By: Jugal Shah | Updated: 2010-03-02 | Comments (1) | Related: > Tools
Problem
The OSQL utility uses ODBC to communicate with SQL Server. The user's problem is that the ODBC driver he is using to connect to the database is performing translations on the character data in the T-SQL script. Extended characters, which are not in the standard ASCII character set, are translated by the driver based on drive settings. The character translation option is ON by default when SQL Server executes scripts through the OSQL utility.
Solution
We can resolve this issue by configuring DNS or T-SQL . To resolve this issue we will take the below example.
Steps to Reproduce Issue
Step 1 - Create an Example table by using the below code.
create table Example
(
id int identity(1,1),
extendedCharactervalue varchar(1000)
);
insert into Example(extendedCharactervalue) values('Rrotégé Company, LLC')
Step 2 - Save below INSERT query into text file/SQL file. I have named the file Query.txt
insert into Example(extendedCharactervalue) values('Rrotégé Company, LLC')
Step 3 - Execute the below OSQL statement from command prompt
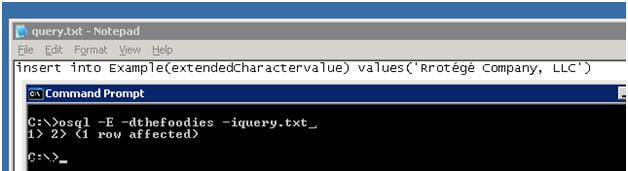
Step 4 - Now query the Example table and you can see the character é is converted to T
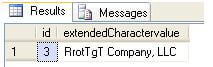
We can fix the below by using one of these solutions.
Solution 1 - Insert Extended character using DNS with OSQL
Step 1 - Create ODBC System DSN. Go to Control Panel -- Administrative Tool -- SELECT Data Sources (ODBC)
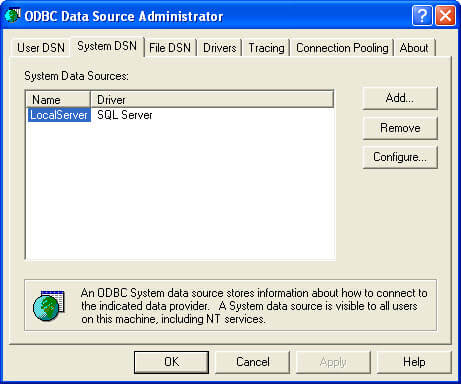
Step 1.2 - Select System DSN tab from Data Sources (ODBC) and click on Add button on the right of the screen.
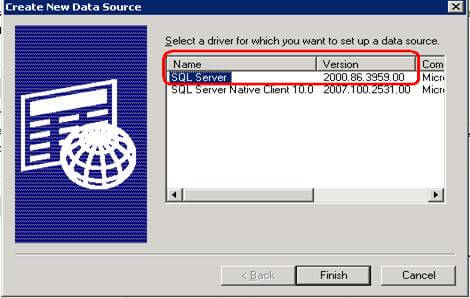
Step 1.3 - Select SQL Server from driver list and click on Finish button
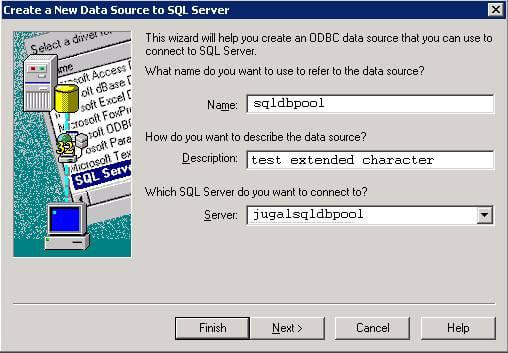
Step 1.4 - Enter the DSN Name and select Server name from list
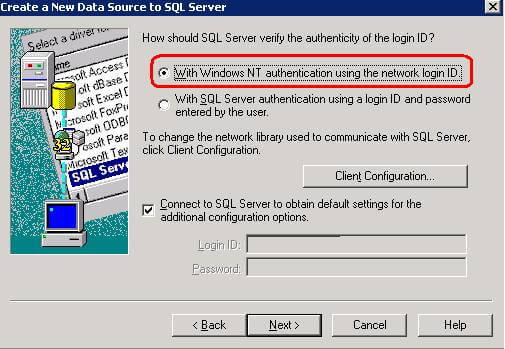
Step 1.5 - Choose the authentication mode and click on Next button
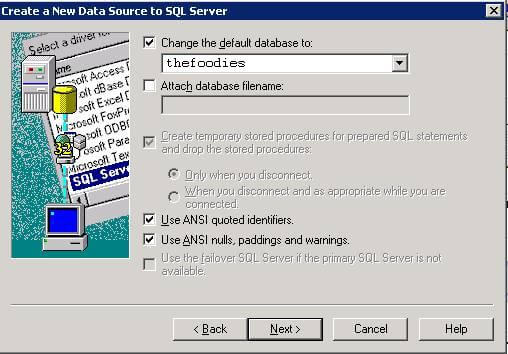
Step 1.6 - Select the database name from list and click on Next button
Step 1.7 - Uncheck the below checked button (Perform translation for character data) and click on Finish button
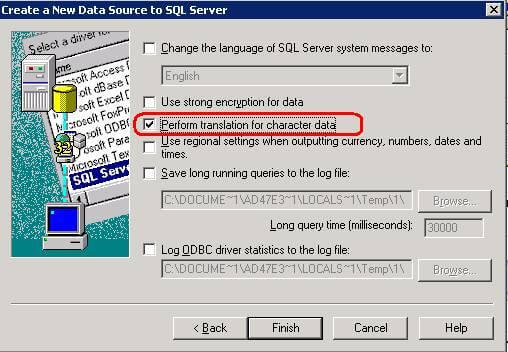
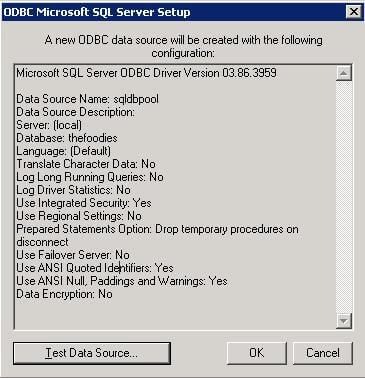
Step 1.8 - In next screen you can see the test data source window, using that you can test the connectivity
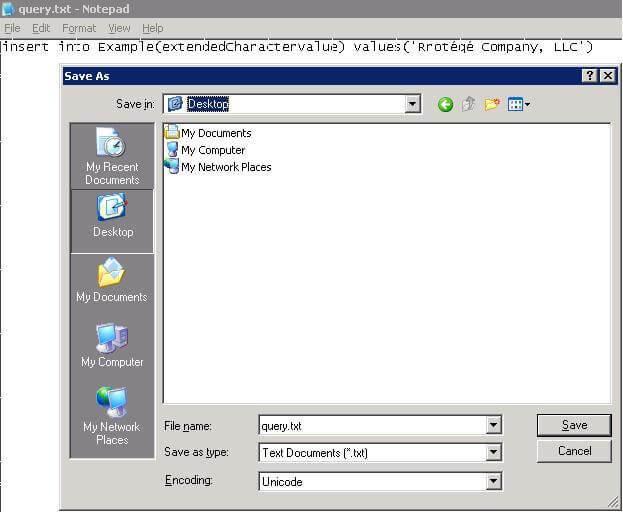
Step 2 - Save As script file as Unicode file (Open the script file in Text Editor (NOTEPAD))
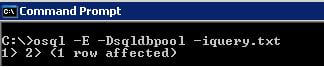
Step 3 - Execute the SQL script using OSQL by passing DSN Name and Script file as parameter
Now query the example table you can see the below output.
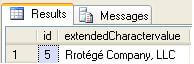
Solution 2 - Using T-SQL
-- ascii function retuns the ascii value of extended character
select ascii('é')
-- char function converts the ascii value to character
select char(233)
insert into Example(extendedCharactervalue)
select 'Rrot' + char(233) + 'g' + char(233) + ' Company, LLC'
Next Steps
- Check out the above solution by adding more extended characters
- Check the solution one without using a DSN and only saving script in the unicode file format.
- Search out more OSQL switches.
About the author
 Jugal Shah has 8+ years of extensive SQL Server experience and has worked on SQL Server 2000, 2005, 2008 and 2008 R2.
Jugal Shah has 8+ years of extensive SQL Server experience and has worked on SQL Server 2000, 2005, 2008 and 2008 R2.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2010-03-02






