By: Rajendra Gupta | Updated: 2016-05-04 | Comments | Related: > SQL Server 2016
Problem
In an earlier tip SQL Server 2016 Database Scoped Configuration, we provided an overview of the important parameters that can be set at the database level which were previously available at the instance level only. In this tip we are going to explore this functionality in more detail.
Solution
Max Degree of Parallelism as a Database Scoped Configuration
By default, Max Degree of Parallelism (MAXDOP) is set to value 0 at the instance level, as shown below.
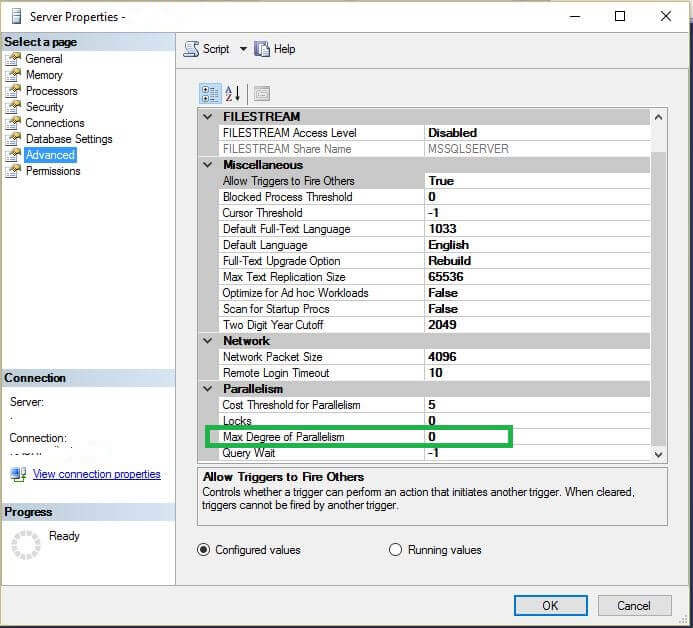
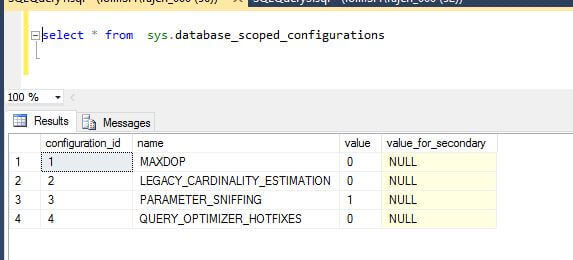
For demo purposes I am going to use the AdventureWorks2016CTP3 database. If we check the database scope parameter default values we can see 0 = Disabled and 1 = Enabled.
If we run the below query with the default options we see the following execution plan.
SELECT * FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail sod INNER JOIN Production.Product p ON sod.ProductID = p.ProductID ORDER BY Style GO
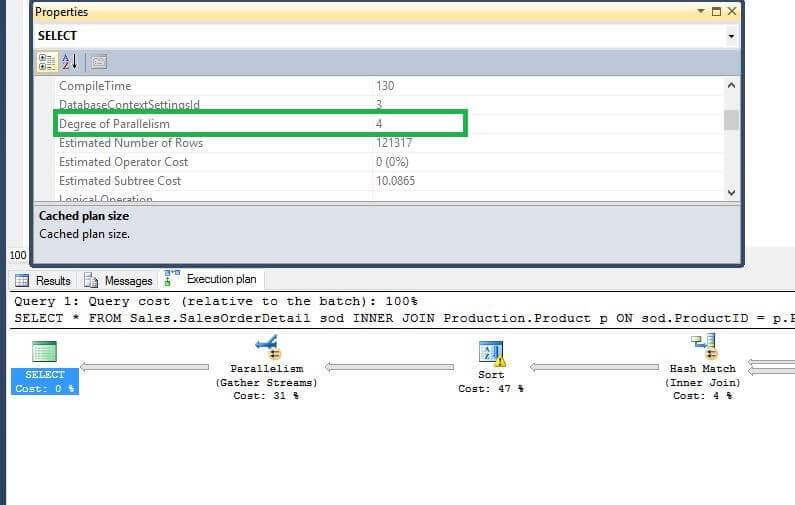
We can see that a parallel execution plan is being created for the query with a Degree of Parallelism of 4.
Now suppose we don't want the Max Degree of Parallelism to be 4 and we want to generate a serial plan. To do so we would set the MAXDOP=1 for this database as shown below.
ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET MAXDOP = 1;
And we verify this setting as shown below.
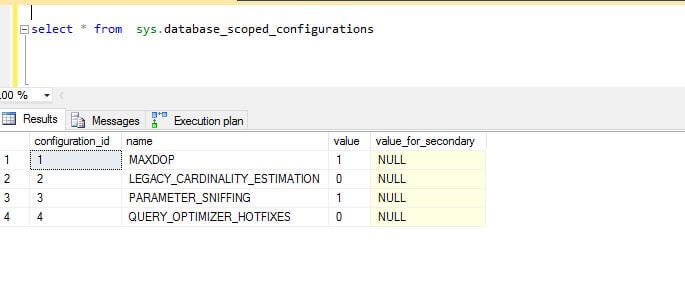
Now if we run the same query, we can see this time a serial plan is generated and the optimizer shows why a parallel plan is not selected.
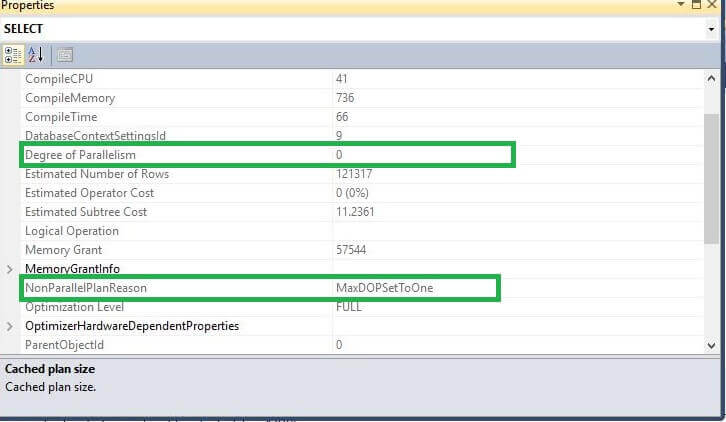
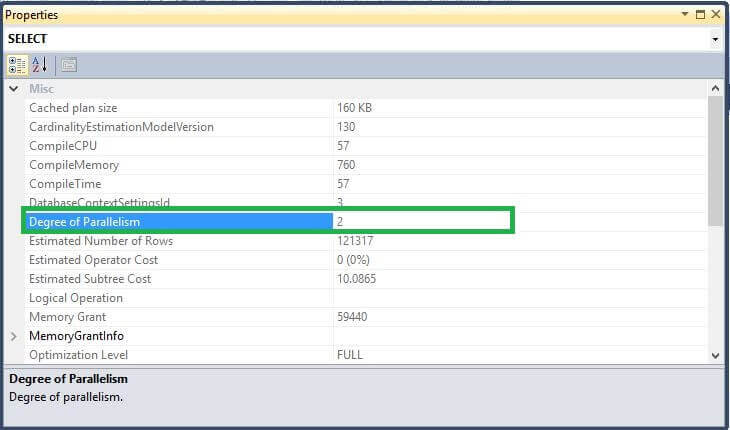
Similarly if we set MAXDOP=2, we can see this setting effects the query execution.
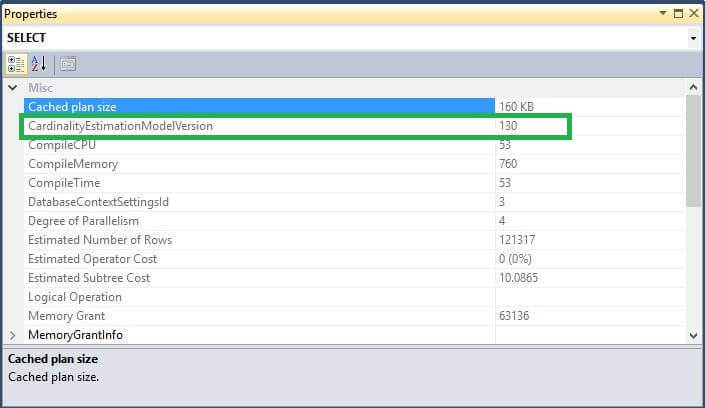
Now we will set MAXDOP = 0 ( default value ) and see the Cardinality Estimation is set to 130.
ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET LEGACY_CARDINALITY_ESTIMATION = ON;
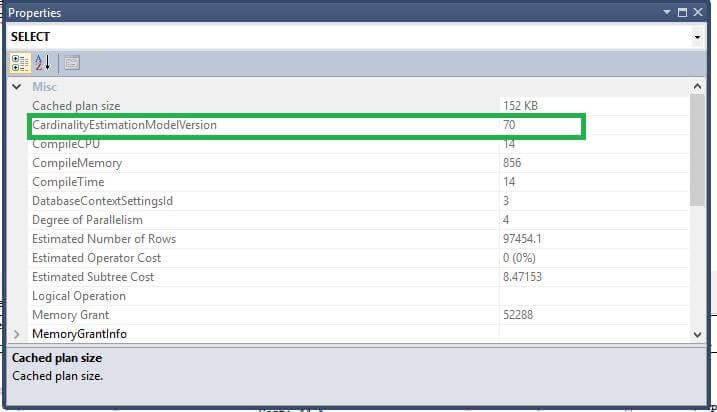
So we can see here that the database engine is now using the legacy cardinality estimation instead of cardinality estimation for SQL Server 2016.
As we can see a value of 70 after setting the Legacy Cardinality estimator ON. This indicates that the cardinality estimation model being used is pre-SQL Server 2016. The cardinality estimator had its last major change back in SQL Server 7.0 (70).
Clear SQL Server Database Procedure Cache
Let's see the current procedure cache for our demo database AdventureWorks2016CTP3 with the following query:
SELECT
d.name AS [db_name],
count(*) as nb_cached_entries
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans AS cp
CROSS APPLY (
SELECT CAST(pa.value AS INT) AS database_id
FROM sys.dm_exec_plan_attributes(cp.plan_handle) AS pa
WHERE pa.attribute = N'dbid'
) AS DB
INNER JOIN sys.databases AS d
ON d.database_id = DB.database_id
where d.database_id=8 --database id for AdventureWorks2016CTP3
GROUP BY d.name
ORDER BY d.name
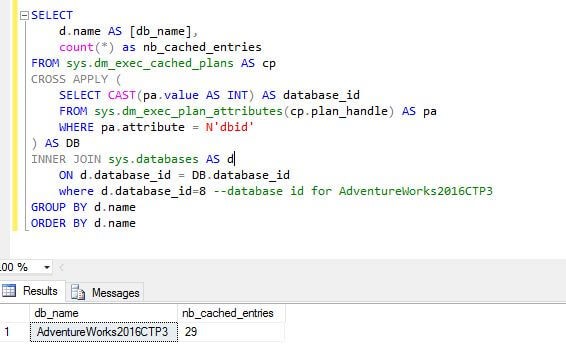
Now if we clear the procedure cache on the AdventureWorks2016CTP3 database we can see 0 rows returned i.e. procedure cache has been cleared.
ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION CLEAR PROCEDURE_CACHE; GO
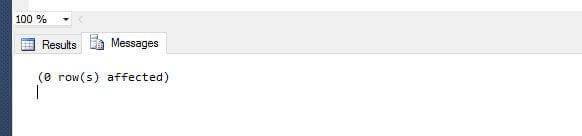
We can see the there are no records returned now i.e. the database level cache has been cleared. This is a very interesting option because previously we could only clear the procedure cache at the instance level.
Cross Database Queries and MAXDOP as a Database Scoped Configuration
Now we will see the MAXDOP behavior when more than one database is involved in a SQL Server query. To test I have created another test database and exported the data for the production.product table.
Example 1 - MAXDOP Disabled for the Database Scope Configuration
If both the databases are configured with MAXDOP=0 as the Database Scope Configuration, then the instance level MAXDOP setting is used as shown below.
SELECT * FROM AdventureWorks2016CTP3.Sales.SalesOrderDetail sod INNER JOIN Testdb.Production.Product p ON sod.ProductID = p.ProductID ORDER BY Style GO
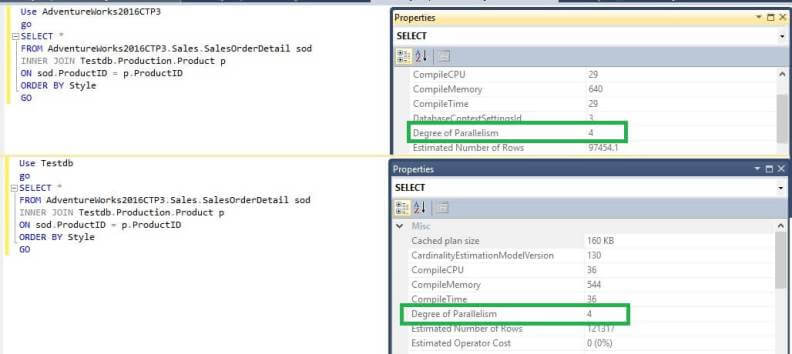
We can see in both databases that the query is being executed with MAXDOP=4.
Example 2 - Different MAXDOP values for the Database Scope Configuration
Now we will change the MAXDOP configuration for both databases, so they are using different MAXDOP values.
Use AdventureWorks2016CTP3 ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET MAXDOP = 3 GO Use TestDB ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET MAXDOP = 2 GO
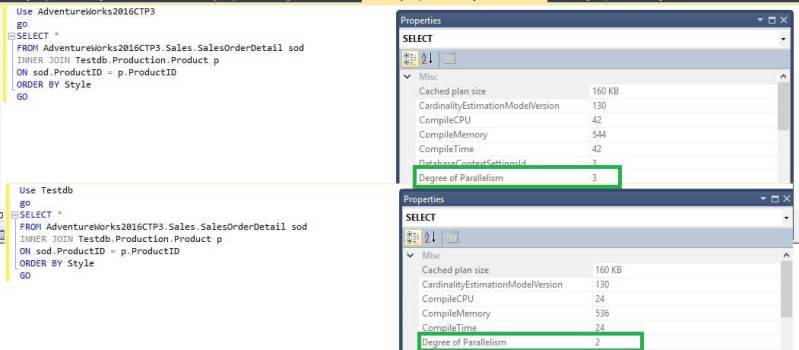
So we can see if the same query is being executed against the AdventureWorks2016CTP3 database, MAXDOP is 3 while executed against the TestDB it is 2 which is per our settings.
Example 3 - Different MAXDOP values for the Database Scope Configuration
Use TestDB go ALTER DATABASE SCOPED CONFIGURATION SET MAXDOP = 1
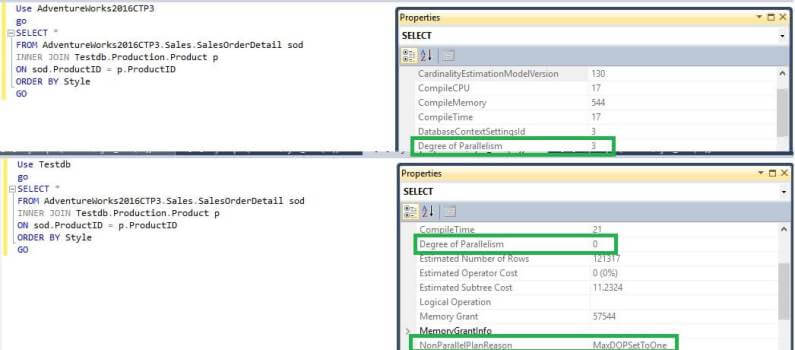
Here we get a serial plan for the query being executed in the TestDB database as we have set MAXDOP = 1 for TestDB.
The SQL Server database where the T-SQL code executes will dictate the MAXDOP setting. So be careful while configuring this option on production servers and enable this setting with proper testing of the workload.
Next Steps
- Download and explore SQL Server 2016 Release candidate 0.
- Read more about Overview of 2016 RC0 Features.
- Read more about Alter database scope configurations.
- Read more about Parameter sniffing.
About the author
 Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.
Rajendra Gupta is a Consultant DBA with 14+ years of extensive experience in database administration including large critical OLAP, OLTP, Reporting and SharePoint databases.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2016-05-04






