info',
@step_id=1,
@cmdexec_success_code=0,
@on_success_action=1,
@on_success_step_id=0,
@on_fail_action=2,
@on_fail_step_id=0,
@retry_attempts=0,
@retry_interval=0,
@os_run_priority=0, @subsystem=N'TSQL',
@command=N'INSERT INTO perf_warehouse.dbo._demo_sessions_alert
SELECT host_name, program_name, login_name, count(c.session_id ) num_sessions, getdate()
FROM sys.dm_exec_connections c JOIN sys.dm_exec_sessions s on c.session_id = s.session_id
GROUP BY host_name,program_name,login_name ORDER BY 4 DESC',
@database_name=N'master',
@flags=0
IF (@@ERROR <> 0 OR @ReturnCode <> 0) GOTO QuitWithRollback
EXEC @ReturnCode = msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_id = @jobId, @start_step_id = 1
IF (@@ERROR <> 0 OR @ReturnCode <> 0) GOTO QuitWithRollback
EXEC @ReturnCode = msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobserver @job_id = @jobId, @server_name = N'(local)'
IF (@@ERROR <> 0 OR @ReturnCode <> 0) GOTO QuitWithRollback
COMMIT TRANSACTION
GOTO EndSave
QuitWithRollback:
IF (@@TRANCOUNT > 0) ROLLBACK TRANSACTION
EndSave:
GOCreate a SQL Server Agent alert
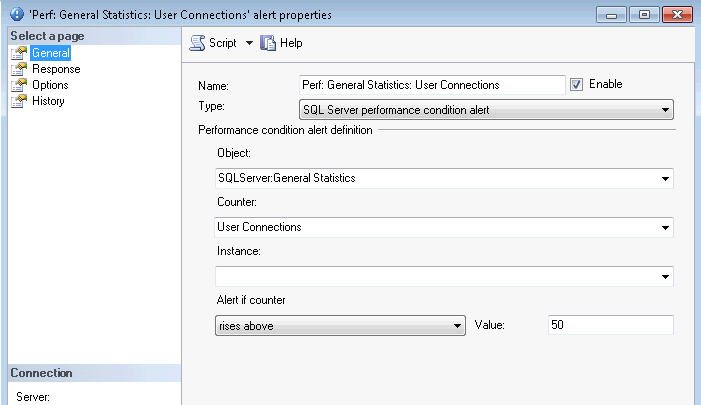
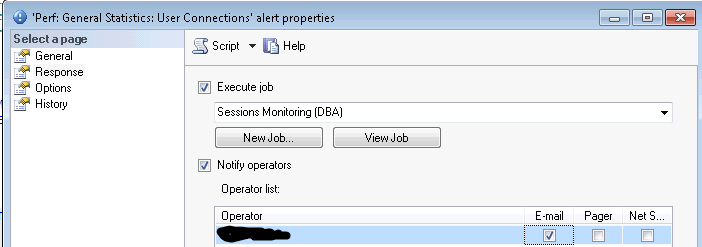
Now we will create a performance condition alert that will be triggered when there are more than 50 connections (with 2 minute intervals). This alert will start the job we created above:
Here is the complete script to create the alert (you will need to update parameter "@operator_name" with your value):
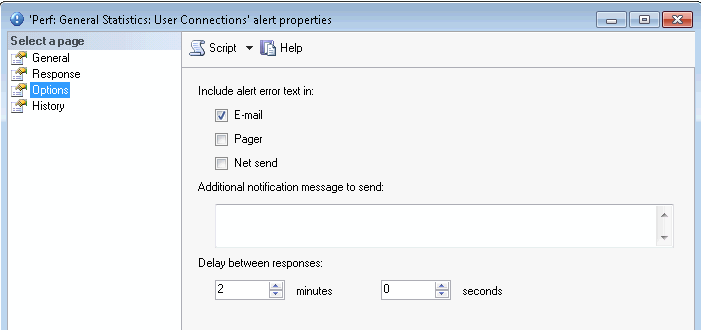
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_alert @name=N'Perf: General Statistics: User Connections', @message_id=0, @severity=0, @enabled=1, @delay_between_responses=120, @include_event_description_in=1, @performance_condition=N'SQLServer:General Statistics|User Connections||>|50', @job_name=N'Sessions Monitoring' GO EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_add_notification @alert_name=N'Perf: General Statistics: User Connections', @operator_name=N'DBA_Operator', -- update with your value @notification_method = 1 GO
Testing the Alert
Now we should be able to receive email notifications when there are more than 50 server connections and we can review the log table that contains the details:
SELECT TOP 5 [host_name]
,[program_name]
,[login_name]
,[num_sessions]
,[capture_time]
FROM [dbo].[_demo_sessions_alert]
ORDER BY [capture_time] DESC, [num_sessions] DESC
GOBelow is the output and we can see the application and host that had the largest number of connections:
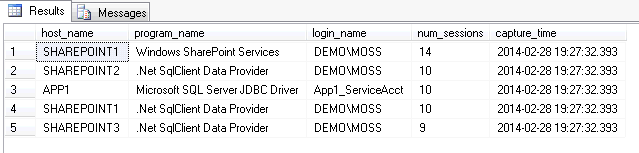
A value of 50 connections could be low for your server and you may get a lot of alerts. For our issue to track applications not closing connections we used a value of 1000 connections.
Next Steps
- Use this tip to monitor your connections and to get a baseline for the number of connections your SQL Server usually has.
- After collecting some data, adjust your monitored number of connections in the alert (for example add 100 to the maximum connections in your baseline).
- Read this tip about How to Automate SQL Server Monitoring with Email Alerts.
- Read this tip about How to setup SQL Server alerts and email operator notifications.
About the author
 Svetlana Golovko is a DBA with 13 years of the IT experience (including SQL Server and Oracle) with main focus on performance.
Svetlana Golovko is a DBA with 13 years of the IT experience (including SQL Server and Oracle) with main focus on performance. This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2014-03-28






