By: Siddharth Mehta | Updated: 2010-11-08 | Comments (7) | Related: 1 | 2 | More > Integration Services Error Handling
Problem
In an ETL solution, error logging is a fundamental requirement for various aspects of the application and is very useful at various stages of the ETL execution life-cycle. Let's consider a scenario where our requirement is to insert records into a SQL Server table. The package should attempt loading all the records and whichever records fail, error details reported by the database engine should be reported. We will look at how to implement this in a SSIS package.
Solution
From a high level view for data loads, there are three main phases in a ETL execution life-cycle.
- When data is being extracted (i.e. read) from source systems
- When data is being transformed
- When data is loaded to the target systems
In the first phase, there can be errors while establishing a connection with the source systems, or the data read from the source might not match the mappings defined in the SSIS package. Similarly, there can be different kinds of errors which can occur during this phase.
In the second phase, when data is being transformed, the only major category of error that can occur is while manipulating the data. We are not considering any errors caused by hardware failures or memory as these category of errors can occur at any phase of the ETL life-cycle.
In the final phase, when data is being loaded into the target system, error logging is required at a very detailed level as there can be many reasons why loading of a particular record failed. After data crosses the SSIS boundary, and is handed over to the database driver for loading into the target system, the database engine takes control of loading the data. And if the data violates the criteria defined by the entity that stores the data, an error message is generated and returned back. Each target system has their own mechanism and translation of reporting the error.
For example, if one attempts to insert a record in a table which would violates the primary / foreign key constraint, that record would definitely fail. Support teams who maintain the ETL solution, would like to know the cause of each and every record failure with the supporting details that can help them clearly understand the reason of failure. One of the ways to deal with this is to log the error message reported by the database engine itself into the error log. Most of the time, the reason why the data manipulation failed becomes very apparent from the error message reported by the target system.
Follow the steps below to develop a solution that deals with the problem in question.
1) Create a new SSIS project and name it something relevant. Change the name of the default package and rename it to something relevant.
2) I take it for granted that the reader has the AdventureWorks database installed on their development machine. We will be using the Address table for our exercise. Create a new table named AddressClone with two columns: AddressID and City. Make AddressID the primary key column. Our purpose is to load the same records in the table twice and check whether primary key errors reported by the database engine are captured by our SSIS package and reported in the error table that we will design in the following steps.
3) Use the below script to create a new error table to log the errors that we would capture from the database.
( [ErrorID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[ErrorRow] [xml] NULL,
[ErrorMessage] [varchar](1000) NULL,
[ErrorIssuingPackage] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ErrorSourceTable] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ErrorDestinationTable] [varchar](50) NULL,
[ErrorLoggingTime] [datetime] NULL )
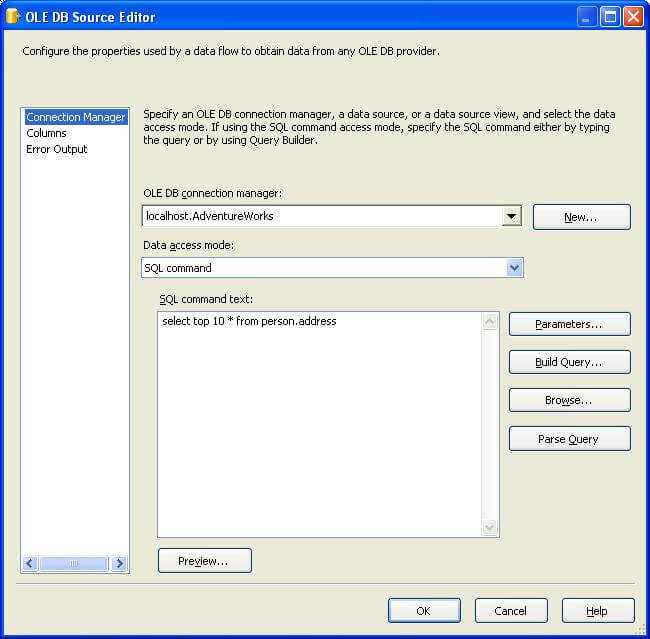
4) Add a new Data Flow task to the package. Edit the Data Flow task, and add a OLE DB Source Adapter. Configure the adapter to read the top 10 rows from the address table as shown below.
5) After the OLE DB Adapter, add a Script transformation. When you add it to the package, you will be prompted with three options asking if you want the it as a Source, Transformation or Destination. Select Destination out of these options.
6) Add a new ADO.NET connection to the package and configure it to connect to the AdventureWorks database.
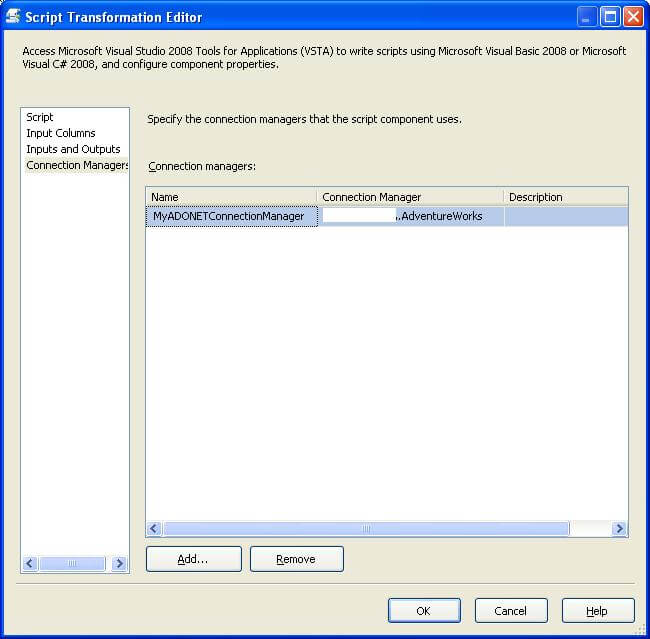
7) Configure the Script transform to use the connection we created above by using the Script Transformation Editor page as shown below. Also make sure that AddressID and City columns are available and checked on the Input Columns page.
8) Edit the Script transform, and add the following code. We are first acquiring a connection in the AcquireConnections method. In the pre-execute we are preparing the command object and configuring it with required parameters. In the ProcessInputRow method which gets executed for each record, we are assigning values from each record to the respective parameter and then we are executing the command which enters a record into the target table.
We have done exception handling at this level, by using the try-catch block. In case an error is reported by the database engine, the error gets captured by the catch block. As we are interested in errors reported by database engine, we have made our exception type specific by making the type of the exception parameter "e" as "SQLException". After an exception is captured, we again prepare the command at that point in time, we assign specific values in alignment with our error table and we report the same in our error table that we created in Step 3.
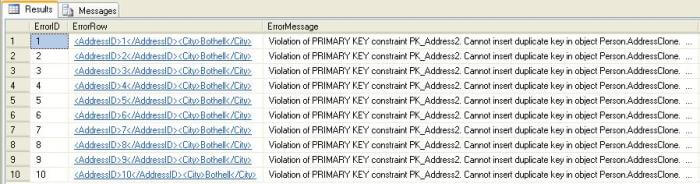
9) Execute the package the first time and there should be no errors Ten records should get inserted into the AddressClone table. Now execute the package again and check the Error table and you should be able to find the error details as shown below.
In this article, we saw how to capture error messages reported by the target system while loading data from SSIS. For the sake of this demonstration, we took SQL Server as the target system, and saw how we can capture errors for each record that failed to load into the database. This technique of error capture is very effective when the primary requirement is to attempt loading each record and also capture errors for each failed record.
Next Steps
- Try implementing this for a non-relational target system like Excel.
- Test whether SQLException works to catch the exceptions or if you need to change this to capture the error
- Read more tips about SSIS
About the author
 Siddharth Mehta is an Associate Manager with Accenture in the Avanade Division focusing on Business Intelligence.
Siddharth Mehta is an Associate Manager with Accenture in the Avanade Division focusing on Business Intelligence.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2010-11-08






