By: Greg Robidoux | Updated: 2007-02-07 | Comments (38) | Related: > Express Edition
Problem
One problem with SQL Server Express is that it does not offer a way to schedule jobs. In a previous tip, Free Job Scheduling Tool for SQL Server Express and MSDE, we looked at a free tool that allows you to create scheduled jobs for SQL Server. The one issue people often face though is what to install and what not to install on their production servers and therefore these items go without resolution. One very important part of managing SQL Server is to ensure you run backups on a set schedule. I often hear about corrupt databases and no backups, so let's take a look at another approach of scheduling backups using the included tools in both the operating system and SQL Server.
Solution
There are two components to this; the first is the backup command and the second is the scheduling needed to run the backups.
SQL Server Backup Commands
There are a few things that we need to setup. The first is to create a stored procedure that allows us to dynamically generate the backup file name as well as what type of backup to run Full, Differential or Transaction Log backup. The default for this stored procedure is to create the backups in the "C:\Backup" folder. This can be changed to any folder you like.
The following stored procedure should be created in the master database. This is just one way of handling this. There are several other options and enhancements that can be made.
USE [master]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
-- =============================================
-- Author: Edgewood Solutions
-- Create date: 2007-02-07
-- Description: Backup Database
-- Parameter1: databaseName
-- Parameter2: backupType F=full, D=differential, L=log
-- =============================================
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_BackupDatabase]
@databaseName sysname, @backupType CHAR(1)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @sqlCommand NVARCHAR(1000)
DECLARE @dateTime NVARCHAR(20)
SELECT @dateTime = REPLACE(CONVERT(VARCHAR, GETDATE(),111),'/','') +
REPLACE(CONVERT(VARCHAR, GETDATE(),108),':','')
IF @backupType = 'F'
SET @sqlCommand = 'BACKUP DATABASE ' + @databaseName +
' TO DISK = ''C:\Backup\' + @databaseName + '_Full_' + @dateTime + '.BAK'''
IF @backupType = 'D'
SET @sqlCommand = 'BACKUP DATABASE ' + @databaseName +
' TO DISK = ''C:\Backup\' + @databaseName + '_Diff_' + @dateTime + '.BAK'' WITH DIFFERENTIAL'
IF @backupType = 'L'
SET @sqlCommand = 'BACKUP LOG ' + @databaseName +
' TO DISK = ''C:\Backup\' + @databaseName + '_Log_' + @dateTime + '.TRN'''
EXECUTE sp_executesql @sqlCommand
END
The second part of this is to create a SQLCMD file to run the backup commands. Here is a simple SQLCMD file that backups databases master, model and msdb.
This file gets saved as backup.sql and for our purposes this is created in the "C:\Backup" folder, but again this could be put anywhere.
sp_BackupDatabase 'master', 'F'
GO
sp_BackupDatabase 'model', 'F'
GO
sp_BackupDatabase 'msdb', 'F'
GO
QUIT
Scheduling SQL Server Backups
Included with the Windows operating system is a the ability to setup and run scheduled tasks. This is generally not used for SQL Server environments, because SQL Server Agent is so robust and gives you a lot more control and options for setting up re-occurring jobs. With SQL Server Express the only choice is to set a scheduled task at the operating system level or look for some third party tool.
To setup a scheduled task you need to open the folder where you can create a new scheduled task. This can be found under Accessories -> System Tools -> Scheduled Tasks or under Control Panel.
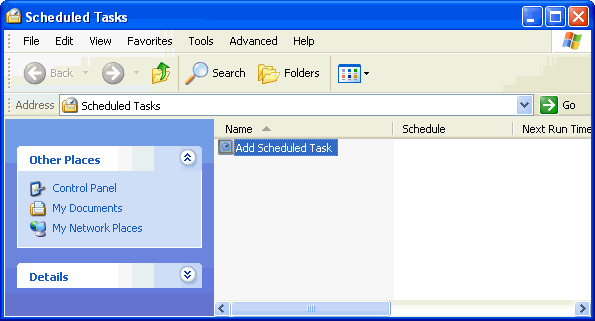
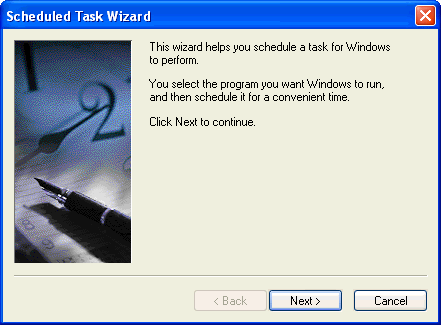
The first thing to do is to click on "Add Scheduled Task" and the following wizard will run.
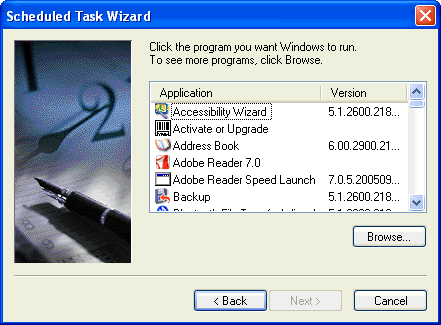
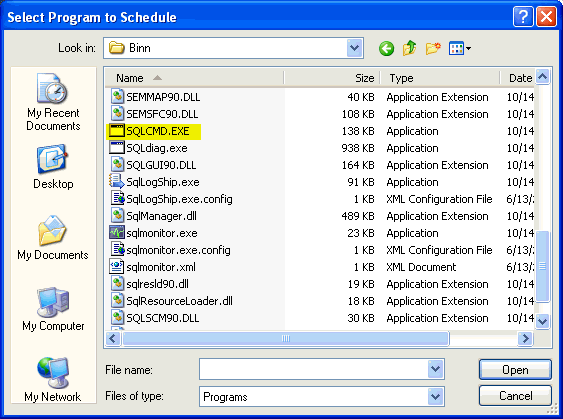
Select the application that you want to run. For our purposes we will be using SQLCMD.EXE. In order to find SQLCMD.EXE you will need to click on the Browse... button.
You should be able to find this in the following directory "C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\90\Tools\Binn".
Give the scheduled task a name and specify when to perform the task.
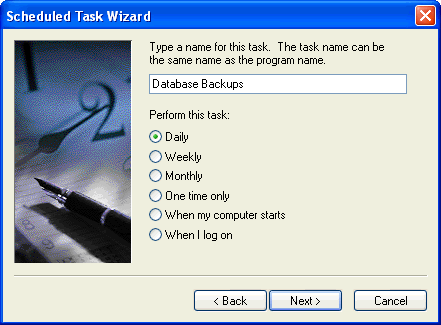
Specify the time that this should be run.
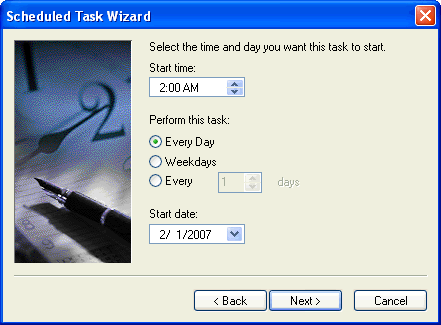
Provide the credentials for the account that will run this task.
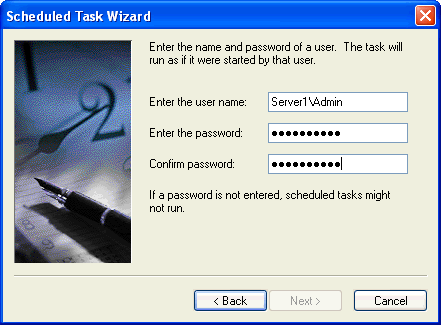
Finish and save the task. One thing you want to do is click on the "Open advanced properties" so you can edit the command.
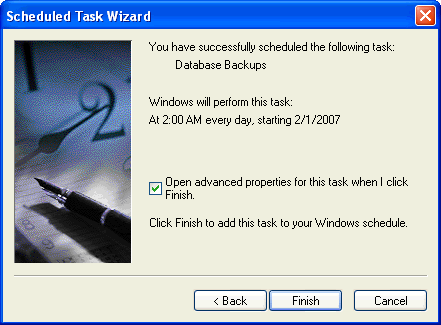
Below is the advanced properties screen. You will need to change the "Run" command to the following:
sqlcmd -S serverName -E -i C:\Backup\Backup.sql
This is broken down as follows:
- sqlcmd
- -S (this specifies the server\instance name for SQL Server)
- serverName (this is the server\instance name for SQL Server)
- -E (this allows you to make a trusted connection)
- -i (this specifies the input command file)
- C:\Backup\Backup.sql (this is the file that we created above with the command steps)
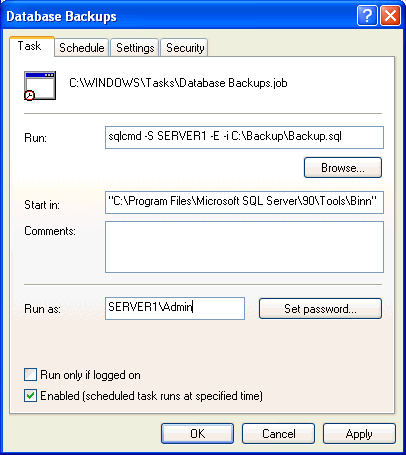
That should do it. The scheduled task should now be setup.
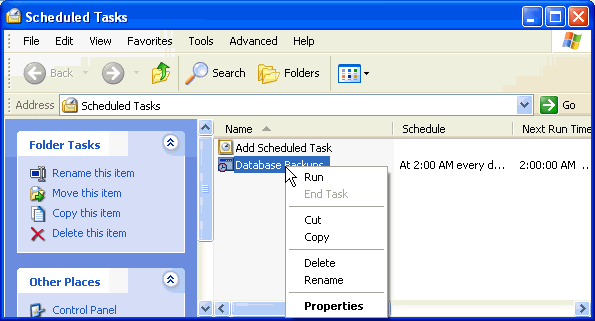
If you want to run the command now to make sure it works go back to the Scheduled Tasks view and right click on the task and select "Run".
Next Steps
- Although this is a pretty simple example this should allow you to backup your SQL Server databases pretty easily
- Modify the process to handle errors and also to take other parameters
- Also take a look at this tip, Free Job Scheduling Tool for SQL Server Express and MSDE, to see if this tool makes more sense for your environment
About the author
 Greg Robidoux is the President and founder of Edgewood Solutions, a technology services company delivering services and solutions for Microsoft SQL Server. He is also one of the co-founders of MSSQLTips.com. Greg has been working with SQL Server since 1999, has authored numerous database-related articles, and delivered several presentations related to SQL Server. Before SQL Server, he worked on many data platforms such as DB2, Oracle, Sybase, and Informix.
Greg Robidoux is the President and founder of Edgewood Solutions, a technology services company delivering services and solutions for Microsoft SQL Server. He is also one of the co-founders of MSSQLTips.com. Greg has been working with SQL Server since 1999, has authored numerous database-related articles, and delivered several presentations related to SQL Server. Before SQL Server, he worked on many data platforms such as DB2, Oracle, Sybase, and Informix.This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
View all my tips
Article Last Updated: 2007-02-07






